Abstract
Purpose
Eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage may cause marked alterations in insulin sensitivity. However, it is not entirely known whether such alterations are also related to changes in adipokine levels. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of muscle damage due to downhill running on inflammation, insulin sensitivity and selected adipokines related to insulin regulation (adiponectin, visfatin, resistin).
Methods
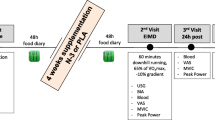
Data were collected from 12 healthy adult women. Each subject participated in two trials, 4 weeks apart. The first trial was reserved for resting measurements only (control trial), while the second trial involved a 45-min exercise (−15 % slope, ~60 % of VO2max) intervention (exercise trial). Insulin sensitivity (HOMA), creatine kinase activity (CK), delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), glucose, insulin, adiponectin, resistin, and visfatin were assessed pre-exercise and 1, 2, 3, and 4 days post-exercise and during the same time points in the control trial.
Results
Analyses revealed that CK, DOMS, TNF-α, IL-6, insulin and HOMA significantly increased (p < 0.05) throughout recovery (days 1–4). Adiponectin and visfatin remained unchanged, while resistin significantly increased (p < 0.05) only 2 days post-exercise. Visfatin was negatively correlated with HOMA at days 1 and 4 of recovery.
Conclusion
Although muscle damage due to downhill running caused a decline of insulin sensitivity, this response was not associated with the changes in adipokine levels.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AdipoR1:
-
Adiponectin receptors 1
- AdipoR2:
-
Adiponectin receptors 2
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CK:
-
Creatine kinase
- DOMS:
-
Delayed onset of muscle soreness
- GLUT-4:
-
Glucose transporter type 4
- HOMA:
-
Homeostasis model assessment
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- IRS-1:
-
Insulin receptor substrate 1
- PI-3:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PBMCs:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- VO2 :
-
Oxygen consumption
- VO2max :
-
Maximal oxygen consumption
References
Anderson P, Mehta N, Wolfe M, Hinkle C, Pruscino L, Comiskey L, Tabita-Martinez J, Sellers KF, Rickels MR, Ahima RS, Reilly M (2007) Innate immunity modulates adipokines in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:2272–2279
Armstrong R (1984) Mechanisms of exercise induced delayed onset muscle soreness: a brief review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 16:529–538
Asp S, Daugaard J, Richter E (1995) Eccentric exercise decreases glucose transporter GLUT4 protein in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 482(Pt 3):705–712
Balducci S, Zanuso S, Nicolucci A, Fernando F, Cavallo S, Cardelli P, Fallucca S, Alessi E, Letizia C, Jimenez A, Fallucca F, Pugliese G (2010) Anti-inflammatory effect of exercise training in subjects with type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome is dependent on exercise modalities and independent of weight loss. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 20:608–617
Beaton L, Tarnopolsky M, Phillips S (2002) Contraction-induced muscle damage in humans following calcium channel blocker administration. J Physiol 544(Pt 3):849–859
Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L, Smith U, Tarkowski A (2005) Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory properties. J Immunol 174(9):5789–5795
Carter A, Dobridge J, Hackney A (2001) Influence of estrogen on markers of muscle tissue damage following eccentric exercise. Fiziol Cheloveka 27(5):133–137
Chen M, Chung F, Chang D, Tsai J, Huang H, Shin S, Lee Y (2006) Elevated plasma level of visfatin/pre B cell colony-enhancing actor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:295–299
Chen T, Nosaka K, Tu J (2007) Changes in running economy following downhill running. J Sports Sci 25(1):55–63
Choi K, Kim J-Y, Cho G, Baik S, Park H, Kim S (2007) Effect of exercise training on plasma visfatin and eotaxin levels. Eur J Endocrinol 157:437–442
Conde J, Scotece M, Gómez R, López V, Gómez-Reino J, Lago F, Gualillo O (2011) Adipokines: biofactors from white adipose tissue. A complex hub among inflammation, metabolism, and immunity. BioFactors 37(6):413–420
Del Aguila L, Krishnan R, Ulbrecht J, Farrell P, Correll P, Lang C, Zierath JR, Kirwan J (2000) Muscle damage impairs insulin stimulation of IRS-1, PI 3-kinase, and Akt-kinase in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279(1):206–212
Dibble L, Hale T, Marcus R, Gerber J, Lastayo P (2006) The safety and feasibility of high-force eccentric resistance exercise in persons with Parkinson’s disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 87(9):1280–1282
Fasshauer M, Paschke R (2003) Regulation of adipocytokines and insulin resistance. Diabetologia 46(12):1594–1603
Fehrenbach E, Schneider M (2006) Trauma-induced systemic inflammatory response versus exercise-induced immunomodulatory effects. Sports Med 36:373–384
Franckhauser S, Elias I, Rotter Sopasakis V, Ferré T, Nagaev I, Andersson CX, Agudo J, Ruberte J, Bosch F, Smith U (2008) Overexpression of Il6 leads to hyperinsulinaemia, liver inflammation and reduced body weight in mice. Diabetologia 51(7):1306–1316
Fruebis J, Tsao T, Javorschi S, Ebbets-Reed D, Erickson M, Yen F, Bihain BE, Lodish H (2001) Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2005–2010
Halberg N, Schraw T, Wang Z, Kim J-Y, Yi J, Hamilton M, Luby-Phelps K, Scherer P (2009) Systemic fate of the adipocyte-derived factor adiponectin. Diabetes 58:1961–1970
Haus J, Solomon T, Marchetti C, O’Leary V, Brooks L, Gonzalez F, Kirwan J (2009) Decreased visfatin after exercise training correlates with improved glucose tolerance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:1255–1260
Heath G, Gavin J III, Hinderliter J, Hag-Berg J, Bloomfield S, Holloszy J (1983) Effects of exercise and lack of exercise on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. J Appl Physiol 55:512–517
Jamurtas A, Theocharis V, Tofas T, Tsiokanos A, Yfanti C, Paschalis V, Koutedakis Y, Nosaka K (2005) Comparison between leg and arm eccentric exercises of the same relative intensity on indices of muscle damage. Eur J Appl Physiol 95(2–3):179–185
Jamurtas A, Theocharis V, Koukoulis G, Stakias N, Fatouros I, Kouretas D, Koutedakis Y (2006) The effects of acute exercise on serum adiponectin and resistin levels and their relation to insulin sensitivity in overweight males. Eur J Appl Physiol 97(1):122–126
Jürimäe J, Rämson R, Mäestu J, Purge P, Jürimäe T, Arciero P, von Duvillard S (2009) Plasma visfatin and ghrelin response to prolonged sculling in competitive male rowers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(1):137–143
Keller P, Moller K, Krabbe K, Pedersen B (2003) Circulating adiponectin levels during human endotoxemia. Clin Exp Immunol 134:107–110
Kendall B, Eston R (2002) Exercise-induced muscle damage and the potential protective role of estrogen. Sports Med 32(2):103–123
Kern P, Di Gregorio G, Lu T, Rassouli N, Ranganathan G (2003) Adiponectin expression from human adipose tissue: relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression. Diabetes 52:1779–1785
Kirwan J, del Aguila L (2003) Insulin signalling, exercise and cellular integrity. Biochem Soc Trans 31(Pt 6):1281–1285
Kirwan JP, Hickner RC, Yarasheski KE, Kohrt WM, Wiethop BV, Holloszy J (1992) Eccentric exercise induces transient insulin resistance in healthy individuals. J Appl Physiol 72(6):2197–2202
Komi P, Buskirk E (1972) Effect of eccentric and concentric muscle conditioning on tension and electrical activity of human muscle. Ergonomics 15:417–434
Lastayo P, Larsen S, Smith S, Dibble L, Marcus R (2010) The feasibility and efficacy of eccentric exercise with older cancer survivors: a preliminary study. J Geriatr Phys Ther 33(3):135–140
Matthews D, Hosker J, Rudenski A, Naylor B, Treacher D, Turner R (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28(7):412–419
Mikines K, Sonne B, Tronier B, Galbo H (1989) Effects of acute exercise and detraining on insulin action in trained men. J Appl Physiol 66:704–711
Moschen A, Gerner R, Tilg H (2010) Pre-B cell colony enhancing factor/NAMPT/visfatin in inflammation and obesity-related disorders. Curr Pharm Des 16(17):1913–1920
Nikolaidis M, Paschalis V, Giakas G, Fatouros I, Sakellariou G, Theodorou A, Koutedakis Y, Jamurtas A (2008) Favorable and prolonged changes in blood lipid profile after muscle-damaging exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(8):1483–1489
Ohmori R, Momiyama Y, Kato R, Taniguchi H, Ogura M, Ayaori M, Nakamura H, Ohsuzu F (2005) Associations between serum resistin levels and insulin resistance, inflammation, and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:379–380
Ouedraogo R, Gong Y, Berzins B, Wu X, Mahadev K, Hough K, Chan L, Goldstein BJ, Scalia R (2007) Adiponectin deficiency increases leukocyte endothelium interactions via upregulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules in vivo. J Clin Invest 117:1718–1726
Paschalis V, Nikolaidis MG, Giakas G, Theodorou AA, Sakellariou GK, Koutedakis Y, Fatouros IG, Jamurtas AZ (2010) Beneficial changes in energy expenditure and lipid profile after eccentric exercise in overweight and lean women. Scand J Med Sci Sports 20(1):103–111
Paschalis V, Nikolaidis M, Theodorou A, Panayiotou G, Fatouros I, Koutedakis Y, Jamurtas AZ (2011) A weekly bout of eccentric exercise is sufficient to induce health-promoting effects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(1):64–73
Peake J, Nosaka K, Suzuki K (2005) Characterization of inflammatory responses to eccentric exercise in humans. Exerc Immunol Rev 11:64–85
Pedersen BK (2011) Muscles and their myokines. J Exp Biol 214(Pt 2):337–346. doi:10.1242/jeb.048074
Rajala MW, Obici S, Scherer PE, Rossetti L (2003) Adipose-derived resistin and gut-derived resistin-like molecule-beta selectively impair insulin action on glucose production. J Clin Invest 111(2):225–230. doi:10.1172/JCI16521
Robinson K, Prins J, Venkatesh B (2011) Clinical review: adiponectin biology and its role in inflammation and critical illness. Crit Care 15(2):221
Senn J, Klover P, Nowak I, Mooney R (2002) Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Diabetes 51:3391–3399
Sethi J, Vidal-Puig A (2005) Visfatin: the missing link between intra-abdominal obesity and diabetes? Trends Mol Med 11(8):344–347
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA (2001) The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 409(6818):307–312. doi:10.1038/35053000
Yang W, Lee W, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Matsuzawa Y, Chao C, Chen CL, Tai TY, Chuang L (2001) Weight reduction increases plasma levels of an adipose-derived anti-inflammatory protein, adiponectin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3815–3819
Yu J, Javorschi S, Hevener A, Kruszynska Y, Norman R, Sinha M, Olefsky J (2002) The effect of thiazolidinediones on plasma adiponectin levels in normal, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes 51:2968–2974
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jean-René Lacour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamurtas, A.Z., Garyfallopoulou, A., Theodorou, A.A. et al. A single bout of downhill running transiently increases HOMA-IR without altering adipokine response in healthy adult women. Eur J Appl Physiol 113, 2925–2932 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2717-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2717-5