Abstract
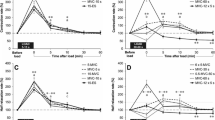
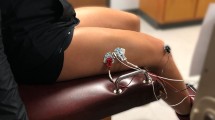
We investigated the relationship between muscle contractile characteristics, collected using percutaneous electrical stimulation, and high-intensity exercise performance. Seventeen participants performed a muscle performance test for the calculation of rate of torque development (RTD), rate of relaxation (RR1/2), rate of fatigue and fatigue resistance. On a second visit the participants completed a Wingate cycle ergometer test with peak power, mean power, fatigue index and fatigue rate calculated. The muscle fatigue index related significantly to the WAnT fatigue index and fatigue rate (p < 0.01). The change in rate of torque development (%ΔRTD) was also related significantly to the fatigue rate (W/s) during the WAnT. Subjects displaying the greatest reduction in RTD had the greatest fatigue rate during the WAnT and greater fatigue during the electrical stimulation protocol. There were no significant relationships between peak (r 0.36; p > 0.01) or mean power (r −0.11, p > 0.01) with any of the muscle performance measures. These findings demonstrate that muscle contractile characteristics, elicited during standardised in vivo electrical stimulation, relate to performance during a Wingate anaerobic test. They suggest that muscle contraction characteristics play an important role in high-intensity exercise performance and indicate that electrical stimulation protocols can be a useful additional tool to explore muscle contraction characteristics in relation to exercise performance and trainability.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arslan C (2005) Relationship between the 30-second Wingate test and characteristics of isometric and explosive leg strength in young subjects. J Strength Cond Res 19:658–666
Barclay CJ, Loiselle DS (1992) Dependence of muscle fatigue on stimulation protocol: effect of hypocaloric diet. J Appl Physiol 72:2278–2284
Bar-Or O (1987) The Wingate anaerobic test. An update on methodology, reliability and validity. Sports Med 4:381–394
Bar-Or O, Dotan R, Inbar O (1977) A 30-second all-out ergometric test—its reliability and validity for anaerobic capacity. Isr J Med Sci 13:89–92
Bar-Or O, Dotan R, Inbar O, Rothstein A, Karlsson J, Tesch P (1980) Anaerobic capacity and muscle fiber type distribution in man. Int J Sports Med 1:82–85
Beneke R, Pollmann C, Bleif I, Leithauser RM, Hutler M (2002) How anaerobic is the Wingate anaerobic test for humans? Eur J Appl Physiol 87:388–392
Brancaccio P, Limongelli FM, D’Aponte A, Narici M, Maffulli N (2008) Changes in skeletal muscle architecture following a cycloergometer test to exhaustion in athletes. J Sci Med Sport 11(6):538–541
Burke RE, Levine DN, Tsairis P, Zajac FE 3rd (1973) Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol 234:723–748
Calbet JA, De Paz JA, Garatachea N, Cabeza de Vaca S, Chavarren J (2003) Anaerobic energy provision does not limit Wingate exercise performance in endurance-trained cyclists. J Appl Physiol 94:668–676
Garland SW, Newham DJ, Turner DL (2004) The amplitude of the slow component of oxygen uptake is related to muscle contractile properties. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:192–198
Gordon DA, Enoka RM, Karst GM, Stuart DG (1990) Force development and relaxation in single motor units of adult cats during a standard fatigue test. J Physiol 421:583–594
Hamada T, Sale DG, MacDougall JD, Tarnopolsky MA (2003) Interaction of fibre type, potentiation and fatigue in human knee extensor muscles. Acta Physiol Scand 178:165–173
Karlsson J, Sjodin B, Jacobs I, Kaiser P (1981) Relevance of muscle fibre type to fatigue in short intense and prolonged exercise in man. Ciba Found Symp 82:59–74
Micklewright D, Alkhatib A, Beneke R (2006) Mechanically versus electro-magnetically braked cycle ergometer: performance and energy cost of the Wingate anaerobic test. Eur J Appl Physiol 96:748–751
Millet GY, Lepers R (2004) Alterations of neuromuscular function after prolonged running, cycling and skiing exercises. Sports Med 34:105–116
Morris MG, Dawes H, Howells K, Scott OM, Cramp M (2008) Relationships between muscle fatigue characteristics and markers of endurance performance. J Sports Sci Med 7:431–436
Scott OM, Vrbova G, Hyde SA, Dubowitz V (1985) Effects of chronic low frequency electrical stimulation on normal human tibialis anterior muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:774–781
Skof B, Strojnik V (2006) Neuromuscular fatigue and recovery dynamics following prolonged continuous run at anaerobic threshold. Br J Sports Med 40:219–222 (discussion 219–222)
Theurel J, Lepers R, Pardon L, Maffiuletti NA (2007) Differences in cardiorespiratory and neuromuscular responses between voluntary and stimulated contractions of the quadriceps femoris muscle. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 157:341–347
Thorstensson A, Larsson L, Tesch P, Karlsson J (1977) Muscle strength and fiber composition in athletes and sedentary men. Med Sci Sports 9:26–30
Vandewalle H, Maton B, Le Bozec S, Guerenbourg G (1991) An electromyographic study of an all-out exercise on a cycle ergometer. Arch Int Physiol Biochim Biophys 99:89–93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Toshio Moritani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morris, M.G., Dawes, H., Howells, K. et al. Muscle contractile characteristics: relationship to high-intensity exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 110, 295–300 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1496-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1496-5