Abstract
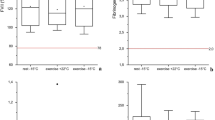
Warm water bathing is a popular recreational activity and is frequently used in rehabilitation medicine. Although well tolerated in most cases, there are reports indicating an increased risk of thrombotic events after hot tub bathing. The effects of a 45 min thermoneutral bath followed by a 50 min bath with increasing water temperature (maximum 41°C) until reaching a body core temperature of 39°C on factors of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis were studied in eight healthy male volunteers. Blood was obtained after a 45-min resting period as control and after the thermoneutral and hyperthermic bath as well as after another 45 min recovery period at the end of the study. Hyperthermic immersion (HI) lead to a shortening of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) (P < 0.05). Fibrinogen concentration decreased immediately after HI (P < 0.05) but increased during recovery (P < 0.05). Plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI) activity decreased during HI (P < 0.05), D-dimer concentration was not found to change. Thrombocyte count increased (P < 0.05) during HI. The increases in tissue-type plasminogen activator concentration as well as leucocyte count during HI were due to haemoconcentration. Prothrombin time, PAI-activity and granulocyte count decreased during thermoneutral immersion (P < 0.05). Warm water bathing leads to haemoconcentration and minimal activation of coagulation. The PAI-1 activity is decreased. A marked risk for thrombotic or bleeding complications during warm water bathing in healthy males could not be ascertained.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal (1984) Der Einfluss einer Hitzeeinwirkung auf das plasmatische Gerinnungs- und Fibrinolysesystem. Inaugural dissertation der Freien Universitaet Berlin
Al Mashhadani SA, Gader AG, al Harthi SS, Kangav D, Shaheen FA, Bogus F (1994) The coagulopathy of heatstroke: alterations in coagulation and fibrinolysis in heatstroke patients during the pilgrimage (Haj) to Makkah. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 5:731–736
Ang C, Dawes J (1994) The effects of hyperthermia on human endothelial monolayers: modulation of thrombotic potential and permeability. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 5:193–199
Angleton P, Chandler WL, Schmer G (1989) Diurnal variation of tissue-type plasminogen activator and its rapid inhibitor (PAI-1). Circulation 79(1):101–106
Arborelius M, Balldin UI, Lilja B, Lundgren CEG (1972) Hemodynamic changes in man during immersion with the head above water. Aerosp Med 43:592–598
Bedrak E, Beer G, Furman KI (1963) Fibrinolytic activity and heat stress. Isr J Exp Med 11:1–6
Bedrak E, Beer G, Furman KI (1964) Fibrinolytic activity and muscular exercise in heat. J Appl Physiol 19(3):469–471
Bergonzelli GE, Kruithof EKO (1991) Induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 biosynthesis by hyperthermia. J Cell Physiol 148:306–313
Bouchama A, Knochel JP (2002) Heat stroke. N Engl J Med 346:1978–1988
Bouchama A, Bridey F, Hammami MM, Lacombe C, Al-Shail E, Al-Ohali Y, Combe F, Al-Sedairy S, de Prost D (1996) Activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis in heatstroke. Thromb and Haemost 76:909–915
Brown NJ, Agirbasli MA, Williams GH (1998) Effect of activation and inhibition of the rennin–angiotensin system on plasma PAI-1. Hypertension 32:965–971
Brown NJ, Kim KS, Chen YQ (2000) Synergistic effect of adrenal steroids and angiotensin II on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 production. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:336–344
Cohen RJ, Epstein LS, Cohen LS, Dennis LH (1967) Alterations in blood fibrinolysis, and blood coagulation induced by exercise and the role of beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulation. Lancet 2:1264–1266
Deguchi A, Deguchi K, Shimura M, Ohnishi K, Hamaguchi H, Kawamura Y, Wada H, Murashima S, Nishikawa M, Shirakawa S (1993) Spa bathing activates fibrinolysis in patients with cerebral infarction. Intern Med 32:619–622
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
El-Sayed M, Sale C, Jones PGW, Chester M (2000) Blood hemostasis in exercise and training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32(5):918–925
Epstein M, Saruta T (1971) Effect of water immersion on renin-aldosterone and renal sodium handling in normal man. J Appl Physiol 31(3):368–374
Eshel GM, Safar P, Sassano J, Stezoski SW (1998) Delayed death after uncomplicated hot tub bathing in dogs and monkeys. Resuscitation 37:189–195
Fukao H, Hagiya Y, Ueshima S (1996) Effect of heat shock on the expression of urokinase-type Plasminogen activator in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 75(2):352–258
Gabrielsen A, Warberg J, Christensen NJ, Bie P, Stadeager C, Pump B, Norsk P (2000) Arterial pulse pressure and vasopressin release during graded water immersion in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 278:R1583–R1588
Gordon CJ, Fogarty AL, Greenleaf JE, Taylor NA, Stocks JM (2003) Direct and indirect methods for determining plasma volume during thermoneutral and cold-water immersion. Eur J Appl Physiol 89:471–474
Greenleaf JE, Shvartz E, Kravik E, Keil LC (1980) Fluid shifts and endocrine responses during chair rest and water immersion in man. J Appl Physiol 48:79–88
Grimaudo V, Hauert J, Bachmann F (1988) Diurnal variations of the fibrinolytic system. Thromb Haemost 59(3):495–499
Günther R, Holzknecht F, Spöttl F (1965) Experimentelle Untersuchungen über den Einfluss von Hyperthermie durch Heißluft (Sauna) auf die fibrinolytische Aktivität des Blutes. Sauna Archiv 4(2):21–38
Kerins DM, Hao Q, Vaughan DE (1995) Angiotensin induction of PAI-1 expression in endothelial cells is mediated by the hexapeptide angiotensin IV. J Clin Invest 96:2515–2520
Koehler M, Miyashita C (1988) Problems in measuring parameters of the fibrinolytic system: circadian rhythm of tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor. Klin Wochenschr 66(Suppl12):62–67
Korz R, Fischer F, Behn C (1969) Renin–angiotensin-system bei simulierter Hypervolämie durch Immersion. Kli Wschr 47(23):1263–1268
Kubota K, Tamura K, Take H, Kurabayashi H, Shirakura T (1997) Acute myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction at Kusatsu-spa. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 34:23–29
Levin EG, Santell L (1987) Conversion of the active to latent plasminogen activator inhibitor from human endothelial cells. Blood 70:1090–1098
Mannuccio PM (1997) Desmopressin (DDAVP) in the treatment of bleeding disorders: the first 20 years. Blood 90(7):2515–2521
Miettinen M (1960) Effect of sauna bath on fibrinolysis. J Appl Physiol 15(5): 943–944
Norsk P, Bonde-Petersen F, Warberg J (1986) Central venous pressure and plasma arginine vasopressin in man during water immersion combined with changes in blood volume. Eur J Appl Physiol 54:608–616
Prowse CV, Cash JD (1984) Physiologic and pharmocologic enhancement of fibrinolysis. Semin Thromb Hemost 10:51–60
Pugh LG, Corbett JL, Johnson RH (1967) Rectal temperatures, weight losses, and sweat rates in marathon running. J Appl Physiol 23:347–352
Roecker L, Taenzer M, Drygas WK (1990) Effect of prolonged physical exercise on the fibrinolytic system. Eur J Appl Physiol 60:478–481
Roecker L, Moeckel M, Westpfahl WKP, Gunga HC (1996) Influence of maximal ergometric exercise on endothelin concentrations in relation to molecular markers of the hemostatic system. J Thromb Haemost 75(4):612–616
Schobersberger W, Fries D, Mittermayr M, Innerhofer P, Sumann G, Schobersberger B, Klingler A, Stollnberger V, Fischbach U, Gunga HC (2002) Changes of biochemical markers and functional tests for clot formation during long-haul flights. Thromb Res 108(1):19–24
Schobersberger W, Mittermayr M, Innerhofer P, Sumann G, Schobersberger B, Klingler A, Simmer M, Streif W, Fischbach U, Fries D (2004) Coagulation changes and edema formation during long-distance bus travel. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 15(5):419–425
Speiser W, Langer W, Pschaik A (1988) Increased blood fibrinolytic activity after physical exercise: comparative study in individuals with different sporting activities and in patients after myocardial infarction taking part in a rehabilitation sports program. Thromb Res 51:543–555
Strauss MB, Davies RK, Rosenbaum JD, Rossmeisl EC (1951) Water diuresis produces during recumbency by the intravenous infusion of isotonic saline solution. J Clin Invest 30:862–868
Streiff M, Bell WR (1994) Exercise and hemostasis in humans. Semin Hematol 31(2):155–165
Strother SV, Bull JM, Branham SA (1986) Activation of coagulation during therapeutic whole body hyperthermia. Thromb Res 43(3):353–360
Tamura K, Kubota K, Kurabayashi H, Shirakura T (1996) Effects of hyperthermal stress on the fibrinolytic system. Int J Hyperthermia 12:31–36
Van den Bom JG, Bots ML, Haverkate F (2003) The 4G5G polymorphism in the gene for PAI-1 and the circadian oscillation of plasma PAI-1. Blood 101:1841–1844
Von Diringshofen H (1948) Die Wirkungen des hydrostatischen Druckes des Wasserbades auf den Blutdruck in den Kapillaren und die Bindegewebsentwässerung. Z Kreislaufforsch 37:382–390
Weiss C, Seitel G, Baertsch P (1998) Coagulation and fibrinolysis after moderate and very heavy exercise in healthy male subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 30(2):246–251
Wojta J, Holzer M, Hufnagl P (1991) Hyperthermia stimulates plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Am J Pathol 139(4):911–919
Zwierzina WD, Herold M, Günther R, Kunz F (1980) Blutgerinnung bei Überwärmungstherapie. Z Rheumatol 39:368–378
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge K. Thorndike and R. Meier-Buttermilch for their support in conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boldt, LH., Fraszl, W., Röcker, L. et al. Changes in the haemostatic system after thermoneutral and hyperthermic water immersion. Eur J Appl Physiol 102, 547–554 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0620-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0620-7