Abstract
Purpose
We highlighted a relationship between decompression-induced bubble formation and platelet micro-particle (PMP) release after a scuba air-dive. It is known that decompression protocol using oxygen-stop accelerates the washout of nitrogen loaded in tissues. The aim was to study the effect of oxygen deco-stop on bubble formation and cell-derived MP release.
Methods
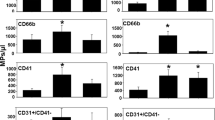
Healthy experienced divers performed two scuba-air dives to 30 msw for 30 min, one with an air deco-stop and a second with 100 % oxygen deco-stop at 3 msw for 9 min. Bubble grades were monitored with ultrasound and converted to the Kisman integrated severity score (KISS). Blood samples for cell-derived micro-particle analysis (AnnexinV for PMP and CD31 for endothelial MP) were taken 1 h before and after each dive.
Results
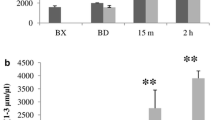
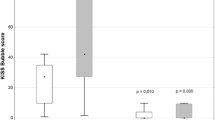
Mean KISS bubble score was significantly lower after the dive with oxygen-decompression stop, compared to the dive with air-decompression stop (4.3 ± 7.3 vs. 32.7 ± 19.9, p < 0.001). After the dive with an air-breathing decompression stop, we observed an increase of the post-dive mean values of PMP (753 ± 245 vs. 381 ± 191 ng/μl, p = 0.003) but no significant change in the oxygen-stop decompression dive (329 ± 215 vs. 381 +/191 ng/μl, p = 0.2). For the post-dive mean values of endothelial MP, there was no significant difference between both the dives.
Conclusions
The Oxygen breathing during decompression has a beneficial effect on bubble formation accelerating the washout of nitrogen loaded in tissues. Secondary oxygen-decompression stop could reduce bubble-induced platelet activation and the pro-coagulant activity of PMP release preventing the thrombotic event in the pathogenesis of decompression sickness.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BIPA:
-
Bubble-induced platelet activation
- DCS:
-
Decompression sickness
- EMP:
-
Endothelial cells derived microparticles
- KISS:
-
Kisman integrated severity score
- MP:
-
Micro-particle
- PECAM:
-
Platelet endothelium adhesion molecule
- PFP:
-
Platelet-free plasma
- PMP:
-
Platelet microparticles
- VGE:
-
Venous gas emboli
References
Arieli Y, Arieli R, Marx A (2002) Hyperbaric oxygen may reduce gas bubbles in decompressed prawns by eliminating gas nuclei. J Appl Physiol 92(6):2596–2599
Arieli R, Boaron E, Abramovich A (2009) Combined effect of denucleation and denitrogenation on the risk of decompression sickness in rats. J Appl Physiol 106:1453–1458
Baj Z, Olszański R, Majewska E, Konarski M (2000) The effect of air and nitrox divings on platelet activation tested by flow cytometry. Aviat Space Environ Med 71(9):925–928
Behnke AR (1965) Problems in the treatment of decompression sickness (and traumatic air embolism). Ann NY Acad Sci 117:843–864
Berckmans RJ, Nieuwland R, Boing AN, Romijn FP, Hack CE, Sturk A (2001) Cell-derived microparticles circulate in healthy humans and support low grade thrombin generation. Thromb Haemost 85:639–646
Blatteau JE, Pontier JM (2009) Effect of in-water recompression with oxygen to 6 msw versus normobaric oxygen breathing on bubble formation in divers. Eur J Appl Physiol 106:691–695
Butler BD, Little T, Cogan V, Powell M (2006) Hyperbaric oxygen pre-breathe modifies the outcome of decompression sickness. Undersea Hyperb Med 33:407–417
Castagna O, Gempp E, Blatteau JE (2009) Pre-dive normobaric oxygen reduces bubble formation in scuba divers. Eur J Appl Physiol 106:167–172
Eftedal O, Brubakk AO (1997) Agreement between trained and untrained observers in grading intravascular bubble signals in ultrasonic images. Undersea Hyperb Med 24:293–299
Gennser M, Blogg SL (2008) Oxygen or carbogen breathing before simulated submarine escape. J Appl Physiol 104:50–56
Hamilton RWT, Edward D (2003) Decompression practice. In: Saunders US, Brubakk Alf O, Neuman Tom S (ed) Bennett and Elliott’s physiology and medicine of diving, 5th edn, pp 477–478
Jacobs MHT, Stewart DR (1942) Observations on the blood of albino rats following rapid decompression. US Natl Res Council Comm Aviat Med, pp 1–5
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM, Horstman LL, Soderland C, Ahn YS (2003a) Endothelial microparticles released in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura express von Willebrand factor and markers of endothelial activation. Br J Haematol 123:896–902
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM, Soderland C, Horstman LL, Ahn YS (2003b) Endothelial cells release phenotypically and quantitatively distinct microparticles in activation and apoptosis. Thrombo Res 109:175–180
Katsenelson K, Arieli Y, Abramovich A, Feinsod M, Arieli R (2007) Hyperbaric oxygen pretreatment reduces the incidence of decompression sickness in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:571–576
Landolfi AYZ, Savini F, Camporesi EM, Faralli F, Bosco G (2006) Pre-treatment with hyperbaric oxygenation reduces bubble formation and platelet activation. Sport Sci Health 1:122–128
Lemaitre F, Meunier N, Bedu M (2002) Effect of air diving exposure generally encountered by recreational divers: oxidative stress? Undersea Hyperbar Med 29:39–49
Madden D, Lozo M, Dujic Z, Ljubkovic M (2013) Exercise after SCUBA diving increases the incidence of arterial gas embolism. J Appl Physiol 115(5):716–722
Madden LA, Laden G (2007) Endothelial micro-particles in vascular disease and as a potential marker of decompression illness. Eur J Underwater Hyperb Med 8:6–10
Madden LA, Laden G (2009) Gas bubbles may not be the underlying cause of decompression illness––the at-depth endothelial dysfunction hypothesis. Med Hypotheses 72:389–392
Madden LA, Greenman J (2004) Microparticles as a marker of vascular endothelial perturbation. Immunology 113:23–29
Mollerlokken A, Gutvik C, Berge VJ, Jorgensen A, Loset A, Brubakk AO (2007) Recompression during decompression and effects on bubble formation in the pig. Aviat Space Environ Med 78:557–560
Nossum V, Hjelde A, Brubakk AO (2002) Small amounts of venous gas embolism cause delayed impairment of endothelial function and increase polymorphonuclear neutrophil infiltration. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:209–214
Piccin A, Murphy WG, Smith OP (2007) Circulating microparticles: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Blood Rev 21:157–171
Pontier JM, Blatteau JE, Vallee N (2008a) Blood platelet count and severity of decompression sickness in rats after a provocative dive. Aviat Space Environ Med 79:761–764
Pontier JM, Gempp E, Ignatescu M (2012) Blood platelet-derived microparticles release and bubble formation after an open-sea air dive. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab (Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme) 37:888–892
Pontier JM, Jimenez C, Blatteau JE (2008b) Blood platelet count and bubble formation after a dive to 30 msw for 30 min. Aviat Space Environ Med 79:1096–1099
Pontier JM, Vallee N, Bourdon L (2009) Bubble-induced platelet aggregation in a rat model of decompression sickness. J Appl Physiol 107:1825–1829
Pontier JM, Vallee N, Ignatescu M, Bourdon L (2011) Pharmacological intervention against bubble-induced platelet aggregation in a rat model of decompression sickness. J Appl Physiol 110:724–729
Radomski MW, Moncada S (1993) The biological and pharmacological role of nitric oxide in platelet function. Adv Exp Med Biol 344:251–264
Thom SR, Milovanova TN, Bogush M, Bhopale VM, Yang M, Bushmann K, Pollock NW, Ljubkovic M, Denoble P, Dujic Z (2012) Microparticle production, neutrophil activation, and intravascular bubbles following open-water SCUBA diving. J Appl Physiol 112:1268–1278
Thorsen T, Ovstedal T, Vereide A, Holmsen H (1986) Effects of platelet antagonists on the reduction in platelet density caused by microbubbles in vitro. Undersea Biomed Res 13:289–303
Webb JT, Pilmanis AA (1999) Preoxygenation time versus decompression sickness incidence. Safe J 29:75–78
Westgren M, Ringden O, Eik-Nes S, Ek S, Anvret M, Brubakk AM, Bui TH, Giambona A, Kiserud T, Kjaeldgaard A, Maggio A, Markling L, Seiger A, Orlandi F (1996) Lack of evidence of permanent engraftment after in utero fetal stem cell transplantation in congenital hemoglobinopathies. Transplantation 61:1176–1179
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the divers and the hyperbaric nurses from the French Navy Diving School in Toulon for participating and helping in this study. The authors would like to acknowledge the PHYPODE project, financed by the European commission under a Marie Curie initial training network (FP7-PEOPLE-2010-ITN program).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by David C. Poole.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pontier, JM., Lambrechts, K. Effect of oxygen-breathing during a decompression-stop on bubble-induced platelet activation after an open-sea air dive. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 1175–1181 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2841-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2841-x