Abstract
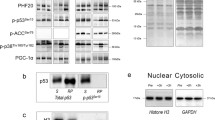
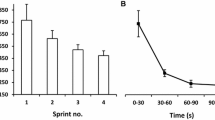
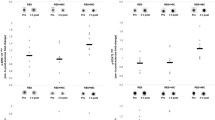
To determine if there is a sex dimorphism in the skeletal muscle signaling response to sprint exercise, 17 men and ten women performed a 30-s Wingate test. Muscle biopsies were taken before, immediately after the exercise and at 30 and 120 min during the recovery period. Thr172-AMPKα, Ser221-ACCβ, Thy705-STAT3, Thr202/Thy204-ERK1/2 and Thr180/Thy182-p38MAPK phosphorylation responses to sprint exercise were not statistically different between men and women. AMPKα phosphorylation was enhanced fourfold 30 min after the sprint exercise in males and females (P < 0.01). ACCβ phosphorylation was enhanced by about threefold just after the sprint test exercise and 30 min into the recovery period in males and females (P < 0.01). STAT3 phosphorylation was increased 2 h after the Wingate test compared to the value observed right after the end of the exercise (P < 0.05), and 30 min after the Wingate test there was a 2.5-fold increase in ERK1/2 phosphorylation, compared to both the pre-exercise and to the value observed right after the Wingate test (both, P < 0.05). In conclusion, the skeletal muscle signaling response to a single bout of sprint exercise mediated by AMPK, ACC, STAT3, ERK and p38MAPK is not statistically different between men and women. Marked increases in AMPKα, ACCβ, STAT3 and ERK phosphorylation were observed after a single 30-s all-out sprint (Wingate test) in the vastus lateralis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronson D, Violan MA, Dufresne SD, Zangen D, Fielding RA, Goodyear LJ (1997) Exercise stimulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in human skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest 99:1251–1257
Astorino TA, Allen RP, Roberson DW, Jurancich M, Lewis R, McCarthy K, Trost E (2011) Adaptations to high-intensity training are independent of gender. Eur J Appl Physiol 111:1279–1286
Bar-Or O (1987) The Wingate anaerobic test. An update on methodology, reliability and validity. Sports Med 4:381–394
Birk JB, Wojtaszewski JF (2006) Predominant alpha2/beta2/gamma3 AMPK activation during exercise in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 577:1021–1032
Bjorbaek C, Kahn BB (2004) Leptin signaling in the central nervous system and the periphery. Recent Prog Horm Res 59:305–331
Boden G, Chen X, Mozzoli M, Ryan I (1996) Effect of fasting on serum leptin in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:3419–3423
Boonsong T, Norton L, Chokkalingam K, Jewell K, Macdonald I, Bennett A, Tsintzas K (2007) Effect of exercise and insulin on SREBP-1c expression in human skeletal muscle: potential roles for the ERK1/2 and Akt signalling pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1310–1311
Calbet JA, Chavarren J, Dorado C (1997) Fractional use of anaerobic capacity during a 30- and a 45-s Wingate test. Eur J Appl Physiol 76:308–313
Calbet JA, De Paz JA, Garatachea N, Cabeza de Vaca S, Chavarren J (2003) Anaerobic energy provision does not limit Wingate exercise performance in endurance-trained cyclists. J Appl Physiol 94:668–676
Cochran AJ, Little JP, Tarnopolsky MA, Gibala MJ (2010) Carbohydrate feeding during recovery alters the skeletal muscle metabolic response to repeated sessions of high-intensity interval exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 108:628–636
Couillard C, Mauriege P, Prud’homme D, Nadeau A, Tremblay A, Bouchard C, Despres JP (2002) Plasma leptin response to an epinephrine infusion in lean and obese women. Obes Res 10:6–13
Creer A, Gallagher P, Slivka D, Jemiolo B, Fink W, Trappe S (2005) Influence of muscle glycogen availability on ERK1/2 and Akt signaling after resistance exercise in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 99:950–956
Cuevas MJ, Almar M, Garcia-Glez JC, Garcia-Lopez D, De Paz JA, Alvear-Ordenes I, Gonzalez-Gallego J (2005) Changes in oxidative stress markers and NF-kappaB activation induced by sprint exercise. Free Radic Res 39:431–439
Cheetham ME, Boobis LH, Brooks S, Williams C (1986) Human muscle metabolism during sprint running. J Appl Physiol 61:54–60
Chen ZP, McConell GK, Michell BJ, Snow RJ, Canny BJ, Kemp BE (2000) AMPK signaling in contracting human skeletal muscle: acetyl-CoA carboxylase and NO synthase phosphorylation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279:E1202–E1206
Davis SN, Galassetti P, Wasserman DH, Tate D (2000) Effects of gender on neuroendocrine and metabolic counterregulatory responses to exercise in normal man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:224–230
Deldicque L, Atherton P, Patel R, Theisen D, Nielens H, Rennie MJ, Francaux M (2008a) Decrease in Akt/PKB signalling in human skeletal muscle by resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 104:57–65
Deldicque L, Atherton P, Patel R, Theisen D, Nielens H, Rennie MJ, Francaux M (2008b) Effects of resistance exercise with and without creatine supplementation on gene expression and cell signaling in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 104:371–378
Dzamko N, Schertzer JD, Ryall JG, Steel R, Macaulay SL, Wee S, Chen ZP, Michell BJ, Oakhill JS, Watt MJ, Jorgensen SB, Lynch GS, Kemp BE, Steinberg GR (2008) AMPK-independent pathways regulate skeletal muscle fatty acid oxidation. J Physiol 586:5819–5831
Egan B, Carson BP, Garcia-Roves PM, Chibalin AV, Sarsfield FM, Barron N, McCaffrey N, Moyna NM, Zierath JR, O’Gorman DJ (2010) Exercise intensity-dependent regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1 mRNA abundance is associated with differential activation of upstream signalling kinases in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 588:1779–1790
Esbjornsson-Liljedahl M, Bodin K, Jansson E (2002) Smaller muscle ATP reduction in women than in men by repeated bouts of sprint exercise. J Appl Physiol 93:1075–1083
Esbjornsson-Liljedahl M, Sundberg CJ, Norman B, Jansson E (1999) Metabolic response in type I and type II muscle fibers during a 30-s cycle sprint in men and women. J Appl Physiol 87:1326–1332
Esbjornsson M, Norman B, Suchdev S, Viru M, Lindhgren A, Jansson E (2009) Greater growth hormone and insulin response in women than in men during repeated bouts of sprint exercise. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 197:107–115
Gaitanos GC, Williams C, Boobis LH, Brooks S (1993) Human muscle metabolism during intermittent maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 75:712–719
Galgani JE, Greenway FL, Caglayan S, Wong ML, Licinio J, Ravussin E (2010) Leptin replacement prevents weight loss-induced metabolic adaptation in congenital leptin-deficient patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:851–855
Gibala MJ, McGee SL, Garnham AP, Howlett KF, Snow RJ, Hargreaves M (2009) Brief intense interval exercise activates AMPK and p38 MAPK signaling and increases the expression of PGC-1alpha in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 106:929–934
Goodyear LJ, Chang PY, Sherwood DJ, Dufresne SD, Moller DE (1996) Effects of exercise and insulin on mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 271:E403–E408
Gorostiaga EM, Navarro-Amezqueta I, Cusso R, Hellsten Y, Calbet JA, Guerrero M, Granados C, Gonzalez-Izal M, Ibanez J, Izquierdo M (2010) Anaerobic energy expenditure and mechanical efficiency during exhaustive leg press exercise. PLoS One 5:e13486
Greenhaff PL, Nevill ME, Soderlund K, Bodin K, Boobis LH, Williams C, Hultman E (1994) The metabolic responses of human type I and II muscle fibres during maximal treadmill sprinting. J Physiol 478:149–155
Guerra B, Fuentes T, Delgado-Guerra S, Guadalupe-Grau A, Olmedillas H, Santana A, Ponce-Gonzalez JG, Dorado C, Calbet JA (2008) Gender dimorphism in skeletal muscle leptin receptors, serum leptin and insulin sensitivity. PLoS One 3:e3466
Guerra B, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Ponce-Gonzalez JG, Martinez-Bello VE, Guadalupe-Grau A, Santana A, Sebastia V, Vina J, Calbet JA (2011a) Repeated muscle biopsies through a single skin incision do not elicit muscle signaling, but IL-6 mRNA and STAT3 phosphorylation increase in injured muscle. J Appl Physiol 110:1708–1715
Guerra B, Guadalupe-Grau A, Fuentes T, Ponce-Gonzalez JG, Morales-Alamo D, Olmedillas H, Guillen-Salgado J, Santana A, Calbet JA (2010) SIRT1, AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and downstream kinases in response to a single bout of sprint exercise: influence of glucose ingestion. Eur J Appl Physiol 109:731–743
Guerra B, Olmedillas H, Guadalupe-Grau A, Ponce-Gonzalez JG, Morales-Alamo D, Fuentes T, Chapinal E, Fernandez-Perez L, De Pablos-Velasco P, Santana A, Calbet JA (2011b) Is sprint exercise a leptin signaling mimetic in human skeletal muscle? J Appl Physiol 111:715–725
Guerra B, Santana A, Fuentes T, Delgado-Guerra S, Cabrera-Socorro A, Dorado C, Lopez Calbet JA (2007) Leptin receptors in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 102:1786–1792
Harber MP, Crane JD, Douglass MD, Weindel KD, Trappe TA, Trappe SW, Fink WF (2008) Resistance exercise reduces muscular substrates in women. Int J Sports Med 29:719–725
Hardie DG (2003) Minireview: the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade: the key sensor of cellular energy status. Endocrinology 144:5179–5183
Harmer AR, McKenna MJ, Sutton JR, Snow RJ, Ruell PA, Booth J, Thompson MW, Mackay NA, Stathis CG, Crameri RM, Carey MF, Eager DM (2000) Skeletal muscle metabolic and ionic adaptations during intense exercise following sprint training in humans. J Appl Physiol 89:1793–1803
Jaworowski A, Porter MM, Holmback AM, Downham D, Lexell J (2002) Enzyme activities in the tibialis anterior muscle of young moderately active men and women: relationship with body composition, muscle cross-sectional area and fibre type composition. Acta Physiol Scand 176:215–225
Jones NL, McCartney N, Graham T, Spriet LL, Kowalchuk JM, Heigenhauser GJ, Sutton JR (1985) Muscle performance and metabolism in maximal isokinetic cycling at slow and fast speeds. J Appl Physiol 59:132–136
Jorgensen SB, Viollet B, Andreelli F, Frosig C, Birk JB, Schjerling P, Vaulont S, Richter EA, Wojtaszewski JF (2004) Knockout of the alpha2 but not alpha1 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase isoform abolishes 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranosidebut not contraction-induced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 279:1070–1079
Kang C, O’Moore KM, Dickman JR, Ji LL (2009) Exercise activation of muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha signaling is redox sensitive. Free Radic Biol Med 47:1394–1400
Kraemer RR, Chu H, Castracane VD (2002) Leptin and exercise. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 227:701–708
Lamont LS, McCullough AJ, Kalhan SC (2003) Gender differences in the regulation of amino acid metabolism. J Appl Physiol 95:1259–1265
Little JP, Safdar A, Cermak N, Tarnopolsky MA, Gibala MJ (2010) Acute endurance exercise increases the nuclear abundance of PGC-1alpha in trained human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R912–R917
Liu C, Wu J, Zhu J, Kuei C, Yu J, Shelton J, Sutton SW, Li X, Yun SJ, Mirzadegan T, Mazur C, Kamme F, Lovenberg TW (2009) Lactate inhibits lipolysis in fat cells through activation of an orphan G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR81. J Biol Chem 284:2811–2822
Maroni P, Bendinelli P, Piccoletti R (2003) Early intracellular events induced by in vivo leptin treatment in mouse skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol 201:109–121
Maroni P, Bendinelli P, Piccoletti R (2005) Intracellular signal transduction pathways induced by leptin in C2C12 cells. Cell Biol Int 29:542–550
McKenna MJ, Schmidt TA, Hargreaves M, Cameron L, Skinner SL, Kjeldsen K (1993) Sprint training increases human skeletal muscle Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase concentration and improves K+ regulation. J Appl Physiol 75:173–180
Minokoshi Y, Kim YB, Peroni OD, Fryer LG, Muller C, Carling D, Kahn BB (2002) Leptin stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 415:339–343
Mueller WM, Gregoire FM, Stanhope KL, Mobbs CV, Mizuno TM, Warden CH, Stern JS, Havel PJ (1998) Evidence that glucose metabolism regulates leptin secretion from cultured rat adipocytes. Endocrinology 139:551–558
Ortenblad N, Lunde PK, Levin K, Andersen JL, Pedersen PK (2000) Enhanced sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) release following intermittent sprint training. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R152–R160
Perez-Gomez J, Rodriguez GV, Ara I, Olmedillas H, Chavarren J, Gonzalez-Henriquez JJ, Dorado C, Calbet JA (2008) Role of muscle mass on sprint performance: gender differences? Eur J Appl Physiol 102:685–694
Powers SK, Nelson WB, Hudson MB (2010) Exercise-induced oxidative stress in humans: Cause and consequences. Free radic Biol Med 51:942–950
Ricci MR, Lee MJ, Russell CD, Wang Y, Sullivan S, Schneider SH, Brolin RE, Fried SK (2005) Isoproterenol decreases leptin release from rat and human adipose tissue through posttranscriptional mechanisms. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E798–E804
Richter EA, Vistisen B, Maarbjerg SJ, Sajan M, Farese RV, Kiens B (2004) Differential effect of bicycling exercise intensity on activity and phosphorylation of atypical protein kinase C and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase in skeletal muscle. J Physiol 560:909–918
Roepstorff C, Thiele M, Hillig T, Pilegaard H, Richter EA, Wojtaszewski JF, Kiens B (2006) Higher skeletal muscle alpha2AMPK activation and lower energy charge and fat oxidation in men than in women during submaximal exercise. J Physiol 574:125–138
Ruderman NB, Saha AK, Vavvas D, Witters LA (1999) Malonyl-CoA, fuel sensing, and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol 276:E1–E18
Sakamoto K, McCarthy A, Smith D, Green KA, Grahame Hardie D, Ashworth A, Alessi DR (2005) Deficiency of LKB1 in skeletal muscle prevents AMPK activation and glucose uptake during contraction. EMBO J 24:1810–1820
Serrano-Sanchez JA, Delgado-Guerra S, Olmedillas H, Guadalupe-Grau A, Arteaga-Ortiz R, Sanchis-Moysi J, Dorado C, Calbet JA (2010) Adiposity and age explain most of the association between physical activity and fitness in physically active men. PLoS One 5:e13435
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Tarnopolsky LJ, MacDougall JD, Atkinson SA, Tarnopolsky MA, Sutton JR (1990) Gender differences in substrate for endurance exercise. J Appl Physiol 68:302–308
Torres M (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in redox signaling. Front Biosci 8:d369–d391
Treebak JT, Birk JB, Rose AJ, Kiens B, Richter EA, Wojtaszewski JF (2007) AS160 phosphorylation is associated with activation of alpha2beta2gamma1—but not alpha2beta2gamma3-AMPK trimeric complex in skeletal muscle during exercise in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E715–E722
Trenerry MK, Carey KA, Ward AC, Cameron-Smith D (2007) STAT3 signaling is activated in human skeletal muscle following acute resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol 102:1483–1489
Trenerry MK, Carey KA, Ward AC, Farnfield MM, Cameron-Smith D (2008) Exercise-induced activation of STAT3 signaling is increased with age. Rejuvenation Res 11:717–724
Vestergaard ET, Hansen TK, Nielsen S, Moller N, Christiansen JS, Jorgensen JO (2005) Effects of GH replacement therapy in adults on serum levels of leptin and ghrelin: the role of lipolysis. Eur J Endocrinol 153:545–549
Widegren U, Jiang XJ, Krook A, Chibalin AV, Bjornholm M, Tally M, Roth RA, Henriksson J, Wallberg-henriksson H, Zierath JR (1998) Divergent effects of exercise on metabolic and mitogenic signaling pathways in human skeletal muscle. FASEB J 12:1379–1389
Widegren U, Wretman C, Lionikas A, Hedin G, Henriksson J (2000) Influence of exercise intensity on ERK/MAP kinase signalling in human skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch 441:317–322
Williamson D, Gallagher P, Harber M, Hollon C, Trappe S (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway activation: effects of age and acute exercise on human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 547:977–987
Yu M, Blomstrand E, Chibalin AV, Krook A, Zierath JR (2001) Marathon running increases ERK1/2 and p38 MAP kinase signalling to downstream targets in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 536:273–282
Zehnder M, Ith M, Kreis R, Saris W, Boutellier U, Boesch C (2005) Gender-specific usage of intramyocellular lipids and glycogen during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:1517–1524
Zhang Y, Matheny M, Zolotukhin S, Tumer N, Scarpace PJ (2002) Regulation of adiponectin and leptin gene expression in white and brown adipose tissues: influence of beta3-adrenergic agonists, retinoic acid, leptin and fasting. Biochim Biophys Acta 1584:115–122
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (BFU2006-13784 and FEDER) and FUNCIS (PI/10/07), Proyecto Estructurante de la ULPGC: ULPAPD-08/01-4, Proyecto del Programa Propio de la ULPGC (ULPGC 2009-07), III Convocatoria de Ayudas a la Investigación Cátedra Real Madrid- UEM (2010/01RM, Universidad Europea de Madrid) and Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (DEP2010-21866). Our special thanks are given to José Navarro de Tuero and María Carmen García Chicano for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Håkan Westerblad.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuentes, T., Guerra, B., Ponce-González, J.G. et al. Skeletal muscle signaling response to sprint exercise in men and women. Eur J Appl Physiol 112, 1917–1927 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2164-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2164-0