Abstract
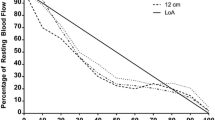
The contribution to the regulation of forearm blood flow (FBF) by different baroreceptor populations has previously only been studied over a limited range of stimuli. Therefore, FBF and R-R interval were recorded during neck suctions and neck pressures ranging from −60 to +40 mmHg. The change in R-R interval (ΔR-R) during neck suction was significantly increased at each stage when compared to the control (P<0.05). ΔR-R did not show any significant change during any of the neck pressure stages (P>0.05). Suction or pressure applied to the neck did not elicit any significant changes in FBF when compared to the control (P>0.05). These data show that widening the range of applied stimuli to carotid sinus baroreceptors does not induce a change in FBF. However, the small transient changes reported previously cannot be discounted.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud FM, Eckberg DL, Johannson UJ, Mark AL (1979) Carotid and cardiopulmonary baroreceptor control of splanchnic and forearm vascular resistance during venous pooling in man. J Physiol (Lond) 286:173–184
Bevegård BS, Castenfors J, Lindblad LE (1977) Effect of carotid sinus stimulation on cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance during changes in blood volume distribution in man. Acta Physiol Scand 101:50–57
Carlsten A, Folkow B, Grimby G, Hamberger C, Thulesius O (1958) Cardiovascular effects of direct stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve in man. Acta Physiol Scand 44:138–145
Carswell F, Hainsworth R, Ledsome JR (1970) The effects of distension of the pulmonary vein–atrial junctions upon peripheral vascular resistance. J Physiol (Lond) 207:1–14
Convertino VA, Doerr DF, Eckberg DL, Fritsch JM, Vernikos-Danellis J (1990) Head-down bed rest impairs vagal baroreflex responses and provokes orthostatic hypotension. J Appl Physiol 68:1458–1464
Crisp AJ, Hainsworth R, Tutt SM (1988) The absence of cardiovascular and respiratory responses to changes in right ventricular pressure in anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol (Lond) 407:1–13
Duprez D, De Pue N, Clement DL (1987) Peripheral vascular responses during carotid baroreceptor stimulation in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Clin Sci (Colch) 73:635–640
Ebert TJ (1983) Carotid baroreceptor reflex regulation of forearm vascular resistance in man. J Physiol (Lond) 337:655–664
Eckberg DL (1976) Temporal response patterns of the human sinus node to brief carotid baroreceptor stimuli. J Physiol (Lond) 258:769–782
Eckberg DL (1980) Nonlinearities of the human carotid baroreceptor-cardiac reflex. Circ Res 47:208–216
Eckberg DL, Sleight P (1992) Human baroreflexes in health and disease. Monographs of The Physiological Society, vol 43. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Eckberg DL, Cavanaugh MS, Mark AL, Abboud FM (1975) A simplified neck suction device for activation of carotid baroreceptors. J Lab Clin Med 85:167–173
Epstein SE, Beiser GD, Goldstein RE, Stampfer M, Wechsler AS, Glick G, Braunwald E (1969) Circulatory effects of electrical stimulation of the carotid sinus nerves in man. Circulation 40: 269–276
Ernsting J, Parry DJ (1957) Some observations on the effects of stimulating the stretch receptors in the carotid artery of man. J Physiol (Lond) 137:45–46P
Escourrou P, Raffestin B, Papelier Y, Pussard E, Rowell LB (1993) Cardiopulmonary and carotid baroreflex control of splanchnic and forearm calculations. Am J Physiol 264:H777–H782
Hainsworth R (1990) Non-invasive investigations of cardiovascular reflexes in humans. Clin Sci (Colch) 78:437–443
Hainsworth R, AL-Shamma YMH (1988) Cardiovascular responses to stimulation of carotid baroreceptors in healthy subjects. Clin Sci (Colch) 75:159–165
Hisdal J, Toska K, Flatebø T, Walløe L (2001) Arterial baroreceptors are activated during onset of mild (−20 mmHg) lower body negative pressure (LBNP) in humans. J Physiol (Lond) 531:41P
Johnson JM, Rowell LB, Neiderberger M, Eisman MM (1974) Human splanchnic and forearm vasoconstrictor responses to reduction of right atrial and aortic pressure. Circ Res 34:515–525
Levine BD, Buckey JC, Fritsch JM, Yancy CW, Watenpaugh DE, Snell PG, Lane LD, Eckberg DL (1991) Physical fitness and cardiovascular regulation: mechanisms of orthostatic intolerance. J Appl Physiol 70:112–122
Lightfoot JT, Claytor RP, Torok DJ, Journell TW, Fortney SM (1989a) Ten weeks of aerobic training do not affect lower body negative pressure responses. J Appl Physiol 67:894–901
Lightfoot JT, Tankersley C, Rowe SA, Freed AN, Fortney SM (1989b) Automated blood pressure measurements during exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 21:698–707
Lightfoot JT, Torok DJ, Journell TW, Turner MJ, Claytor P (1994) Resistance training increases lower body negative pressure tolerance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 26:1003–1011
Lindblad LE, Wallin BG, Bevegård S (1982) Transient vasodilation in the forearm on stimulation of carotid baroreceptors in man. J Auton Nerv Syst 5:373–379
Ludbrook J, Mancia G, Ferrari A, Zanchetti A (1976) Factors influencing the carotid baroreceptor response to pressure changes in a neck chamber. Clin Sci Mol Med 51:347–349S
Mack GW, Convertino VA, Nadel ER (1993) Effect of exercise training on cardiopulmonary baroreflex control of forearm vascular resistance in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:722–726
Pawelczyk JA, Raven PB (1989) Reductions in central venous pressure improve carotid baroreflex responses in humans. Am J Physiol 257:H1389–H1395
Potts JT, Shi X, Raven PB (1995) Cardiopulmonary baroreceptors modulate carotid baroreflex control of heart rate during dynamic exercise. Am J Physiol 268:H1567–H1576
Rea RF, Eckberg DL (1987) Carotid baroreceptor-muscle sympathetic relation in humans. Am J Physiol 253: R929–R934
Rowell LB (1993) Human cardiovascular control. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Shi X, Potts JT, Foresman BH, Raven LB (1993) Carotid baroreflex responsiveness to lower body positive pressure-induced increases in central venous pressure. Am J Physiol 265:H918–H922
Sprenkle JM, Eckberg DL, Goble RL, Schelhorn JJ, Halliday HC (1986) Device for rapid quantification of human carotid baroreceptor-cardiac reflex responses. J Appl Physiol 60:727–732
Sugiyama Y, Matsukawa T, Sahafuzzaman ASM, Okada H, Watanabe T, Mano T (1996) Delayed and diminished pressor response to muscle sympathetic nerve activity in the elderly. J Appl Physiol 80:869–875
Thompson CA, Tatro DL, Ludwig DA, Convertino VA (1990) Baroreflex responses to acute changes in blood volume in humans. Am J Physiol 259:R792–R798
Thompson CA, Ludwig DA, Convertino VA (1991) Carotid baroreceptor influence on forearm vascular resistance during low-level lower body negative pressure. Aviat Space Environ Med 62:930–933
Victor RG, Mark AL (1985) Interaction of cardiopulmonary and carotid baroreflex control of vascular resistance in humans. J Clin Invest 76:1592–1598
Vukasovic JL, Al-Timman JKA, Hainsworth R (1990) The effects of lower body negative pressure on baroreceptor responses in humans. Exp Physiol 75:81–93
Wallin BG, Sundlöf G, Delius W (1975) The effect of carotid sinus stimulation on muscle and skin nerve sympathetic activity in man. Pflugers Arch 358:101–110
Whitney RJ (1953) The measurement of volume changes in human limbs. J Physiol (Lond) 121:1–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howden, R., Lightfoot, J.T., Turner, M.J. et al. A wide range of baroreflex stimulation does not alter forearm blood flow. Eur J Appl Physiol 93, 124–129 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1181-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-004-1181-7