Abstract
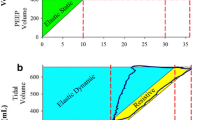
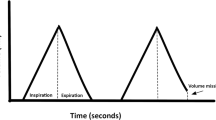
We tested the hypothesis that the pattern of chest wall configuration during speech production correlates with the pattern of chest wall motion during resting breathing. Twenty-one men (age 40 ± 8 years) with ankylosing spondylitis and varied degrees of ribcage involvement participated in the study. None of the patients had an obvious speech abnormality. Ribcage and abdominal displacements during quiet breathing and during reading were measured with a respiratory plethysmograph. Measurements were taken in the sitting and standing body positions. In each body position, ribcage or abdominal displacements during quiet breathing correlated with the corresponding chest wall displacements recorded during reading (P < 0.001). In addition, linear regression analysis showed that the slope of the chest wall motion loop during quiet breathing correlated with the ratio of ribcage to abdomen contribution to lung volume displacement during reading (r = 0.78, P < 0.001 for sitting and r = 0.64, P = 0.002 for standing position). The slopes of the regression lines did not differ between the sitting and standing body position (P > 0.05). We conclude that the relative contribution of the ribcage and abdomen to lung volume displacement during speech production correlates with the relative ribcage and abdomen contribution to tidal volume during quiet breathing; our data support the notion that the pattern of chest wall configuration during quiet breathing largely predicts the pattern of ribcage and abdomen displacement during speech.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banzett RB, Mahan ST, Garner DM, Brughera A, Loring SH (1995) A simple and reliable method to calibrate respiratory magnetometers and Respitrace. J Appl Physiol 79:2169–2176
Binazzi B, Lanini B, Bianchi R, Romagnoli I, Nerini M, Gigliotti F, Duranti R, Milic-Emili J, Scano G (2006) Breathing pattern and kinematics in normal subjects during speech, singing and loud whispering. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 186:233–246
Estenne M, Zocchi L, Ward M, Macklem PT (1990) Chest wall motion and expiratory muscle use during phonation in normal humans. J Appl Physiol 68:2075–2082
Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A (1994) A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity index. J Rheumatol 21:2286–2291
Goldman MD, Grimby G, Mead J (1976) Mechanical work of breathing derived from rib cage and abdominal V-P partitioning. J Appl Physiol 41:752–763
Hixon TJ, Goldman MD, Mead J (1973) Kinematics of the chest wall during speech production: volume displacements of the rib cage, abdomen, and lung. J Speech Hear Res 16:78–115
Hixon TJ, Mead J, Goldman MD (1976) Dynamics of the chest wall during speech production: function of the thorax, rib cage, diaphragm, and abdomen. J Speech Hear Res 19:297–356
Hodge MM, Rochet AP (1989) Characteristics of speech breathing in young women. J Speech Hear Res 32:466–480
Hoit JD, Hixon TJ (1986) Body type and speech breathing. J Speech Hear Res 29:313–324
Hoit JD, Plassman BL, Lansing RW, Hixon TJ (1988) Abdominal muscle activity during speech production. J Appl Physiol 65:2656–2664
Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA, Whitelock HC, Kennedy LG, Garrett SL, Calin A (1994) Defining spinal mobility in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The Bath AS metrology index. J Rheumatol 21:1694–1698
Jones SD, Steiner A, Garrett SL, Calin A (1996) The Bath ankylosing spondylitis patient global score (BAS-G). Br J Rheumatol 35:66–71
Kalliakosta G, Mandros C, Tzelepis GE (2007) Chest wall motion during speech production in patients with advanced ankylosing spondylitis. J Speech Lang Hear Res 50:109–118
Kennedy LG, Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA, Whitelock HC, Garrett SL, Calin A (1995) Ankylosing spondylitis: the correlation between a new metrology score and radiology. Br J Rheumatol 34:767–770
Konno K, Mead J (1967) Measurement of the separate volume changes of rib cage and abdomen during breathing. J Appl Physiol 22:407–422
Macrae IF, Wright V (1969) Measurement of back movement. Ann Rheum Dis 28:584–589
McCool FD, Loring SH, Mead J (1985) Rib cage distortion during voluntary and involuntary breathing acts. J Appl Physiol 58:1703–1712
Mead J (1960) Control of respiratory frequency. J Appl Physiol 15:325–336
Sharp JT, Goldberg NB, Druz WS, Danon J (1975) Relative contributions of rib cage and abdomen to breathing in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol 39:608–618
Verschakelen JA, Demedts MG (1995) Normal thoracoabdominal motions. Influence of sex, age, posture, and breath size. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:399–405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandros, C., Kampolis, C., Kalliakosta, G. et al. Relative contributions of the ribcage and abdomen to lung volume displacement during speech production. Eur J Appl Physiol 102, 425–430 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0603-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0603-8