Abstract
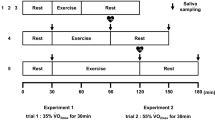
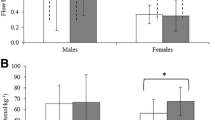
Oral peroxidase, one of the most important salivary antioxidant enzymes, is subjected to alternation due to various body conditions. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of exercise intensity on salivary peroxidase activity. Using a randomized design, ten healthy male university students (mean age, 23.22; s x = 2.34 years) completed treadmill runs with initial velocity 6.73 km/h at the rate of 1.58 km/h increase every 3 min until exhaustion. Unstimulated whole saliva collected over a 5-min period in pre-weighed tubes before, immediately after exercise, and 1 h after exercise was analyzed for total protein and saliva peroxidase activity. The saliva flow rate ranged from 0.08 to 1.40 ml min−1 at rest and was not significantly affected by the exercise. Peroxidase activity in each sample was measured using 4-amino antipyrine as substrate. In the incremental exhaustion run and also at 75% VO2max, the secretion rates of peroxidase increased. No significant changes in saliva flow rate were observed in any treadmill run. Treadmill runs at 75% VO2max and to exhaustion increased the activity of peroxidase immediately after exercise which decreased after 1 h. It was concluded that short-duration, high-intensity exercise increases the activity rate of peroxidase despite no change in the saliva flow rate. These effects appear to be associated with changes in sympathetic activity and not the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allgrove JE, Gomes E, Hough J, Gleeson M (2008) Effects of exercise intensity on salivary antimicrobial proteins and markers of stress in active men. J Sport Sci 26(6):653–661
American College of Sport Medicine (1990) Position stand on the recommended quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardio respiratory and muscular fitness in healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 22:265–274
Aune TM, Thomas EL (1977) Accumulation of hypothiocyanite ion during peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of thiocyanate ion. Eur J Biochem 80:209–214
Borg GAV (1998) Borg’s rating of perceived exertion and pain scales. Human Kinetics, Champaign
Bradford M (1976) Total protein assay. Anal Biochem 72:248–251
Dayan D, Hirshberg A, Kaplan I, Rotem N, Bodner L (1997) Experimental tongue cancer in desalivated rats. Oral Oncol 33:105–109
Everse J, Everse KE, Grisham MB (1991) Peroxidases in chemistry and biology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 1–23
Gaspar T, Penel C, Greppin H (eds) (1992) Plant peroxidases. progress and prospects in biochemistry and physiology
Knak R, Rutsatz K, Gocke R (1998) Salivary investigations in oral lichen planus (abstract). J Dent Res 77:2783–2788
Mandel ID (1989) The role of saliva in maintaining oral homeostasis. J Am Dent Assoc 119:298–304
Meucci E, Littarru C, Deli G, Luciani G, Tazza L, Littarru GP (1998) Antioxidant status and dialysis: plasma and saliva antioxidant activity in patients with fluctuating urate levels. Free Radic Res 29:367–376
Moore S, Calder KAC, Miller NJ, Rice-Evans CA (1994) Antioxidant activity of saliva and periodontal disease. Free Radic Res 21:417–425
Nagler RM, Klein I, Zarzhevsky N, Drigues N, Reznick AZ (2002) Characterization of the differentiated antioxidant profile of human saliva. Free Radic Biol Med 32:268–277
Nair UJ, Floyd RA, Nair J, Bussachini V, Friesen M, Bartsch H (1987) Formation of reactive oxygen species and of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in DNA in vitro with betel quid ingredients. Chem Biol Interact 63:157–169
Nishioka H, Hishi K, Kyokane K (1981) Human saliva inactivates mutagenicity of carcinogens. Mutat Res 85:323–333
Peters EM, Bateman ED (1983) Ultramarathon running and upper respiratory tract infections. S Afr Med J 64:582–584
Pretz W (1984) Running from infection. Run World 19:78–79
Pruitt KM, Kamau DN, Miller K, Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Rahemtulla F (1990) Quantitative, standardized assays for determining the concentrations of bovine lactoperoxidase, human salivary peroxidase, and human myeloperoxidase. Anal Biochem 191:278–286
Tenovuo JD (1991) Salivary peroxidase. In: Everse J, Everse KE, Grisham MB (eds) Peroxidase in chemistry and biology, vol I. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 181–197
Tra GP, Barnes M (1990) Reduction of immunoglobulin-A by swim training. Eur J Appl Physiol 60:61–64
van der Vliet A, Nguyen MN, Shigenada MK, Eiserich JP, Marelich GP, Cross CE (2000) Myeloperoxidase and protein oxidation in cystic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279:L537–L546
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank University of Guilan for providing financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Susan Ward.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damirchi, A., Kiani, M., Jafarian, V. et al. Response of salivary peroxidase to exercise intensity. Eur J Appl Physiol 108, 1233–1237 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1331-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1331-z