Abstract
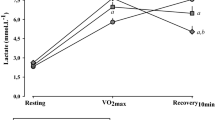
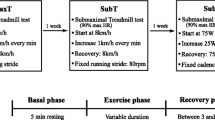
The purpose of this study was to examine hemodynamic responses and cardiovascular autonomic regulation following supramaximal exercise. Electrocardiographic R–R intervals and beat-to-beat hemodynamics were recorded before and for 10 min after a 30-s Wingate test in 11 males. Spectral analysis of heart rate (HR) and arterial pressure variability, analysis of HR complexity, the sequence technique and the cross-spectral transfer function were used to quantify autonomic regulation and baroreflex sensitivity. After exercise, the high frequency component of HR variability (vagal-related index) was lower than pre-exercise values, whereas the ratio low frequency to high frequency (index of sympathovagal balance) and the low frequency component of blood pressure variability (index of sympathetic vasomotor tone) were greater than baseline (p < 0.05). Post-exercise HR complexity and baroreflex sensitivity were reduced compared to baseline, p < 0.05. Cardiovascular autonomic control requires more than 10 min to fully recover after intense physical exertion of only 30-s in young healthy males.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai Y, Saul JP, Albrecht P, Hartley LH, Lilly LS, Cohen RJ, Colucci WS (1989) Modulation of cardiac autonomic activity during and immediately after exercise. Am J Physiol 256:H132–H141
Billman GE (2002) Aerobic exercise conditioning: a nonpharmacological antiarrhythmic intervention. J Appl Physiol 92:446–454
Brock-Utne JG, Blake GT, Bosenberg AT, Gaffin SL, Humphrey D, Downing JW (1984) An evaluation of the pulse-contour method of measuring cardiac output. S Afr Med J 66:451–453
Carter R 3rd, Watenpaugh DE, Wasmund WL, Wasmund SL, Smith ML (1999) Muscle pump and central command during recovery from exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 87:1463–1469
Cooke WH, Carter JR (2005) Strength training does not affect vagal-cardiac control or cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity in young healthy subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 93:719–725. doi:10.1007/s00421-004-1243-x
Crisafulli A, Orru V, Melis F, Tocco F, Concu A (2003) Hemodynamics during active and passive recovery from a single bout of supramaximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 89:209–216. doi:10.1007/s00421-003-0796-4
deBoer RW, Karemaker JM, Strackee J (1987) Hemodynamic fluctuations and baroreflex sensitivity in humans: a beat-to-beat model. Am J Physiol 253:H680–H689
Goulopoulou S, Heffernan KS, Fernhall B, Yates G, Baxter-Jones AD, Unnithan VB (2006) Heart rate variability during recovery from a Wingate test in adolescent males. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:875–881
Heffernan KS, Collier SR, Kelly EE, Jae SY, Fernhall B (2007) Arterial stiffness and baroreflex sensitivity following bouts of aerobic and resistance exercise. Int J Sports Med 28:197–203
Hussain ST, Smith RE, Medbak S, Wood RF, Whipp BJ (1996) Haemodynamic and metabolic responses of the lower limb after high intensity exercise in humans. Exp Physiol 81:173–187
Javorka M, Zila I, Balharek T, Javorka K (2002) Heart rate recovery after exercise: relations to heart rate variability and complexity. Braz J Med Biol Res 35:991–1000
Johnson EC, Hudson TL, Greene ER (1990) Left ventricular hemodynamics during exercise recovery. J Appl Physiol 69:104–111
Kaikkonen P, Nummela A, Rusko H (2007) Heart rate variability dynamics during early recovery after different endurance exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:79–86
Kilgour RD, Mansi JA, Williams PA (1995) Cardiodynamic responses during seated and supine recovery from supramaximal exercise. Can J Appl Physiol 20:52–64
Kuusela TA, Jartti TT, Tahvanainen KU, Kaila TJ (2002) Nonlinear methods of biosignal analysis in assessing terbutaline-induced heart rate and blood pressure changes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 282:H773–H783
Lipsitz LA (1995) Age-related changes in the “complexity” of cardiovascular dynamics: a potential marker of vulnerability to disease. Chaos 5:102–109
Martinmaki K, Rusko H (2008) Time-frequency analysis of heart rate variability during immediate recovery from low and high intensity exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:353–360
Niemela TH, Kiviniemi AM, Hautala AJ, Salmi JA, Linnamo V, Tulppo MP (2008) Recovery pattern of baroreflex sensitivity after exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:864–870
Niewiadomski W, Gasiorowska A, Krauss B, Mroz A, Cybulski G (2007) Suppression of heart rate variability after supramaximal exertion. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 27:309–319
Parlow J, Viale JP, Annat G, Hughson R, Quintin L (1995) Spontaneous cardiac baroreflex in humans. Comparison with drug-induced responses. Hypertension 25:1058–1068
Perini R, Veicsteinas A (2003) Heart rate variability and autonomic activity at rest and during exercise in various physiological conditions. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:317–325
Piepoli M, Coats AJ, Adamopoulos S, Bernardi L, Feng YH, Conway J, Sleight P (1993) Persistent peripheral vasodilation and sympathetic activity in hypotension after maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 75:1807–1814
Pincus SM, Goldberger AL (1994) Physiological time-series analysis: what does regularity quantify? Am J Physiol 266:H1643–H1656
Porta A, Guzzetti S, Furlan R, Gnecchi-Ruscone T, Montano N, Malliani A (2007a) Complexity and nonlinearity in short-term heart period variability: comparison of methods based on local nonlinear prediction. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54:94–106
Porta A, Gnecchi-Ruscone T, Tobaldini E, Guzzetti S, Furlan R, Montano N (2007b) Progressive decrease of heart period variability entropy-based complexity during graded head-up tilt. J Appl Physiol 103:1143–1149
Richman JS, Moorman JR (2000) Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H2039–H2049
Rimoldi O, Pierini S, Ferrari A, Cerutti S, Pagani M, Malliani A (1990) Analysis of short-term oscillations of R–R and arterial pressure in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 258:H967–H976
Rudas L, Crossman AA, Morillo CA, Halliwill JR, Tahvanainen KU, Kuusela TA, Eckberg DL (1999) Human sympathetic and vagal baroreflex responses to sequential nitroprusside and phenylephrine. Am J Physiol 276:H1691–H1698
Savin WM, Davidson DM, Haskell WL (1982) Autonomic contribution to heart rate recovery from exercise in humans. J Appl Physiol 53:1572–1575
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Terziotti P, Schena F, Gulli G, Cevese A (2001) Post-exercise recovery of autonomic cardiovascular control: a study by spectrum and cross-spectrum analysis in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:187–194
Yeragani VK, Rao R, Jayaraman A, Pohl R, Balon R, Glitz D (2002) Heart rate time series: decreased chaos after intravenous lactate and increased non-linearity after isoproterenol in normal subjects. Psychiatry Res 109:81–92
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulopoulou, S., Fernhall, B. & Kanaley, J.A. Hemodynamic responses and linear and non-linear dynamics of cardiovascular autonomic regulation following supramaximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 105, 525–531 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0930-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0930-4