Abstract
Objective
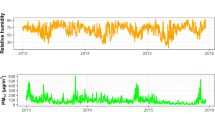
This study aims to investigate the association between the diurnal temperature range (DTR) and allergic rhinitis (AR) outpatient visits in Lanzhou, China, utilizing more than 7 years of participant surveys.
Methods
Our study used the distributed lag non-linear model (DLNM) aimed to evaluate the association between DTR and AR outpatient visits. We also performed subgroup analyses in order to find susceptible populations by gender and age groups.
Results
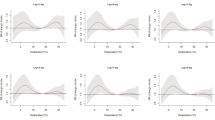
In 2013–2019, DTR in Lanzhou demonstrates a non-linear correlation with outpatient visits for AR, which is S-shaped. In addition, when DTR was located in the 0.9–5.3 °C and 12–20 °C compared with 12 °C, the risk of outpatient visits for AR increased. Moreover, males appeared to be more vulnerable to the DTR effect than females, the risk of children visits exceeded both the adult and the elderly groups at the higher DTR.
Conclusion
Our study adds to the evidence that DTR is a possible risk factor for outpatient visits for AR; therefore, the public health sector and medical staff should take DTR into account when it comes to preventing AR onset.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Some or all data or models generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Crimi P et al (2004) Correlation between meteorological conditions and Parietaria pollen concentration in Alassio, north-west Italy. Int J Biometeorol 49(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-004-0212-8
Davis RE, Hondula DM, Sharif H (2020) Examining the diurnal temperature range enigma: why is human health related to the daily change in temperature? Int J Biometeorol 64(3):397–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01825-8
de Marco R et al (2012) Trends in the prevalence of asthma and allergic rhinitis in Italy between 1991 and 2010. Eur Respir J 39(4):883–892. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00061611
Diesel DA, Lebel JL, Tucker A (1991) Pulmonary particle deposition and airway mucociliary clearance in cold-exposed calves. Am J Vet Res 52(10):1665–1671
Evcimik MF, Dogru M, Cirik AA, Nepesov MI (2015) Adenoid hypertrophy in children with allergic disease and influential factors. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79(5):694–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.02.017
Graudenz GS et al (2006) The role of allergic rhinitis in nasal responses to sudden temperature changes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118(5):1126–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2006.07.005
Hu Y, Cheng J, Yin Y (2022) Association of childhood asthma with intra-day and inter-day temperature variability in Shanghai China. Environ Res 204(Pt D):112350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112350
Kakli HA, Riley TD (2016) Allergic Rhinitis. Prim Care 43(3):465–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2016.04.009
Khan DA (2014) Allergic rhinitis and asthma: epidemiology and common pathophysiology. Allergy Asthma Proc 35(5):357–361. https://doi.org/10.2500/aap.2014.35.3794
Kim JJ (2004) Ambient air pollution: health hazards to children. Pediatrics 114(6):1699–1707. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2004-2166
Kim H, Kim H, Lee JT (2018) Assessing the cold temperature effect on hospital visit by allergic rhinitis in Seoul, Korea. Science Total Environ 633:938–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.166
Okubo K et al (2017) Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2017. Allergol Int 66(2):205–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2016.11.001
Pawankar R, Bunnag C, Khaltaev N, Bousquet J (2012) Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma in Asia Pacific and the ARIA update 2008. World Allerg Organ J 5(Suppl 3):S212–S217. https://doi.org/10.1097/WOX.0b013e318201d831
Pawankar R, Canonica GW, Holgate ST et al (2013) World Allergy Organization (WAO) white book on allergy, Update 2013. World Allergy Organization, Milwaukee
Song X et al (2018) The impact of heat waves and cold spells on respiratory emergency department visits in Beijing, China. Science Total Environ 615:1499–1505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.108
Wang X, Cheng J, Ling L, Su H, Zhao D, Ni H (2020) Impact of temperature variability on childhood allergic rhinitis in a subtropical city of China. BMC Public Health 20(1):1418. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09531-6
Wei Q et al (2020) Diurnal temperature range and childhood asthma in Hefei, China: does temperature modify the association? Science Total Environ 724:138206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138206
Wise SK et al (2018) International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: allergic rhinitis. Int Forum Allerg Rhinol 8(2):108–352. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22073
Xie MY et al (2017) Effect of diurnal temperature range on the outpatient visits for acute bronchitis in children: a time-series study in Hefei, China. Public Health 144:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2016.12.016
Xu Z, Huang C, Su H, Turner LR, Qiao Z, Tong S (2013a) Diurnal temperature range and childhood asthma: a time-series study. Environ Health 12:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069x-12-12
Xu Z, Huang C, Turner LR, Su H, Qiao Z, Tong S (2013b) Is diurnal temperature range a risk factor for childhood diarrhea? PLoS ONE 8(5):e64713. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064713
Xu Z, Hu W, Tong S (2014) Temperature variability and childhood pneumonia: an ecological study. Environ Health 13(1):51. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069x-13-51
Ye X, Wolff R, Yu W, Vaneckova P, Pan X, Tong S (2012) Ambient temperature and morbidity: a review of epidemiological evidence. Environ Health Perspect 120(1):19–28. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1003198
Zhang Y (2014) Prevalence of allergic rhinitis in china. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 6(2):105–113. https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.2.105
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Plan of Gansu Province (21JR7RA864); Hospital Fund of Lanzhou University First Affiliated Hospital (ldyyyn2020-57).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KC and JJ contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by KC and YL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KC and YW, and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, K., Li, Y., Ji, J. et al. Diurnal temperature range impacts on outpatients department visits for allergic rhinitis in Lanzhou, China. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 96, 587–595 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-023-01951-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-023-01951-2