Abstract
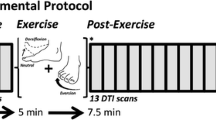
In this study, we assessed the physiological changes after exercising or cooling skeletal muscles on the basis of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values in magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted images (DWIs). DWIs of the ankle dorsiflexors were acquired with a 1.5-T MR device before and after exercising (22 subjects) or cooling (19 subjects). The exercise comprised a 5-min walk with the ankles dorsiflexed and a 30-time ankle dorsiflexion. Cooling (0°C) of the ankle dorsiflexors was performed for 30 min. ADC values were calculated as ADC1—reflecting diffusion and perfusion and ADC2—approximating the true diffusion coefficient of the ankle dorsiflexors before and after exercising or cooling. ADC1 and ADC2 significantly increased with exercise and decreased with cooling (P < 0.05). Considering both diffusion and perfusion, ADC values allowed us to evaluate the intramuscular changes induced by exercising or cooling in terms of the motion of water molecules and microcirculation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burdette JH, Elster AD, Ricci PE (1999) Acute cerebral infarction: quantification of spin-density and T2 shine-through phenomena on diffusion-weighted MR images. Radiology 212:333–339
Cagnie B, Dickx N, Peeters I, Tuytens J, Achten E, Cambier D, Danneels L (2008) The use of functional MRI to evaluate cervical flexor activity during different cervical flexion exercises. J Appl Physiol 104:230–235. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00918.2007
DeLorey DS, Shaw CN, Shoemaker JK, Kowalchuk JM, Paterson DH (2004) The effect of hypoxia on pulmonary O2 uptake, leg blood flow and muscle deoxygenation during single-leg knee-extension exercise. Exp Physiol 89:293–302. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2003.026864
Doran M, Bydder GM (1990) Magnetic resonance: perfusion and diffusion imaging. Neuroradiology 32:392–398. doi:10.1007/BF00588472
Fotedar LK, Slopis JM, Narayana PA, Fenstermacher MJ, Pivarnik J, Butler IJ (1990) Proton magnetic resonance of exercise-induced water changes in gastrocnemius muscle. J Appl Physiol 69:1695–1701
Heemskerk AM, Drost MR, van Bochove GS, van Oosterhout MF, Nicolay K, Strijkers GJ (2006) DTI-based assessment of ischemia-reperfusion in mouse skeletal muscle. Magn Reson Med 56:272–281. doi:10.1002/mrm.20953
Hiroyuki H, Hamaoka T, Sako T, Nishio S, Kime R, Murakami M, Katsumura T (2002) Oxygenation in vastus lateralis and lateral head of gastrocnemius during treadmill walking and running in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 87:343–349. doi:10.1007/s00421-002-0644-y
Kenny GP, Reardon FD, Zaleski W, Reardon ML, Haman F, Ducharme MB (2003) Muscle temperature transients before, during, and after exercise measured using an intramuscular multisensor probe. J Appl Physiol 94(6):2350–2357
Koh DM, Takahara T, Imai Y, Collins DJ (2007) Practical aspects of assessing tumors using clinical diffusion-weighted imaging in the body. Magn Reson Med Sci 6:211–224. doi:10.2463/mrms.6.211
Larsen RG, Ringgaard S, Overgaard K (2007) Localization and quantification of muscle damage by magnetic resonance imaging following step exercise in young women. Scand J Med Sci Sports 17:76–83
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161:401–407
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168:497–505
Le Rumeur E, De Certaines J, Toulouse P, Rochcongar P (1987) Water phases in rat striated muscles as determined by T2 proton NMR relaxation times. Magn Reson Imaging 5:267–272. doi:10.1016/0730-725X(87)90003-8
Morvan D (1995) In vivo measurement of diffusion and pseudo-diffusion in skeletal muscle at rest and after exercise. Magn Reson Imaging 13:193–199. doi:10.1016/0730-725X(94)00096-L
Morvan D, Leroy-Willig A (1995) Simultaneous measurements of diffusion and transverse relaxation in exercising skeletal muscle. Magn Reson Imaging 13:943–948. doi:10.1016/0730-725X(95)02006-F
Morvan D, Leroy-Willig A, Malgouyres A, Cuenod CA, Jehenson P, Syrota A (1993) Simultaneous temperature and regional blood volume measurements in human muscle using an MRI fast diffusion technique. Magn Reson Med 29:371–377. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910290313
Phuttharak W, Galassi W, Laopaiboon V, Laopaiboon M, Hesselink JR (2007) Abnormal diffusivity of normal appearing brain tissue in multiple sclerosis: a diffusion-weighted MR imaging study. J Med Assoc Thai 90:2689–2694
Ploutz-Snyder LL, Convertino VA, Dudley GA (1995) Resistance exercise-induced fluid shifts: change in active muscle size and plasma volume. Am J Physiol 269:R536–R543
Sendowski I, Savourey G, Launay JC, Besnard Y, Cottet-Emard JM, Pequignot JM, Bittel J (2000) Sympathetic stimulation induced by hand cooling alters cold-induced vasodilatation in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 81:303–309. doi:10.1007/s004210050047
Sjogaard G, Saltin B (1982) Extra- and intracellular water spaces in muscles of man at rest and with dynamic exercise. Am J Physiol 243:271–280
Turner R, Le Bihan D, Maier J, Vavrek R, Hedges LK, Pekar J (1990) Echo-planar imaging of intravoxel incoherent motion. Radiology 177:407–414
Yanagisawa O, Homma T, Okuwaki T, Shimao D, Takahashi H (2007) Effects of cooling on human skin and skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 100:737–745. doi:10.1007/s00421-007-0470-3
Yanagisawa O, Kudo H, Takahashi N, Yoshioka H (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of cooling on blood flow and oedema in skeletal muscles after exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:737–740. doi:10.1007/s00421-004-1060-2
Yanagisawa O, Niitsu M, Takahashi H, Goto K, Itai Y (2003) Evaluations of cooling exercised muscle with MR imaging and 31P MR spectroscopy. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:1517–1523. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000084418.96898.2E
Yanagisawa O, Shimao D, Maruyama K, Nielsen M, Irie T, Niitsu M (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of human skeletal muscles: Gender-, age-, and muscle-related differences in apparent diffusion coefficient. Magn Reson Imaging 27:69–78. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2008.05.011
Yao L, Sinha U (2000) Imaging the microcirculatory proton fraction of muscle with diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging. Acad Radiol 7:27–32. doi:10.1016/S1076-6332(00)80440-7
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists) from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanagisawa, O., Shimao, D., Maruyama, K. et al. Evaluation of exercised or cooled skeletal muscle on the basis of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Appl Physiol 105, 723–729 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0954-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0954-9