Abstract
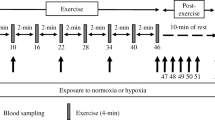
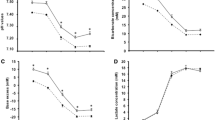
The purpose of this study was to determine the electrolyte concentration changes in arterial plasma from high-intensity repeated bouts of cycling exercise in well-trained females and to determine the relationships between arterial plasma lactate, potassium (K+), bicarbonate (HCO −3 ), and pH with minute ventilation. Fourteen female subjects (mean age = 27 ± 4 years; mean height = 170 ± 7 cm; mean weight = 62 ± 7 kg; maximal oxygen uptake = 50 ± 6 ml/kg/min) were recruited to perform 3 × 5 min bouts of exercise at 236 ± 27 W with 10 min recovery between each set. Minute ventilation, arterial plasma lactate, potassium, calcium, chloride, and sodium ion concentrations were measured a minute 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 of each set and midway through recovery (21 sampling points total per subject). The results showed that the strongest relationship was between arterial plasma K+ concentration and minute ventilation (r 2 = 0.91), and, that arterial plasma lactate mirrored both arterial plasma HCO −3 and pH. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that women exhibit similar electrolyte responses as reported elsewhere in men, and support the idea that K+ may partly contribute to controlling ventilation during high-intensity exercise and recovery.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American College of Sports Medicine (2000) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, 6th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p 77
Asmussen E, Nielsen M (1946) Studies on the regulation of respiration in heavy work. Acta Physiol Scand 12:171–188
van Beaumont W, Strand JC, Petrofsky JS, Hipskind SG, Greenleaf JE (1973) Changes in total plasma content of electrolytes and proteins with maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 34:102–106
Bouhuys A, Pool J, Binkhorst RA, van Leeuwen P (1966) Metabolic acidosis of exercise in healthy males. J Appl Physiol 21:1040–1046
Buono MJ, Roby FB (1982) Acid-base, metabolic, and ventilatory responses to repeated bouts of exercise. J Appl Physiol 53:436–439
Busse MW, Maassen N (1989) Effect of consecutive exercise bouts on plasma potassium concentration during exercise and recovery. Med Sci Sports Exerc 21:489–493
Costill DL, Verstappen F, Kuipers H, Janssen E, Fink W (1984) Acid-base balance during repeated bouts of exercise: influence of HCO3. Int J Sports Med 5:228–231
Dempsey JA, Rankin J (1967) Physiologic adaptations of gas transport systems to muscular work in health and disease. Am J Phys Med 46:582–647
Dempsey JA, Forster HV, Ainsworth DM (1995) Regulation of hyperpnea, hyperventilation, and respiratory muscle recruitment during exercise. In: Dempsey JA, Pack AI (eds) Regulation of breathing. Second edition revised and expanded. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, pp 1065–1134
Hagberg JM, Coyle EF, Carroll JE, Miller JM, Martin WH, Brooke MH (1982) Exercise hyperventilation in patients with McArdle’s disease. J Appl Physiol 52:991–994
Hankinson JL, Odencrantz JR, Fedan KB (1999) Spirometric reference values from a sample of the general US population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:179–187
Juel C (2001) Current aspects of lactate exchange: lactate/H+ transport in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:12–16
Juel C, Bangsbo J, Graham T, Saltin B (1990) Lactate and potassium fluxes from human skeletal muscle during and after intense, dynamic, knee extensor exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 140:147–159
Juel C, Hellsten Y, Saltin B, Bangsbo J (1999) Potassium fluxes in contracting human skeletal muscle and red blood cells. Am J Physiol 276:R184–R188
Kilburn KH (1966) Muscular origin of elevated plasma potassium during exercise. J Appl Physiol 21:675–678
Lindinger MI, Heigenhauser GJ, McKelvie RS, Jones NL (1992) Blood ion regulation during repeated maximal exercise and recovery in humans. Am J Physiol 262:R126–R136
Lindinger MI, McKelvie RS, Heigenhauser GJ (1995) K+ and Lac- distribution in humans during and after high-intensity exercise: role in muscle fatigue attenuation? J Appl Physiol 78:765–777
McKelvie RS, Lindinger MI, Heigenhauser GJ, Jones NL (1991) Contribution of erythrocytes to the control of the electrolyte changes of exercise. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 69:984–993
Medbo JI, Sejersted OM (1990) Plasma potassium changes with high intensity exercise. J Physiol 421:105–122
Medbo JI, Toska K (2001) Lactate release, concentration in blood, and apparent distribution volume after intense bicycling. Jpn J Physiol 51:303–312
Osnes JB, Hermansen L (1972) Acid-base balance after maximal exercise of short duration. J Appl Physiol 32:59–63
Paterson DJ (1992) Potassium and ventilation in exercise. J Appl Physiol 72:811–820
Paterson DJ (1997) Potassium and breathing in exercise. Sports Med 23:149–163
Paterson DJ, Friedland JS, Bascom DA, Clement ID, Cunningham DA, Painter R, Robbins PA (1990) Changes in arterial K+ and ventilation during exercise in normal subjects and subjects with McArdle’s syndrome. J Physiol 429:339–348
Pruitt WC, Jacobs M (2004) Interpreting arterial blood gases: easy as ABC. Nursing 34:50–53
Putman CT, Jones NL, Heigenhauser GJ (2003) Effects of short-term training on plasma acid-base balance during incremental exercise in man. J Physiol 550:585–603
Qayyum MS, Barlow CW, O’Connor DF, Paterson DJ, Robbins PA (1994) Effect of raised potassium on ventilation in euoxia, hypoxia and hyperoxia at rest and during light exercise in man. J Physiol 476:365–372
Rubenowitz E, Landin K, Wilhelmsen L (1998) Skeletal muscle magnesium and potassium by gender and hypertensive status. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 58:47–54
Storer TW, Davis JA, Caiozzo VJ (1990) Accurate prediction of VO2max in cycle ergometry. Med Sci Sports Exerc 22:704–712
Wasserman K, Van Kessel AL, Burton GG (1967) Interaction of physiological mechanisms during exercise. J Appl Physiol 22:71–85
Yoshida T, Chida M, Ichioka M, Makiguchi K, Eguchi J, Udo M (1990) Relationship between ventilation and arterial potassium concentration during incremental exercise and recovery. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 61:193–196
Zavorsky GS, Saul L, Murias JM, Ruiz P (2006a) Pulmonary gas exchange does not worsen during repeat exercise in women. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 153:226–236
Zavorsky GS, Saul L, Decker A, Ruiz P (2006b) Radiographic evidence of pulmonary edema during high-intensity interval training in women. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 153:181–190
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Lloyd Saul for helping out with the data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zavorsky, G.S., Gow, J. & Murias, J.M. Potassium kinetics and its relationship with ventilation during repeated bouts of exercise in women. Eur J Appl Physiol 99, 173–181 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-006-0330-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-006-0330-6