Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate possible relationships between different right-hand finger-length ratios and different fasting hormone concentrations in young swimmers. Fifty-five young swimmers participated in this study (26 boys and 29 girls, aged 10–17 years). The original method of Visnapuu and Jürimäe (J Strength Cond Res 21:923–929, 2007) was used for the measurement of length parameters of the hand. The following finger-length ratios were calculated: 1D:2D, 1D:3D, 1D:4D, 1D:5D, 2D:3D, 2D:4D, 2D:5D, 3D:4D, 3D:5D, and 4D:5D. All finger-length ratios were significantly higher in girls compared with boys. Ghrelin, leptin, testosterone in boys, estradiol in girls, insulin-like growth-factor I (IGF-I), IGFBP-3, and insulin were analyzed. Leptin and insulin concentrations were lower in boys compared with girls. In both groups, the relationships between finger-length ratios and basic anthropometric parameters were not significant. In girls, estradiol correlated negatively with 2D:3D (r = −0.51) and 2D:4D (r = −0.49) finger ratios. In boys, ghrelin concentration correlated with most of the finger-length ratios (r = 0.37–0.40). In girls, the relationship of ghrelin with the 2D:3D (r = 0.45) and 2D:4D (r = 0.48) finger ratios was significant. In boys, but not in girls, IGF-I (r = 0.42) and IGFBP-3 (r = 0.44) correlated only with the 2D:4D finger ratio. Leptin and insulin did not correlate with the finger-length ratios. In boys, the most important hormone to characterize several finger-length ratios was ghrelin (13.7–15.6% variance accounted for). Ghrelin and testosterone together accounted for 20.3% (R 2 × 100) of the variance in the 2D:4D ratio. In girls, estradiol was correlated with the 2D:3D ratio (25.7%) and estradiol in combination with ghrelin with the 2D:4D ratio (30.0%). In conclusion, ghrelin appears to be a further biochemical parameter in addition to the sex steroids which correlated with different digit-length ratios at least in boys.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bang AK, Carlsen E, Holm M et al (2005) A study of finger length, semen quality and sex hormones in 360 young men from the general Danish population. Hum Reprod 20:3109–3113, doi:10.1093/humrep/dei170
Brown WM, Hines M, Fane BA et al (2002) Masculinized finger length patterns in human males and females with congenital adrenal hyperplasma. Horm Behav 42:380–386, doi:10.1006/hbeh.2002.1830
Cortelazzi D, Cappiello V, Morpurgo PS et al (2003) Circulating levels of ghrelin in human fetuses. Eur J Endocrinol 149:111–116, doi:10.1530/eje.0.1490111
Fuqlsang J, Skiaerbaek C, Espelund U et al (2005) Ghrelin and its relationship to growth hormones during normal pregnancy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 62:554–559, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02257.x
Geladas ND, Nassis GP, Davlicevic S (2005) Somatic and physical traits affecting sprint swimming performance in young swimmers. Int J Sports Med 26:139–144, doi:10.1055/s-2004-817862
Ho KY, Evans WS, Blizzard RM et al (1987) Effects of age and sex on the 24-hour profile of growth hormone secretion in man: importance of endogenous estradiol concentrations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 64:51–58
Holmes SJ, Shalet SM (1996) Role of growth hormone and sex steroids in achieving and maintaining normal bone mass. Horm Res 45:86–93
Hönekopp J, Bartholdt L, Baier L et al (2007) Second to fourth digit length ratio (2D:4D) and adult sex hormone levels: new data and a meta-analytic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32:313–321, doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2007.01.007
Jürimäe J, Cicchella A, Jürimäe T et al (2007) Regular physical activity influences plasma ghrelin concentration in adolescent girls. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:1736–1741, doi:10.1210/jc.78.3.744
Juul A, Bang P, Hertel NT et al (1994) Serum insulin-like growth factor-I in 1030 healthy children, adolescents, and adults-relation to age, sex, stage of puberty, testicular size, and body-mass index. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 78:744–752
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y et al (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660, doi:10.1038/45230
Kondo T, Zakany J, Innis J et al (1997) Of fingers, toes, and penises. Nature 390:29, doi:10.1038/36234
Lutchmaya S, Baron-Cohen S, Raggatt P et al (2004) 2nd and 4th digit ratio, fetal testosterone and estradiol. Early Hum Dev 77:23–28, doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2003.12.002
Malas M, Dogan S, Evcil EH et al (2006) Fetal development of the hand, digits and digits ratio. Early Hum Dev 82:469–475, doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2005.12.002
Manning JT (2002a) The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length and performance in skiing. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 42:446–450
Manning JT (2002b) Digit ratio: a pointer to fertility, behavior, and health. Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick
Manning JT, Taylor R (2001) Second to fourth digit ratio and male ability in sport implications for sexual selection in humans. Evol Hum Behav 22:61–69, doi:10.1093/humrep/13.11.3000
Manning JT, Scutt D, Wilson J et al (1998) The ratio of the 2nd and 4th digit length: a predictor of sperm numbers and concentrations of testosterone, luteinizing hormone and oestrogen. Hum Reprod 13:3000–3004, doi:10.1016/S1090-5138(00)00029-5
Manning JT, Barley L, Walton J et al (2000) The 2nd:4th digit ratio, sexual dimorphism, population differences and reproductive success: evidence for sexually antagonistic genes? Evol Hum Behav 21:163–183, doi:10.1016/S1090-5138(00)00063-5
Manning JT, Bundred PE, Taylor R (2003) The ratio of 2nd and 4th digit length: a prenatal correlate of ability in sport. In: Reilly T, Marfell-Jones M (eds) Kinanthropometry VIII. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference of the International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry (ISAK), Routledge, pp 165–174
McFadden D, Shubel E (2002) Relative lengths of fingers and toes in human males and females. Horm Behav 42:492–500, doi:10.1006/hbeh.2002.1833
McIntyre MH, Ellison PT, Lieberman DE et al (2005) The development of sex differences in digital formula from infancy in the Fels Longitudinal Study. Proc Biol Sci 272:1473–1479, doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3100
Pagotto V, Gambineri A, Pelusi C et al (2003) Testosterone replacement therapy restores normal ghrelin in hypogonadal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:4139–4143, doi:10.1210/jc.2003-030554
Paul SN, Kato BS, Hunkin JL et al (2006) The big finger: the second to fourth digit ratio is a predictor of sporting ability in women. Br J Sports Med 40:981–983, doi:10.1136/bjsm.2006.027193
Peichel CL, Prabhakaran B, Vogt TF (1997) The mouse ulnaless mutation deregulates posters HoxD gene expression and alters appendicular patterning. Development 124:3481–3492
Pirazzoli P, Lanari M, Zucchini S et al (2005) Active and total ghrelin concentrations in the newborn. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 18:379–384
Pokrywka L, Rachon D, Suchecka-Rachon K et al (2005) The second to fourth digit ratio in elite and non-elite female athletes. Am J Hum Biol 17:796–800, doi:10.1002/ajhb.20449
Pomerants T, Tillmann V, Jürimäe T et al (2006) Relationship between ghrelin and anthropometrical, body composition parameters and testosterone levels in boys at different stages of puberty. J Endocrinol Invest 29:962–967
Robertson J, Zhang W, Liu JJ et al (2008) Radiographic assessment of the index to ring finger ratio (2D:4D) in adults. J Anat 212:42–48
Rogers I, Metcalfe C, Gunnell D et al (2006) AVON Longitudinal Study of Parents Children Study Team. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and growth in height, leg length, and trunk length between ages 5 and 10 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:2514–2519, doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0388
Rogol AD, Roemmich JN, Clark PA (2002) Growth at puberty. J Adolesc Health 31:192–200, doi:10.1016/S1054-139X(02)00485-8
Romano M, Rubolini D, Martinelli R et al (2005) Experimental manipulation of yolk testosterone affects digit length ratio in the ring-necked pheasant (Phasianus colchicus). Horm Behav 48:342–346, doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2005.03.007
Rosenfeld RG, Wilson DM, Lee PDK et al (1986) Insulin-like growth factors I and II in evaluation of growth retardation. J Pediatr 109:428–433, doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(86)80112-3
Rusinska A, Chlebna-Sokol D (2006) Insulin-like growth factor-1 and mineral metabolism markers in children with idiopathic decrease in bone mass. Clin Chim Acta 366:257–263, doi:10.1016/j.cca.2005.10.014
Sanders G, Bereczkei T, Csatho A et al (2005) The ratio of the 2nd to 4th finger length predicts spatial ability in men but not women. Cortex 41:789–795, doi:10.1016/S0010-9452(08)70297-1
Schwarz MF (2001) Brain pathways controlling food intake and body weight. Exp Biol Med 226:978–981
Stevenson JC, Everson PM, Williams DC et al (2007) Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms and digit ratios in college sample. Am J Hum Biol 19:41–50, doi:10.1002/ajhb.20571
Tanaka M, Hayashida Y, Nakao N et al (2001) Testis-specific and developmentally induced expression of a ghrelin gene-derived transcript that encodes a novel polypeptide in a mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta 1522:62–65
Tanner J (1962) Growth at adolescents, 2nd edn edn. Blackwell, Oxford
Tena-Sempere M (2005) Exploring the role of ghrelin as novel regulator of gonadal function. Growth Horm IGF Res 15:83–88, doi:10.1016/j.ghir.2005.02.001
Tena-Sempere M, Barreiro ML, Gonzales LC et al (2002) Novel expression and functional role of ghrelin in rat testes. Endocrinology 143:717–725, doi:10.1210/en.143.2.717
Tester N, Campell A (2007) Sporting achievement: what is the contribution of digit ratio? J Pers 75:663–677, doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.2007.00452.x
Trivers R, Manning J, Jacobson A (2006) A longitudinal study of digit ratio (2D:4D) and other finger ratios in Jamaican children. Horm Behav 49:150–156, doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2005.05.023
van Anders SM, Vernon PA, Wilbur CJ (2006) Finger-length ratios show evidence of prenatal hormone-transfer between opposite-sex twins. Horm Behav 49:315–319, doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2005.08.003
Vehmas T, Solovieva S, Lino-Arjas P (2006) Radiographic 2D:4D index in females: no relation to anthropometric, behavioural, occupational or fertility variables. J Negat Results Biomed (electronic resources) 5:12, doi:10.1186/1477-5751-5-12
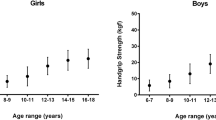
Visnapuu M, Jürimäe T (2007) Handgrip strength and hand dimensions in young handball and basketball players. J Strength Cond Res 21:923–929, doi:10.1519/1533-4287(2007)21[923:HSAHDI]2.0.CO;2
Voracek M, Reimer B, Ertl C et al (2006) Digit ratio (2D:4D), lateral preferences, and performance in fencing. Percept Mot Skills 103:427–446, doi:10.2466/PMS.103.6.427-446
Whatmore AJ, Hall CM, Jones J et al (2003) Ghrelin concentrations in healthy children and adolescents. Clin Endocrinol 59:649–654, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2265.2003.01903.x
Acknowledgments
Funding of this study was provided by Estonian Science Foundation Grant GKKSP 6225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jürimäe, T., Voracek, M., Jürimäe, J. et al. Relationships between finger-length ratios, ghrelin, leptin, IGF axis, and sex steroids in young male and female swimmers. Eur J Appl Physiol 104, 523–529 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0801-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0801-z