Abstract
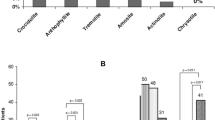
Objective: To ascertain the lung burden of asbestos fibres in Hungarian lung cancer patients in comparison with the cumulative asbestos exposure estimated from the occupational history. Methods: For 25 Hungarian lung cancer patients, lung tissue fibre analysis was performed by scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and counting of ferruginous bodies (FBs) by light microscopy. Cumulative asbestos exposure in fibre-years was assessed from a standardised occupational history using the report “fibre years” of the German Berufsgenossenschaften. Results: Median and maximum concentrations of fibres longer 5 μm per gram dry lung tissue (g dry) were 0.03 and 7.38 million fibres/g dry for chrysotile, 0.00 and 0.21 million fibres/g dry for amphibole and 0.22 and 0.62 million fibres/g dry for other mineral fibres (OMFs). The maximum values were observed in one patient for whom a high asbestos exposure was evident in advance from the occupational history. Conclusions: In comparison with reference values obtained by the same method for German patients with no indication of workplace asbestos exposure, increased concentrations of more than 0.2 million chrysotile fibres/g dry were obtained for six of the 25 Hungarian patients (24%). For one of them, the second highest estimate of a workplace exposure of 60 fibre-years and the highest tissue concentration of 7.38 million chrysotile fibres/g dry substantiate a high probability of a causal relationship to asbestos. A further comparison can be made with the results for 66 German patients treated by surgical lung resection for a disorder other than mesothelioma, mainly lung cancer. For the Hungarian lung cancer patients, similar amounts of chrysotile but distinctly lower amounts of amphibole fibres and distinctly higher amounts of OMFs were observed. A correlation between exposure estimates from occupational history and concentration of fibres in the lung tissue was observed for amphibole (Spearman: R=0.66, P < 0.001, Pearson: R=0.50, P=0.01) and for chrysotile (Pearson: R=0.48, P=0.02).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 May 2000 / Accepted: 14 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rödelsperger, K., Mándi, A., Tossavainen, A. et al. Inorganic fibres in the lung tissue of Hungarian and German lung cancer patients. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 74, 133–138 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200000202
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200000202