Abstract
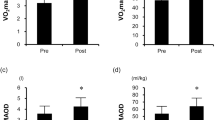
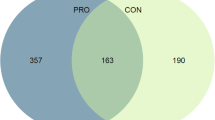
Stoppage of endurance exercise training leads to complete loss of maximal oxygen uptake (\( \dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2\max } \)) gain but not submaximal exercise blood lactate concentrations. However, the detailed mechanisms are still unknown. Thus, we investigated the effects of exercise-training cessation at lactate threshold (LT) intensity on physiological adaptations and global mRNA expressions in human skeletal muscle. The \( \dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2\max } \), muscle capillaries density and global gene expression were measured after 12 weeks of LT training, and after 12 weeks of detraining. Twelve weeks of detraining reversed the effect of 12 weeks LT training on \( \dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2\max } \) and \( \dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2} \) at LT intensity, although the later value was higher than the pre-training level. Moreover, the training cessation did not affect the number of capillaries around type I fiber, which was increased by training. The training modulated 243 characterized transcripts, in which 77% showed a significant reversible effect by detraining. However, the transcripts most-induced by the training were still elevated after the same period of detraining. The pathway and network analysis revealed that these genes were related to oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos), calcium signalling and tissue development. Therefore, these physiological and transcriptional changes suggest improved oxygen supply and OxPhos in the skeletal muscle, which may contribute to the incomplete loss of absolute \( \dot{V}{\text{O}}_{ 2} \) at LT intensity after training cessation. The present study does not only demonstrate, for the first time, sustained effects of training after detraining at the transcriptional level, but also indicates the possible signalling pathways.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen P (1975) Capillary density in skeletal muscle of man. Acta Physiol Scand 95:203–205
Bergman BC, Wolfel EE, Butterfield GE, Lopaschuk GD, Casazza GA, Horning MA, Brooks GA (1999) Active muscle and whole body lactate kinetics after endurance training in men. J Appl Physiol 87:1684–1696
Block BA (1994) Thermogenesis in muscle. Annu Rev Physiol 56:535–577
Bottinelli R, Reggiani C (2000) Human skeletal muscle fibres: molecular and functional diversity. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 73:195–262
Coyle EF, Martin WH 3rd, Sinacore DR, Joyner MJ, Hagberg JM, Holloszy JO (1984) Time course of loss of adaptations after stopping prolonged intense endurance training. J Appl Physiol 57:1857–1864
Coyle EF, Martin WH 3rd, Bloomfield SA, Lowry OH, Holloszy JO (1985) Effects of detraining on responses to submaximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 59:853–859
Davison RC, Coleman D, Balmer J, Nunn M, Theakston S, Burrows M, Bird S (2000) Assessment of blood lactate: practical evaluation of the Biosen 5030 lactate analyzer. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:243–247
Dinel S, Bolduc C, Belleau P, Boivin A, Yoshioka M, Calvo E, Piedboeuf B, Snyder EE, Labrie F, St-Amand J (2005) Reproducibility, bioinformatic analysis and power of the SAGE method to evaluate changes in transcriptome. Nucl Acids Res 33:e26
Dubouchaud H, Butterfield GE, Wolfel EE, Bergman BC, Brooks GA (2000) Endurance training, expression, and physiology of LDH, MCT1, and MCT4 in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E571–E579
Duteil S, Bourrilhon C, Raynaud JS, Wary C, Richardson RS, Leroy-Willig A, Jouanin JC, Guezennec CY, Carlier PG (2004) Metabolic and vascular support for the role of myoglobin in humans: a multiparametric NMR study. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R1441–R1449
Friedmann B, Kinscherf R, Borisch S, Richter G, Bartsch P, Billeter R (2003) Effects of low-resistance/high-repetition strength training in hypoxia on muscle structure and gene expression. Pflugers Arch 446:742–751
Goldman RF, Buskirk ER (eds) (1961) A method for underwater weighing and the determination of body density. National Research Council, Washington DC
Hashimoto T, Brooks GA (2008) Mitochondrial lactate oxidation complex and an adaptive role for lactate production. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:486–494
Hashimoto T, Hussien R, Oommen S, Gohil K, Brooks GA (2007) Lactate sensitive transcription factor network in L6 cells: activation of MCT1 and mitochondrial biogenesis. FASEB J 21:2602–2612
Houston ME, Bentzen H, Larsen H (1979) Interrelationships between skeletal muscle adaptations and performance as studied by detraining and retraining. Acta Physiol Scand 105:163–170
Kanatous SB, Mammen PP (2010) Regulation of myoglobin expression. J Exp Biol 213:2741–2747
Keller P, Vollaard N, Babraj J, Ball D, Sewell DA, Timmons JA (2007) Using systems biology to define the essential biological networks responsible for adaptation to endurance exercise training. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1306–1309
Klausen K, Andersen LB, Pelle I (1981) Adaptive changes in work capacity, skeletal muscle capillarization and enzyme levels during training and detraining. Acta Physiol Scand 113:9–16
Lange S, Auerbach D, McLoughlin P, Perriard E, Schafer BW, Perriard JC, Ehler E (2002) Subcellular targeting of metabolic enzymes to titin in heart muscle may be mediated by DRAL/FHL-2. J Cell Sci 115:4925–4936
Lange S, Xiang F, Yakovenko A, Vihola A, Hackman P, Rostkova E, Kristensen J, Brandmeier B, Franzen G, Hedberg B, Gunnarsson LG, Hughes SM, Marchand S, Sejersen T, Richard I, Edstrom L, Ehler E, Udd B, Gautel M (2005) The kinase domain of titin controls muscle gene expression and protein turnover. Science 308:1599–1603
Lange S, Ehler E, Gautel M (2006) From A to Z and back? Multicompartment proteins in the sarcomere. Trends Cell Biol 16:11–18
Lash AE, Tolstoshev CM, Wagner L, Schuler GD, Strausberg RL, Riggins GJ, Altschul SF (2000) SAGEmap: a public gene expression resource. Genome Res 10:1051–1060
Mall S, Broadbridge R, Harrison SL, Gore MG, Lee AG, East JM (2006) The presence of sarcolipin results in increased heat production by Ca2+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 281:36597–36602
McGrath MJ, Cottle DL, Nguyen MA, Dyson JM, Coghill ID, Robinson PA, Holdsworth M, Cowling BS, Hardeman EC, Mitchell CA, Brown S (2006) Four and a half LIM protein 1 binds myosin-binding protein C and regulates myosin filament formation and sarcomere assembly. J Biol Chem 281:7666–7683
Mujika I, Padilla S (2001) Cardiorespiratory and metabolic characteristics of detraining in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:413–421
Neufer PD (1989) The effect of detraining and reduced training on the physiological adaptations to aerobic exercise training. Sports Med 8:302–320
Nishida Y, Tokuyama K, Nagasaka S, Higaki Y, Shirai Y, Kiyonaga A, Shindo M, Kusaka I, Nakamura T, Ishibashi S, Tanaka H (2004) Effect of moderate exercise training on peripheral glucose effectiveness, insulin sensitivity, and endogenous glucose production in healthy humans estimated by a two-compartment-labeled minimal model. Diabetes 53:315–320
Nishida Y, Tanaka H, Tobina T, Murakami K, Shono N, Shindo M, Ogawa W, Yoshioka M, St-Amand J (2010) Regulation of muscle genes by moderate exercise. Int J Sports Med 31:656–670
Ookawara T, Suzuk K, Haga S, Ha S, Chung KS, Toshinai K, Hamaoka T, Katsumura T, Takemasa T, Mizuno M, Hitomi Y, Kizaki T, Suzuki K, Ohno H (2002) Transcription regulation of gene expression in human skeletal muscle in response to endurance training. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 111:41–54
Orlander J, Kiessling KH, Karlsson J, Ekblom B (1977) Low intensity training, inactivity and resumed training in sedentary men. Acta Physiol Scand 101:351–362
Padykula HA, Herman E (1955) The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem 3:170–195
Parsons SA, Wilkins BJ, Bueno OF, Molkentin JD (2003) Altered skeletal muscle phenotypes in calcineurin Aalpha and Abeta gene-targeted mice. Mol Cell Biol 23:4331–4343
Philippar U, Schratt G, Dieterich C, Muller JM, Galgoczy P, Engel FB, Keating MT, Gertler F, Schule R, Vingron M, Nordheim A (2004) The SRF target gene Fhl2 antagonizes RhoA/MAL-dependent activation of SRF. Mol Cell 16:867–880
Sakuma K, Yamaguchi A (2010) The functional role of calcineurin in hypertrophy, regeneration, and disorders of skeletal muscle. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:721219
Shono N, Urata H, Saltin B, Mizuno M, Harada T, Shindo M, Tanaka H (2002) Effects of low intensity aerobic training on skeletal muscle capillary and blood lipoprotein profiles. J Atheroscler Thromb 9:78–85
Smith WS, Broadbridge R, East JM, Lee AG (2002) Sarcolipin uncouples hydrolysis of ATP from accumulation of Ca2+ by the Ca2+-ATPase of skeletal-muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J 361:277–286
St-Amand J, Okamura K, Matsumoto K, Shimizu S, Sogawa Y (2001) Characterization of control and immobilized skeletal muscle: an overview from genetic engineering. FASEB J 15:684–692
Svedahl K, MacIntosh BR (2003) Anaerobic threshold: the concept and methods of measurement. Can J Appl Physiol 28:299–323
Tanaka H, Nishida Y, Tobina T, Murakami K, Shono N, Shindo M, Yoshioka M, St-Amand J (2006) Moderate exercise training at lactate threshold favorably modulates gene expression in human skeletal muscle. Obes Rev 7:154
Teran-Garcia M, Rankinen T, Koza RA, Rao DC, Bouchard C (2005) Endurance training-induced changes in insulin sensitivity and gene expression. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E1168–E1178
Timmons JA (2011) Variability in training-induced skeletal muscle adaptation. J Appl Physiol (in press)
Timmons JA, Larsson O, Jansson E, Fischer H, Gustafsson T, Greenhaff PL, Ridden J, Rachman J, Peyrard-Janvid M, Wahlestedt C, Sundberg CJ (2005) Human muscle gene expression responses to endurance training provide a novel perspective on Duchenne muscular dystrophy. FASEB J 19:750–760
Timmons JA, Norrbom J, Scheele C, Thonberg H, Wahlestedt C, Tesch P (2006) Expression profiling following local muscle inactivity in humans provides new perspective on diabetes-related genes. Genomics 87:165–172
Timmons JA, Knudsen S, Rankinen T, Koch LG, Sarzynski M, Jensen T, Keller P, Scheele C, Vollaard NB, Nielsen S, Akerstrom T, MacDougald OA, Jansson E, Greenhaff PL, Tarnopolsky MA, van Loon LJ, Pedersen BK, Sundberg CJ, Wahlestedt C, Britton SL, Bouchard C (2010) Using molecular classification to predict gains in maximal aerobic capacity following endurance exercise training in humans. J Appl Physiol 108:1487–1496
Tupling AR, Asahi M, MacLennan DH (2002) Sarcolipin overexpression in rat slow twitch muscle inhibits sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake and impairs contractile function. J Biol Chem 277:44740–44746
Vogt M, Puntschart A, Geiser J, Zuleger C, Billeter R, Hoppeler H (2001) Molecular adaptations in human skeletal muscle to endurance training under simulated hypoxic conditions. J Appl Physiol 91:173–182
Wu H, Rothermel B, Kanatous S, Rosenberg P, Naya FJ, Shelton JM, Hutcheson KA, DiMaio JM, Olson EN, Bassel-Duby R, Williams RS (2001) Activation of MEF2 by muscle activity is mediated through a calcineurin-dependent pathway. EMBO J 20:6414–6423
Yoshioka M, Boivin A, Ye P, Labrie F, St-Amand J (2006) Effects of dihydrotestosterone on skeletal muscle transcriptome in mice measured by serial analysis of gene expression. J Mol Endocrinol 36:247–259
Acknowledgments
We thank all subjects who participated in this study. This work was supported by a grant from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (No. 15200050) as well as the Fukuoka University Institute for Physical Activity and the Global FU Program grant by Fukuoka University. Jonny St-Amand is an investigator supported by the Fonds de la recherche en santé du Québec (FRSQ).
Conflict of interest
None of the authors of this article have any conflicts of interest or financial conflicts to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Dick F. Stegeman.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
St-Amand, J., Yoshioka, M., Nishida, Y. et al. Effects of mild-exercise training cessation in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 112, 853–869 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2036-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2036-7