Abstract
Purpose
Post-activation depression (PaD) refers to the inhibition of the H-reflex induced by a preceding conditioning stimulus able to activate the afferents mediating the H-reflex itself. PaD can be investigated assessing the frequency-related depression of the H-reflex. This parameter, which is highly correlated to the severity of spasticity, has been used in the longitudinal assessment of spastic patients, in particular to assess the effect of drugs and rehabilitation over the years. However, in such longitudinal assessment, changes observed might be age related and not only disease related. The aim of this study was to investigate the possible age effects on PaD.
Methods
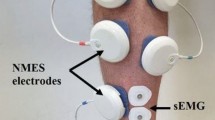
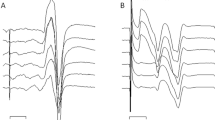
The frequency-related depression of the flexor carpi radialis (FCR) H-reflex was examined in two groups of young (20 subjects; 28 ± 3 years) and aged (18 subjects; 69 ± 6 years) healthy subjects. PaD was evaluated by comparing the H-reflex amplitudes obtained with a stimulation frequency of 0.1 Hz with those obtained using higher frequencies (0.33–0.5–1–2 Hz).
Results
The results showed that frequency-related depression of the FCR H-reflex is similar in young and elderly subjects at all frequencies, with the exception of 2 Hz.
Conclusion
Our study shows that ageing does not affect the frequency-related depression of the FCR H-reflex at the frequencies of 1 Hz or lower, supporting the reliability of this method to assess PaD in the clinical practice, particularly for the longitudinal assessment of spasticity. A decrease of GABA-ergic presynaptic inhibition seems to be the more likely explanation for the age-related changes that we observed at the frequency of 2 Hz.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PaD:
-
Post-activation depression
- FCR:
-
Flexor carpi radialis muscle
References
Achache V, Roche N, Lamy J, Boakye M, Lackmy A, Gastal A, Quentin V, Katz R (2010) Transmission within several spinal pathways in adults with cerebral palsy. Brain 133:1470–1483
Aymard C, Katz R, Lafitte C, Lo E, Pénicaud A, Pradat-Diehl P, Raoul S (2000) Presynaptic inhibition and homosynaptic depression: a comparison between lower and upper limbs in normal human subjects and patients with hemiplegia. Brain 123:1688–1702
Butchart P, Farquhar R, Part NJ, Roberts RC (1993) The effect of age and voluntary contraction on presynaptic inhibition of soleus muscle Ia afferent terminals in man. Exp Physiol 78:235–242
Calancie B, Broton JG, Klose KJ, Traad M, Difini J, Ayyar DR (1993) Evidence that alterations in presynaptic inhibition contribute to segmental hypo- and hyperexcitability after spinal cord injury in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 89:177–186
Capek R, Esplin B (1977) Homosynaptic depression and transmitter turnover in spinal monosynaptic pathway. J Neurophysiol 40:95–105
Clair JM, Anderson-Reid JM, Graham CM, Collins DF (2011) Post-activation depression and recovery of reflex transmission during repetitive electrical stimulation of the human tibial nerve. J Neurophysiol 106:184–192
Crone C, Nielsen J (1989) Methodological implications of the post activation depression of the soleus H-reflex in man. Exp Brain Res 78:28–32
Curtis DR, Eccles JC (1960) Synaptic action during and after repetitive stimulation. J Physiol 150:374–398
Eccles JC (1964) The physiology of synapses. Springer, Berlin
Eccles JC, Schmidt R, Willis WD (1963) Pharmacological studies on presynaptic inhibition. J Physiol 168:500–530
Grey MJ, Klinge K, Crone C, Lorentzen J, Biering-Sørensen F, Ravnborg M, Nielsen JB (2008) Post-activation depression of soleus stretch reflexes in healthy and spastic humans. Exp Brain Res 185:189–197
Hultborn H, Illert M, Nielsen J, Paul A, Ballegaard M, Wiese H (1996) On the mechanism of the post-activation depression of the H-reflex in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 108:450–462
Ishikawa K, Ott K, Porter RW, Stuart D (1966) Low frequency depression of the H wave in normal and spinal man. Exp Neurol 15:140–156
Kanda K, Hashizume K (1989) Changes in properties of the medial gastrocnemius motor units in aging rats. J Neurophysiol 61:737–746
Kohn AF, Floeter MK, Hallett M (1997) Presynaptic inhibition compared with homosynaptic depression as an explanation for soleus H-reflex depression in humans. Exp Brain Res 116:375–380
Lamy J, Wargon I, Mazevet D, Ghanim Z, Pradat-Diehl P, Katz R (2009) Impaired efficacy of spinal presynaptic mechanisms in spastic stroke patients. Brain 132:734–748
Lundbye-Jensen J, Nielsen JB (2008) Immobilization induces changes in presynaptic control of group Ia afferents in healthy humans. J Physiol 586:4121–4135
Meunier S, Kwon J, Russmann H, Ravindran S, Mazzocchio R, Cohen L (2007) Spinal use-dependent plasticity of synaptic transmission in humans after a single cycling session. J Physiol 579:375–388
Miwa T, Miwa Y, Kanda K (1995) Dynamic and static sensitivities of muscle spindle primary endings in aged rats to ramp stretch. Neurosci Lett 201:179–182
Nielsen J, Petersen N, Ballegaard M, Biering-Sørensen F, Kiehn O (1993) H-reflexes are less depressed following muscle stretch in spastic spinal cord injured patients than in healthy subjects. Exp Brain Res 97:173–176
Robertson CT, Koceja DM (2003) Post-activation depression of the soleus H-reflex in the elderly. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 43:103–111
Rossi-Durand C, Jones KE, Adams S, Bawa P (1999) Comparison of the depression of H-reflexes following previous activation in upper and lower limb muscles in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 126:117–127
Schieppati M, Crenna P (1984) From activity to rest: gating of excitatory autogenetic afferences from the relaxing muscle in man. Exp Brain Res 56:448–457
Schindler-Ivens S, Shields RK (2000) Low frequency depression of H-reflexes in humans with acute and chronic spinal-cord injury. Exp Brain Res 133:233–241
Shields RK, Dudley-Javoroski S, Oza PD (2011) Low-frequency H-reflex depression in trained human soleus after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett 499:88–92
Swash M, Fox KP (1972) Techniques for the demonstration of human muscle spindle innervation in neuromuscular disease. J Neurol Sci 15:291–302
Trimble MH, Kukulka CG, Behrman AL (1998) The effect of treadmill gait training on low-frequency depression of the soleus H-reflex: comparison of a spinal cord injured man to normal subjects. Neurosci Lett 246:186–188
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Alain Martin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trompetto, C., Marinelli, L., Mori, L. et al. The effect of age on post-activation depression of the upper limb H-reflex. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 359–364 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2778-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2778-5