Abstract
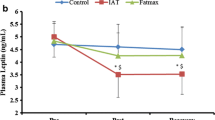
The aim was to investigate the effect of high-volume low intensity resistance training protocol combined with endurance training on plasma neuropeptide Y (NPY) concentration in rowers. Additionally, leptin and ghrelin, as markers for body energy balance concentrations, were monitored. 12 highly trained national and international level male rowers participated in this study. The participants were tested three times—after reference week (T1), after 2 weeks of high-volume training (T2) and after a recovery week (T3) for aerobic performance, energy intake and expenditure, and blood biochemical parameters. The submaximal rowing performance decreased significantly (P = 0.019) at T2. Fasting leptin decreased significantly (from 2.05 ± 0.88 to 1.28 ± 0.53 ng/mL; P = 0.009) at T2 and increased significantly (from 1.28 ± 0.53 to 1.79 ± 0.79 ng/mL; P = 0.002) at T3. Fasting ghrelin decreased significantly (from 980 ± 300.2 to 873.35 ± 198.6 pg/mL; P = 0.036) at T3 compared to T2, while no changes were found in fasting NPY. Significant decreases in exercise-induced leptin were observed at T2 (from 1.13 ± 0.5 to 1.08 ± 0.5 ng/mL; P = 0.012), PRE and POST test leptin values at T2 were significantly decreased compared to T1(1.40 ± 0.9 to 1.13 ± 0.5 and 1.44 ± 0.8 to 1.08 ± 0.5, respectively). Acute exercise-induced increases in NPY were found at T2 (from 128.1 ± 23.2 to 155.1 ± 28.9 pmol/L; P = 0.002) and at T3 (from 131.3 ± 20.5 to 159.7 ± 32.8 pmol/L, P = 0.004). In conclusion, the combination of high-volume training protocol and energy imbalance induces significant post-exercise changes in NPY, leptin, and ghrelin concentrations and decreases fasting leptin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Leblanc C, Lortie G, Savard R, Thériault G (1983) A method to assess energy expenditure in children and adults. Am J Clin Nutr 37:461–467
Burns SF, Broom DR, Miyashita M, Mundy C, Stensel DJ (2007) A single session of treadmill running has no effect on plasma total ghrelin concentrations. J Sports Sci 25:635–642
Chen JX, Zhao X, Wang ZF (2007) Influence of acute and chronic treadmill exercise on rat plasma lactate and brain NPY, L-ENK, DYN A1–13. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:1–10
Chowdhury I, Chien JT, Chatterjee A, Yu JY (2004) Effects of leptin and neuropeptide-Y on transcript levels of thyrotropin beta and common alpha subunits of rat pituitary in vitro. Life Sci 75:2897–2909
Cummings DE, Frayo RS, Marmonier C, Aubert R, Chapelot D (2004) Plasma ghrelin levels and hunger scores in humans initiating meals voluntarily without time- and food-related cues. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287:297–304
Desgorces FD, Chennaoui M, Gomez-Merino D, Drogou C, Guezennec CY (2004) Leptin response to acute prolonged exercise after training in rowers. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:677–681
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Fletcher MA, Rosenthal M, Antoni M, Ironson G, Zeng XR, Barnes Z, Harvey JM, Hurwitz B, Levis S, Broderick G, Klimas NG (2010) Plasma neuropeptide Y: a biomarker for symptom severity in chronic fatigue syndrome. Behav Brain Funct 6:7
Foster-Schubert KE, McTiernan A, Scott Frayo R, Schwartz RS, Rajan KB, Yasui Y, Dvoroger SS, Cummings DE (2005) Human plasma levels of ghrelin increase during a one-year exercise program. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 90:820–825
Ghanbari-Niaki A, Abednazari H, Tayebi SM, Hossaini-Kakhak A, Kraemer RR (2009) Treadmill training enhances rat agouti-related protein in plasma and reduces ghrelin levels in plasma and soleus muscle. Metabolism 58:1747–1752
Hagobian TA, Sharoff CG, Braun B (2008) Effects of short term exercise and energy surplus on hormones related to regulation of energy balance. Metabolism 57:393–398
Heilig M (2004) The NPY system in stress anxiety and depression. Neuropeptides 38:213–224
Hofmann P, Jürimae J, Jürimae T, Mäestu J, Purge P, Pokan R, von Duvillard SP (2007) HRTP, prolonged ergometer exercise and single sculling. Int J Sports Med 28:964–969
Irwin MR (2008) Human psychoneuroimmunology: 20 years of discovery. Brain Behav Immunol 22:129–139
Joannic JL, Oppert JM, Lahlou N, Basdevant A, Auboiron S, Raison J, Bornet F, Guy-Grand B (1998) Plasma leptin and hunger ratings in healthy humans. Appetite 30:129–138
Jürimäe J, Mäestu J, Jürimäe T (2003) Leptin as a marker of training stress in highly trained male rowers? Eur J Appl Physiol 90:533–538
Jürimäe J, Hofmann P, Jürimäe T, Palm R, Mäestu J, Purge P, Sudi K, Rom K, von Duvillard SP (2007) Plasma ghrelin responses to acute sculling exercises in elite male rowers. Eur J Appl Physiol 99:467–474
Jürimäe J, Rämson R, Mäestu J, Purge P, Jürimäe T, Arciero PJ, von Duvillard SP (2009) Plasma visfatin and ghrelin response to prolonged sculling in competitive male rowers. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:137–143
Karamouzis I, Karamouzis M, Vrabas IS, Christoulas K, Kyriasis N, Giannoulis E, Mandroukas K (2002) The effects of marathon swimming on serum leptin and plasma neuropeptide Y levels. Clin Chem Lab Med 40:132–136
Kokot F, Ficek R (1999) Effects of neuropeptide Y on appetite. Miner Electrolyte Metab 25:303–305
Kraemer RR, Durand RJ, Acevedo EO, Johnson LG, Kraemer GR, Hebert EP, Castracane VD (2004) Rigorous running increases growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I without altering ghrelin. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 229:240–246
Kuo LE, Zukowska Z (2007) Stress, NPY and vascular remodeling: implications for stress related diseases. Peptides 28:435–440
Levenson CW, Moore JB (1998) Response of rat adrenal neuropeptide Y and tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA to acute stress is enhanced by long term voluntary exercise. Neurosci Lett 20:177–179
Mäestu J, Jürimäe J, Jürimäe T (2003) Hormonal reactions during heavy training stress and following tapering in highly trained male rowers. Horm Metab Res 35:109–113
Mäestu J, Jürimäe J, Jürimäe T (2005) Monitoring of performance and training in rowing. Sports Med 35:597–617
Mäestu J, Jürimäe J, Valter I, Jürimäe T (2008) Increases in ghrelin and decreases in leptin without altering adiponectin during extreme weight loss in male competitive bodybuilders. Metabolism 57:221–225
Mikulic P, Vucetic V, Sentija D (2011) Strong relationship between heart rate deflection point and ventilatory threshold in trained rowers. J Strength Cond Res 25:360–366
Morgan CA, Rasmusson AM, Wang S, Hoyt G, Hauger RL, Hazlett G (2002) Neuropeptide-Y, cortisol and subjective distress in human exposed to acute stress replication and extension of previous report. Biol Psychiatr 52:136–142
Rämson R, Jürimäe J, Jürimäe T, Mäestu J (2008) The influence of increased training volume on cytokines and ghrelin concentration in college level male rowers. Eur J Appl Physiol 104:839–846
Rämson R, Jürimäe J, Jürimäe T, Mäestu J (2009) Behaviour of testosterone and cortisol during an intensity-controlled high-volume training period measured by a training task-specific test in men rowers. J Strength Cond Res 23:645–651
Richard D (1995) Exercise and the neurobiological control of food intake and energy expenditure. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 19:73–79
Shin MS, Kim H, Chang HK, Lee TH, Jang MH, Shin MC, Lim BV, Lee HH, Kim YP, Yoon JH, Jeong IG, Kim CJ (2003) Treadmill exercise suppresses diabetes induced increment of neuropeptide Y expression in the hypothalamus of rats. Neurosci Lett 346:157–160
Simsch C, Lormes W, Petersen KG, Baur S, Liu Y, Hackney AC, Lehmann M, Steinacker JM (2002) Training intensity influences leptin and thyroid hormones in highly trained rowers. Int J Sports Med 23:422–427
Steinacker JM, Lormes W, Reissnecker S, Liu Y (2004) New aspects of the hormone and cytokine responses to training. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:382–391
Urhausen A, Kindermann W (2002) Diagnosis of overtraining. What tools do we have? Sports Med 32:95–102
Van der Lely AJ, Tschop M, Heiman M, Chigo E (2004) Biological, physiological, pathophysiological and pharmacological aspects of ghrelin. Endocr Rev 25:426–457
Verger P, Lanteaume MT, Louis-Sylvestre J (1994) Free food choice after acute exercise in men. Appetite 22:159–164
Wang J, Chen C, Wang RY (2008) Influence of short- and long-term treadmill exercises on levels of ghrelin, obestatin and NPY in plasma and brain extraction of obese rats. Endocrine 33:77–83
Zukowska-Grojec Z, Wahlestedtc B (1993) Origin and action of neuropeptide Y in the cardiovascular system. In: Colmalmers WF, Wahlenstedt C (eds) The biology of neuropeptide Y and related peptides. Human Press Inc, New Jersey, pp 315–387
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Susan A. Ward.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rämson, R., Jürimäe, J., Jürimäe, T. et al. The effect of 4-week training period on plasma neuropeptide Y, leptin and ghrelin responses in male rowers. Eur J Appl Physiol 112, 1873–1880 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2166-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2166-y