Abstract.
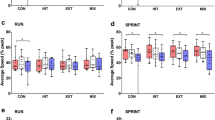
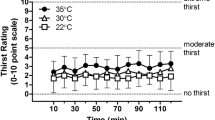
The aim of this investigation was to examine the effect of water ingestion on physiological responses to prolonged cycling (CYC) and running (RUN). A group of 11 men with mean (SEM) maximal oxygen uptake (V˙O2max) 48.5 (1.8) ml·kg–1·min–1 on a cycle-ergometer and 52.1 (2.2) ml·kg–1·min–1 on a treadmill (P<0.01) exercised for 90 min on four occasions, twice on each ergometer, at 60% of mode specific V˙O2max. No fluid was taken (D) in one trial on each ergometer, whereas 60% of fluid losses were replaced by drinking water in the other trial (W). In CYC, water ingestion attenuated the change in cardiac output (\(\Delta {\rm \dot Q}_{\rm c} \) ) and the reduction in stroke volume (ΔSV) [ΔSV: –22.7 (3.8) in D, –10.7 (2.9) ml·beat–1 in W, P<0.01; \(\Delta {\rm \dot Q}_{\rm c} \) : –1.9 (0.5) in D, –0.2 (0.4) l·min–1 in W at 85 min, P<0.01], but did not affect rectal temperature [T re at 90 min: 38.8 (0.1)°C in D, 38.7 (0.1)°C in W]. In contrast, fluid replacement reduced hyperthermia in RUN [T re at 90 min: 39.6 (0.2) in D, 39.1 (0.2)°C in W, P<0.01], and this was linked with a higher skin blood flow [RUN-W 88.9 (8.5), RUN-D 70.7 (8.4)%, P<0.05]. The \(\Delta {\rm \dot Q}_{\rm c} \) and ΔSV were also attenuated with water ingestion in this mode of exercise (P<0.05). It is concluded that water ingestion improves physiological function in both cycling and running, but that the underlying mechanism is different in the two modes of exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nassis, G.P., Geladas, N.D. Effect of water ingestion on cardiovascular and thermal responses to prolonged cycling and running in humans: a comparison. Eur J Appl Physiol 88, 227–234 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0682-5
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0682-5