Abstract
Purpose
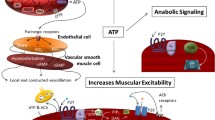
ATP could play an important role in skeletal muscle blood flow regulation by inducing vasodilation via purinergic P2 receptors. This study investigated the role of P2 receptors in exercise hyperemia in miniature swine.
Methods
We measured regional blood flow with radiolabeled-microsphere technique and systemic hemodynamics before and after arterial infusion of the P2 receptor antagonist reactive blue 2 during treadmill exercise (5.2 km/h, ~60 % VO2max) and arterial ATP infusion in female Yucatan miniature swine (~29 kg).
Results
Mean blood flow during exercise from the 16 sampled skeletal muscle tissues was 138 ± 18 mL/min/100 g (mean ± SEM), and it was reduced in 11 (~25 %) of the 16 sampled skeletal muscles after RB2 was infused. RB2 also lowered diaphragm blood flow and kidney blood flow, whereas lung tissue blood flow was increased (all P < 0.05). Infusion of RB2 increased arterial lactate concentration during exercise from 1.6 ± 0.5 to 3.4 ± 0.6 mmol/L and heart rate from 216 ± 12 to 230 ± 9 beats/min, whereas blood pressure was unaltered. Arterial ATP infusion caused a ~twofold increase in blood flow in 15 of the 16 sampled muscle tissues and this effect was abolished after RB2 infusion.
Conclusions
These results indicate that P2 receptors play a role in regulating skeletal muscle blood flow during exercise in miniature swine.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Adr:
-
Adrenal
- Bic Br:
-
Biceps brachii
- Bic Fem:
-
Biceps femoris
- Brach:
-
Brachialis
- Dia:
-
Diaphragm
- EDHF:
-
Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor
- Int:
-
Intestines
- Kid:
-
Kidney
- LV:
-
Left ventricle
- Pan:
-
Pancreas
- RB2:
-
Reactive blue 2
- RF:
-
Rectus femoris
- RV:
-
Right ventricle
- Semit:
-
Semitendinosus
- Stom:
-
Stomach
- Sup:
-
Superficial portion
- TAH:
-
Triceps brachii accessory head
- TLH:
-
Triceps brachii long head
- TltH:
-
Triceps brachii lateral head
- TMH:
-
Triceps brachii medial head
- VI:
-
Vastus intermedius
- VL:
-
Vastus lateralis
- VM:
-
Vastus medialis
References
Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Knight GE, Fumagalli M, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA (2006) International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol Rev 58:281–341
Bergfeld GR, Forrester T (1992) Release of ATP from human erythrocytes in response to a brief period of hypoxia and hypercapnia. Cardiovasc Res 26:40–47
Brunschweiger A, Müller CE (2006) P2 receptors activated by uracil nucleotides—an update. Curr Med Chem 13:289–312
Burnstock G (1999) Release of vasoactive substances from endothelial cells by shear stress and purinergic mechanosensory transduction. J Anat 194:335–342
Burnstock G (2007) Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1471–1483
Burnstock G (2010) Control of vascular tone by purines and pyrimidines. Br J Pharmacol 161:527–529
Burnstock G, Ralevic V (2014) Purinergic signaling and blood vessels in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 66:102–192
Burnstock G, Warland JJ (1987) P2-purinoceptors of two subtypes in the rabbit mesenteric artery: reactive blue 2 selectively inhibits responses mediated via the P2y-but not the P2x-purinoceptor. Br J Pharmacol 90:383–391
Chen BC, Lee CM, Lin WW (1996) Inhibition of ecto-ATPase by PPADS, suramin and reactive blue in endothelial cells, C6 glioma cells and RAW 264.7 macrophages. Br J Pharmacol 119:1628–1634
Dietrich HH, Ellsworth ML, Sprague RS, Dacey RG Jr (2000) Red blood cell regulation of microvascular tone through adenosine triphosphate. Am J Physiol 278:H1294–H1298
Duncker DJ, Stubenitsky R, Tonino PAL, Verdouw PD (2000) Nitric oxide contributes to the regulation of vasomotor tone but does not modulate O2-consumption in exercising swine. Cardiovasc Res 47:738–748
Ellsworth ML, Sprague RS (2012) Regulation of blood flow distribution in skeletal muscle: role of erythrocyte-released ATP. J Physiol 590:4985–4991
Ellsworth ML, Forrester T, Ellis CG, Dietrich HH (1995) The erythrocyte as a regulator of vascular tone. Am J Physiol 269:H2155–H2161
Erlinge D, Burnstock G (2008) P2 receptors in cardiovascular regulation and disease. Purinergic Signal 4:1–20
González-Alonso J, Olsen DB, Saltin B (2002) Erythrocyte and the regulation of human skeletal muscle blood flow and oxygen delivery: role of circulating ATP. Circ Res 91:1046–1055
Gordon JL (1986) Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J 233:309–319
Hammer LW, Overstreet CR, Choi J, Hester RL (2003) ATP stimulates the release of prostacyclin from perfused veins isolated from the hamster hindlimb. Am J Physiol 285:R193–R199
Hellsten Y, Nyberg M, Jensen LG, Mortensen SP (2012a) Vasodilator interactions in skeletal muscle blood flow regulation. J Physiol 590:6297–6305
Hellsten Y, Nyberg M, Mortensen SP (2012b) Contribution of intravascular versus interstitial purines and nitric oxide in the regulation of exercise hyperaemia in humans. J Physiol 590:5015–5023
Hillig T, Krustrup P, Fleming I, Osada T, Saltin B, Hellsten Y (2003) Cytochrome P450 2C9 plays an important role in the regulation of exercise-induced skeletal muscle blood flow and oxygen uptake in humans. J Physiol 546:307–314
Inscho EW (2009) ATP, P2 receptors and the renal microcirculation. Purinergic Signal 5:447–460
Kirby BS, Voyles WF, Carlson RE, Dinenno FA (2008) Graded sympatholytic effect of exogenous ATP on postjunctional alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction in the human forearm: implications for vascular control in contracting muscle. J Physiol 586:4305–4316
Laughlin MH, Klabunde RE, Delp MD, Armstrong RB (1989) Effects of dipyridamole on muscle blood flow in exercising miniature swine. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 257:H1507–H1515
Laughlin MH, Davis MJ, Secher NH, van Lieshout JJ, Arce-Esquivel AA, Simmons GH, Bender SB, Padilla J, Bache RJ, Merkus D, and Duncker DJ (2012) Peripheral circulation. Compr Physiol 2:321–447
Majid DSA, Iinscho EW, Navar LG (1999) P2 purinoceptor saturation by adenosine triphosphate impairs renal autoregulation in dogs. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:492–498
McAllister RM, Newcomer SC, Pope ER, Turk JR, Laughlin MH (2008) Effects of chronic nitric oxide synthase inhibition on responses to acute exercise in swine. J Appl Physiol 104:186–197
McCullough WT, Collins DM, Ellsworth ML (1997) Arteriolar responses to extracellular ATP in striated muscle. Am J Physiol 272:H1886–H1891
Mitchell C, Syed N, Tengah A, Gurney AM, Kennedy C (2012) Identification of contractile P2Y1, P2Y6, and P2Y12 receptors in rat intrapulmonary artery using selective ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 343:755–762
Mortensen SP, González-Alonso J, Damsgaard R, Saltin B, Hellsten Y (2007) Inhibition of nitric oxide and prostaglandins, but not endothelial-derived hyperpolarizing factors, reduces blood flow and aerobic energy turnover in the exercising human leg. J Physiol 581:853–861
Mortensen SP, Gonzalez-Alonso J, Bune LT, Saltin B, Pilegaard H, Hellsten Y (2009a) ATP-induced vasodilation and purinergic receptors in the human leg: roles of nitric oxide, prostaglandins, and adenosine. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R1140–R1148
Mortensen SP, Gonzalez-Alonso J, Nielsen JJ, Saltin B, Hellsten Y (2009b) Muscle interstitial ATP and norepinephrine concentrations in the human leg during exercise and ATP infusion. J Appl Physiol 107:1757–1762
Mortensen SP, Nyberg M, Thaning P, Saltin B, Hellsten Y (2009c) Adenosine contributes to blood flow regulation in the exercising human leg by increasing prostaglandin and nitric oxide formation. Hypertension 53:993–999
Mortensen SP, Thaning P, Nyberg M, Saltin B, Hellsten Y (2011) Local release of ATP into the arterial inflow and venous drainage of human skeletal muscle: insight from ATP determination with the intravascular microdialysis technique. J Physiol 589:1847–1857
Rådegran G, Calbet JA (2001) Role of adenosine in exercise-induced human skeletal muscle vasodilatation. Acta Physiol Scand 171:177–185
Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50:413–492
Remensnyder J, Mitchell JH, Sarnoff SJ (1962) Functional sympatholysis during muscular activity. Observations on influence of carotid sinus on oxygen uptake. Circ Res 11:370–380
Rosenmeier JB, Hansen J, González-Alonso J (2004) Circulating ATP-induced vasodilatation overrides sympathetic vasoconstrictor activity in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 558:351–365
Rosenmeier JB, Yegutkin GG, Gonzalez-Alonso J (2008) Activation of ATP/UTP selective receptors increase blood flow and blunt sympathetic vasoconstriction in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 586:4993–5002
Rubino A, Burnstock G (1996) Evidence for a P2-purinoceptor mediating vasoconstriction by UTP, ATP and related nucleotides in the isolated pulmonary vascular bed of the rat. Br J Pharmacol 118:1415–1420
Saiag B, Bodin P, Shacoori V, Catheline M, Rault B, Burnstock G (1995) Uptake and flow-induced release of uridine nucleotides from isolated vascular endothelial cells. Endothelium 2:279–285
Saunders NR, Dinenno FA, Pyke KE, Rogers AM, Tschakovsky ME (2005) Impact of combined NO and PG blockade on rapid vasodilation in a forearm mild-to-moderate exercise transition in humans. Am J Physiol 288:H214–H220
Schrage WG, Dietz NM, Joyner MJ (2006) Effects of combined inhibition of ATP-sensitive potassium channels, nitric oxide, and prostaglandins on hyperemia during moderate exercise. J Appl Physiol 100:1506–1512
Smits P, Williams SB, Lipson DE, Banitt P, Rongen GA, Creager MA (1995) Endothelial release of nitric oxide contributes to the vasodilator effect of adenosine in humans. Circulation 92:2135–2141
Sprague RS, Ellsworth ML, Stephenson AH, Lonigro AJ (1996) ATP: the red blood cell link to NO and local control of the pulmonary circulation. Am J Physiol 271:H2717–H2722
Thaning P, Bune LT, Hellsten Y, Pilegaard H, Saltin B, Rosenmeier JB (2010) Attenuated purinergic receptor function in patients with type 2 diabetes. [Article]. Diabetes 59:182–189
van Ginneken EE, Meijer P, Verkaik N, Smits P, Rongen GA (2004) ATP-induced vasodilation in human skeletal muscle. Br J Pharmacol 141:842–850
Wihlborg AK, Balogh J, Wang L, Borna C, Dou Y, Joshi BV, Lazarowski E, Jacobson KA, Arner A, Erlinge D (2006) Positive inotropic effects by uridine triphosphate (UTP) and uridine diphosphate (UDP) via P2Y2 and P2Y6 receptors on cardiomyocytes and release of UTP in man during myocardial infarction. Circ Res 98:970–976
Yegutkin GG, Samburski SS, Mortensen SP, Jalkanen S, Gonzalez-Alonso J (2007) Intravascular ADP and soluble nucleotidases contribute to acute prothrombotic state during vigorous exercise in humans. J Physiol 579:553–564
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Novo Nordisk foundation. The technical assistance of Cory Weimer, Dave Harah and Denise Holiman is gratefully acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Carsten Lundby.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortensen, S.P., McAllister, R.M., Yang, H.T. et al. The effect of purinergic P2 receptor blockade on skeletal muscle exercise hyperemia in miniature swine. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 2147–2155 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2932-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2932-8