Abstract
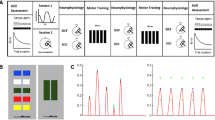
Training of skilled movements leads to typical changes in motor evoked potentials (MEPs). To explore how such changes are related to motor performance and hand preference, a goal-directed movement task was implemented on a haptic interface. Right and left hands of right-handed subjects were trained in two sessions separated by a pause of 10 min. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) was applied contralaterally to the trained hand before and after each session. Effects of right hand training: after session #1 MEP-facilitation was +60%, intracortical inhibition (ICI) was reduced and task improvement was +37%. Following session #2 all variables remained unchanged. Left hand training: after session #1 MEP-facilitation was +59%, ICI remained unchanged and task improvement was +30%. Following session #2 all variables remained unchanged. It is concluded that mainly the early phase of skill acquisition induces neuroplastic changes. The asymmetry in ICI obviously reflects functional side differences in hand motor control.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asanuma H, Pavlides C (1997) Neurobiological basis of motor learning in mammals. Neuroreport 8(4):I–VI Review
Classen J, Liepert J, Wise SP, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1998) Rapid plasticity of human cortical movement representation induced by practice. J Neurophysiol 79:1117–1123
Classen J, Liepert J, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1999) Plasticity of movement representation in the human motor cortex. In: Paulus W, Rothwell JC, Hallett M, Rossini PM (eds) Transcranial magnetic stimulation. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam, pp 162–173
Donoghue JP (1995) Plasticity of adult sensorymotor representations. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5:749–754
Floyer-Lea A, Matthews PM (2004) Changing brain networks for visuomotor control with increased movement automaticity. J Neurophysiol 92:2405–2412
Floyer-Lea A, Matthews PM (2005) Distinguishable brain activation networks for short- and long-term motor skill learning. J Neurophysiol 94:512–518
Garry MI, Kamen G, Nordstrom MA (2004) Hemispheric differences in the relationship between corticomotor excitability changes following a fine-motor task and motor learning. J Neurophysiol 91:1570–1578
Grafton ST, Mazziotta JC, Presty S, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS, Phelps ME (1992) Functional anatomy of human procedural learning determined with regional cerebral blood flow and PET. J Neurosci 12:2542–2548
Honda M, Deiber MP, Ibanez V, Pascual-Leone A, Zhuang P, Hallett M (1998) Dynamic cortical involvement in implicit and explicit motor sequence learning. A PET study. Brain 121:2159–2173
Jacobs KM, Donoghue JP (1991) Reshaping the cortical motor map by unmasking latent intracortical connections. Science 251:944–947
Kaelin-Lang A, Luft AR, Sawaki L, Burstein A, Sohn YH, Cohen LG (2002) Modulation of human corticomotor excitability by somatosensory input. J Physiol 540:623–633
Karni A, Meyer G, Jezzard P, Adams MM, Turner R, Ungerleider LG (1995) Functional MRI evidence for adult motor cortex plasticity during motor skill learning. Nature 377:155–158
Kawashima R, Roland PE, O’Sullivan BT (1994) Fields in human motor areas involved in preparation for reaching, actual reaching, and visuomotor learning: a positron emission tomography study. J Neurosci 14:3462–3474
Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Ferbert A, Wroe S, Asselman P, Marsden CD (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 471:501–519
Liepert J, Oreja-Guevara C, Cohen LG, TegenthoV M, Hallett M, Malin JP (1999a) Plasticity of cortical hand muscle representation in patients with hemifacial spasm. Neurosci Lett 272:33–36
Liepert J, Terborg C, Weiller C (1999b) Motor plasticity induced by synchronized thumb and foot movements. Exp Brain Res 125:435–439
Malinow R, Mainen ZF, Hayashi Y (2000) LTP mechanisms: from silence to four-lane traffic. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:352–357
Martin SJ, Grimwood PD, Morris RG (2000) Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:649–711
Muellbacher W, Ziemann U, Boroojerdi B, Cohen L, Hallett M (2001) Role of the human motor cortex in rapid motor learning. Exp Brain Res 136:431–438
Muellbacher W, Ziemann U, Wissel J, Dang N, Kofler M, Facchini S, Boroojerdi B, Poewe W, Hallett M (2002) Early consolidation in human primary motor cortex. Nature 415:640–644
Nudo RJ, Milliken GW (1996) Reorganization of movement representations in primary motor cortex following focal ischemic infarcts in adult squirrel monkeys. J Neurophysiol 75:2144–2149
Nudo RJ, Jenkins WM, Merzenich MM, Prejean T, Grenda R (1992) Neurophysiological correlates of hand preference in primary motor cortex of adult squirrel monkeys. J Neurosci 12:2918–2947
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Pascual-Leone A, Nguyet D, Cohen LG, Brasil-Neto JP, Cammarota A, Hallett M (1995) Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J Neurophysiol 74:1037–1045
Pleger B, Schwenkreis P, Dinse HR, Ragert R, Höffken O, Malin JP, Tegenthoff M (2003) Pharmacological suppression of plastic changes in human primary somatosenory cortex after motor learning. Exp Brain Res 148:525–532
Sanes JN, Donoghue JP (2000) Plasticity and primary motor cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:393–415
Woody CD, Gruen E, Birt D (1991) Changes in membrane currents during Pavlovian conditioning of single cortical neurons. Brain Res 539:76–84
Ziemann U, Muellbacher W, Hallett M, Cohen LG (2001) Modulation of practice-dependent plasticity in human motor cortex. Brain 124:1171–1181
Ziemann U, Ilic TV, Pauli C, Meintzschel F, Ruge D (2004) Learning modifies subsequent induction of long-term potentiation-like and long-term depression-like plasticity in human motor cortex. J Neurosci 24:1666–1672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallasch, E., Christova, M., Krenn, M. et al. Changes in motor cortex excitability following training of a novel goal-directed motor task. Eur J Appl Physiol 105, 47–54 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0871-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0871-y