Abstract
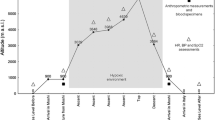
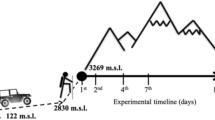
The effects of a high-altitude exposure were studied in six mountaineers who spent 3 weeks at an altitude range between 5,250 and 7,161 m after 1 week in an acclimatization trek (2,800–5,250 m). Blood drawn from the antecubital vein was collected at sea level 1 day before and 1 day after the expedition to analyse some haematological variables [haemoglobin (Hb), haematocrit (Htc) and red blood cell (RBC) count], erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activity [superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione reductase (Gr)] and membrane fatty acid profile [mono-unsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), saturated fatty acids (SFA), trans fatty acids (TRANS)]. Moreover, total antioxidant status (TAS), thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), thiol protein groups (SH), SOD, GPx and Gr were measured in plasma. High-altitude exposure induced polycythaemia, with significant increases in RBC count (5.26%), Hb concentration (4.83%) and Htc (6.26%). Furthermore, a significant increase in plasma TBARS, SOD and Gr was observed after the expedition, whereas SH, TAS and GPx decreased. Erythrocyte glutathione-cycle-related antioxidant enzyme activity was upregulated, whereas SOD activity was maintained after the expedition. In addition, despite the unchanged (MUFA+PUFA)/SFA ratio, the membrane erythrocyte fatty acid content showed a significant increase in PUFAs and a decrease in TRANS, suggesting enhanced membrane fluidity. In conclusion, it seems that high-altitude exposure, besides quantitative variations in RBC expression, induced plasma oxidative stress and damage, and significant changes in erythrocyte components, namely in antioxidant enzyme activity and membrane fatty acid profile that might modify RBC functionality.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral JS, Casal S, Pereira JA, Seabra RM, Oliveira BP (2003) Determination of sterol and fatty acid compositions, oxidative stability, and nutritional value of six walnut (Juglans regia L.) cultivars grown in Portugal. J Agric Food Chem 26:7698–7702
Avissar N, Finkelstein JN, Horowitz S, Willey JC, Coy E, Frampton MW, Watkins RH, Khullar P, Xu YL, Cohen HJ (1996) Extracellular glutathione peroxidase in human lung epithelial lining fluid and in lung cells. Am J Physiol 2:L173–L182
Bailey D, Davies B, Davison G, Young I (2000) Oxidatively stressed out at high-altitude! International Society for Mountain Medicine Newsletter 4:3–13
Bailey DM, Davies B, Young IS (2001) Intermittent hypoxic training: implications for lipid peroxidation induced by acute normoxic exercise in active men. Clin Sci (Lond) 5:465–475
Bertholf RL, Nicholson JR, Wills MR, Savory J (1987) Measurement of lipid peroxidation products in rabbit brain and organs (response to aluminum exposure). Ann Clin Lab Sci 6:418–423
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Med Sci 8:911–917
Celedon G, Gonzalez G, Sotomayor CP, Behn C (1998) Membrane lipid diffusion and band 3 protein changes in human erythrocytes due to acute hypobaric hypoxia. Am J Physiol 6:C1429–C1431
Childs A, Jacobs C, Kaminski T, Halliwell B, Leeuwenburgh C (2001) Supplementation with vitamin C and N-acetyl-cysteine increases oxidative stress in humans after an acute muscle injury induced by eccentric exercise. Free Radic Biol Med 6:745–753
De Haan JB, Cristiano F, Iannello R, Bladier C, Kelner MJ, Kola I (1996) Elevation in the ratio of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase to glutathione peroxidase activity induces features of cellular senescence and this effect is mediated by hydrogen peroxide. Hum Mol Genet 2:283–292
Frei B, Stocker R, Ames BN (1988) Antioxidant defenses and lipid peroxidation in human blood plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 24:9748–9752
Gaeta LM, Tozzi G, Pastore A, Federici G, Bertini E, Piemonte F (2002) Determination of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities in blood of healthy pediatric subjects. Clin Chim Acta 1–2:117–120
Ghiselli A, Serafini M, Natella F, Scaccini C (2000) Total antioxidant capacity as a tool to assess redox status: critical view and experimental data. Free Radic Biol Med 11:1106–1114
Gonzalez NC, Wood JG (2001) Leukocyte–endothelial interactions in environmental hypoxia. Adv Exp Med Biol 39–60
Grandjean D, Sergheraert R, Valette JP, Driss F (1998) Biological and nutritional consequences of work at high altitude in search and rescue dogs: the scientific expedition Chiens des Cimes-Licancabur 1996. J Nutr 12[Suppl]: 2694S–2697S
Griffiths MJ, Ndungu F, Baird KL, Muller DP, Marsh K, Newton CR (2001) Oxidative stress and erythrocyte damage in Kenyan children with severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Br J Haematol 2:486–491
Guezennec CY, Nadaud JF, Satabin P, Leger F, Lafargue P (1989) Influence of polyunsaturated fatty acid diet on the hemorrheological response to physical exercise in hypoxia. Int J Sports Med 4:286–291
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University Press, New York
Horiuchi M, Tsutsui M, Tasaki H, Morishita T, Suda O, Nakata S, Nihei S, Miyamoto M, Kouzuma R, Okazaki M, Yanagihara N, Adachi T, Nakashima Y (2004) Upregulation of vascular extracellular superoxide dismutase in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1:106–111
Hu M-L (1990) Measurement of protein thiol groups and GSH in plasma. In: Parker L (ed) Methods in enzymology. Academic, San Diego, Calif., 380–385
Joanny P, Steinberg J, Robach P, Richalet JP, Gortan C, Gardette B, Jammes Y (2001) Operation Everest III (Comex’97): the effect of simulated severe hypobaric hypoxia on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in human blood at rest and after maximal exercise. Resuscitation 3:307–314
Maddipati KR, Marnett LJ (1987) Characterization of the major hydroperoxide-reducing activity of human plasma. Purification and properties of a selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase. J Biol Chem 36:17398–17403
Magalhães J, Ascensao A, Soares JM, Ferreira R, Neuparth MJ, Oliveira J, Amado F, Marques F, Duarte JA (2004a) Acutely and chronically exposed mice to severe hypoxia: the role of acclimatization against skeletal muscle oxidative stress. Int J Sports Med (in press)
Magalhães J, Ascensao A, Soares JM, Neuparth MJ, Ferreira R, Oliveira J, Amado F, Duarte JA (2004b) Acute and severe hypobaric hypoxia-induced muscle oxidative stress in mice: the role of glutathione against oxidative damage. Eur J Appl Physiol 2–3:185–191
Moller P, Loft S, Lundby C, Olsen NV (2001) Acute hypoxia and hypoxic exercise induce DNA strand breaks and oxidative DNA damage in humans. FASEB J 7:1181–1186
Samaja M (2001) Hypoxia-dependent protein expression: erythropoietin. High Alt Med Biol 2:155–163
Singh MV, Salhan AK, Rawal SB, Tyagi AK, Kumar N, Verma SS, Selvamurthy W (2003) Blood gases, hematology, and renal blood flow during prolonged mountain sojourns at 3500 and 5800 m. Aviat Space Environ Med 5:533–536
Singh SN, Vats P, Kumria MM, Ranganathan S, Shyam R, Arora MP, Jain CL, Sridharan K (2001) Effect of high altitude (7,620 m) exposure on glutathione and related metabolism in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 3:233–237
Solans R, Motta C, Sola R, La Ville AE, Lima J, Simeon P, Montella N, Armadans-Gil L, Fonollosa V, Vilardell M (2000) Abnormalities of erythrocyte membrane fluidity, lipid composition, and lipid peroxidation in systemic sclerosis: evidence of free radical-mediated injury. Arthritis Rheum 4:894–900
Spranger M, Krempien S, Schwab S, Donneberg S, Hacke W (1997) Superoxide dismutase activity in serum of patients with acute cerebral ischemic injury. Correlation with clinical course and infarct size. Stroke 12:2425–2428
Stadtman ER, Levine RL (2000) Protein oxidation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 191–208
Suarez A, Ramirez-Tortosa M, Gil A, Faus MJ (1999) Addition of vitamin E to long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched diets protects neonatal tissue lipids against peroxidation in rats. Eur J Nutr 4:169–176
Subczynski WK, Wisniewska A (2000) Physical properties of lipid bilayer membranes: relevance to membrane biological functions. Acta Biochim Pol 3:613–625
Tham DM, Whitin JC, Cohen HJ (2002) Increased expression of extracellular glutathione peroxidase in mice with dextran sodium sulfate-induced experimental colitis. Pediatr Res 5:641–646
West JB (1996) Physiology of extreme altitude. In: Fregly M, Blatteis C (eds) Handbook of physiology, section 4, Environmental physiology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1307–1325
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge to João Garcia for his contribution as leader of the Pumori expedition, and we especially thank all the climbers who kindly participated in this study and disposed themselves to all the constraints related to data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magalhães, J., Ascensão, A., Marques, F. et al. Effect of a high-altitude expedition to a Himalayan peak (Pumori, 7,161 m) on plasma and erythrocyte antioxidant profile. Eur J Appl Physiol 93, 726–732 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1222-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1222-2