Abstract
Objective
Assess cadmium (Cd) exposure of adults living in two estuarine communities in Aratu bay, Bahia, Brazil and its association with effects on renal function.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 88 volunteers aged 17–55 years, living in the following two communities: Santa Luzia (SL) located more intimately in the bay and Cotegipe (CT), a bit further and closer to a ferro-manganese alloy plant. Cd in blood (CdB) and urine (CdU), along with blood lead (PbB) levels were determined by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Renal function was evaluated by the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and tubular cell biomarkers: retinol binding protein (RBP), β2-microglobulin (β2M), and N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase (NAG).
Results
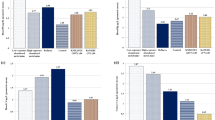
The median CdU levels in villagers of the two communities were 0.20 and 0.44 µg/g creat. and SL vs CT, respectively. Age range (> 35 years), cigarette smoking and lower family income were significantly associated with more elevated CdU levels. Multiple linear regression analysis demonstrated a significant association between LnCdU and LnRBP levels (β = 0.200, 95%CI 0.074–0.365) after adjusted for sex, urinary creatinine and blood lead levels.
Conclusion
These data show consistent evidences of association between Cd exposure and elevated tubular cell biomarker excretion in estuarine villagers living close to an industrial site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerstrom M, Sallsten G, Lundh T, Barregard L (2013) Associations between urinary excretion of cadmium and proteins in a nonsmoking population: renal toxicity or normal physiology? Environ Health Perspect 121:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp1205418
Araújo CFS, Lopes MV, Vasquez MR, Porcino TS, Ribeiro ASV, Rodrigues JLG, Oliveira SSP, Menezes-Filho JA (2016) Cadmium and lead in seafood from the Aratu Bay, Brazil and the human health risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 188:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5262-y
Bernard A (2004) Renal dysfunction induced by cadmium: biomarkers of critical effects. Biometals 17:519–523. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOM000004573175602b9
Bernard A (2016) Confusion about cadmium risks: the unrecognized limitations of an extrapolated paradigm. Environ Health Perspect 124:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp1509691
Boonprasert K, Kongjam P, Limpatanachote P, Ruengweerayut R, Na-Bangchang K (2011) Urinary and blood cadmium levels in relation to types of food and water intake and smoking status in a Thai population residing in cadmium-contaminated areas in Mae Sot Southeast Asian. J Trop Med Public Health 42:1521
Calao-Ramos C, Bravo AG, Paternina-Uribe R, Marrugo-Negrete J, Díez S (2021) Occupational human exposure to mercury in artisanal small-scale gold mining communities of Colombia. Environ Int 146:106216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106216
Chen X, Zhu G, Lei L, Jin T (2013) The association between blood pressure and blood cadmium in a Chinese population living in cadmium polluted area. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:595–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/jetap201306006
Chen X, Zhu G, Wang Z, Zhou H, He P, Liu Y, Jin T (2019) The association between lead and cadmium co-exposure and renal dysfunction. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 173:429–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/jecoenv201901121
Chen X, Chen X, Wang X, Wang M, Liang Y, Zhu G, Jin T (2021) The association between estimated glomerular filtration rate and cadmium exposure: an 8-year follow-up study. Int J Hyg Environ Health 235:113774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.1137747
Chunhabundit R (2016) Cadmium exposure and potential health risk from foods in contaminated area Thailand. Toxicol Res 32:65–72. https://doi.org/10.5487/TR2016321065
Cui X, Cheng H, Liu X, Giubilato E, Critto A, Sun H, Zhang L (2018) Cadmium exposure and early renal effects in the children and adults living in a tungsten-molybdenum mining area of South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:15089–15101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1631-0
Eom SY, Seo MN, Lee YS, Park KS, Hong YS, Sohn SJ, Kim YD, Choi BS, Lim JA, Kwon HJ, Kim H, Park JD (2017) Low-level environmental cadmium exposure induces kidney tubule damage in the general population of Korean adults. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 73:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0443-4
Franceschini N, Fry RC, Balakrishnan P, Navas-Acien A, Oliver-Williams C, Howard AG, Cole A, Haack K, Lang EM, Howard BV, Best LG, Francesconi KA, Goessler W, Umans G, Tellez-Plaza M (2017) Cadmium body burden and increased blood pressure in middle-aged American Indians: the Strong Heart Study. J Hum Hypertens 31:225–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh201667
IBGE—Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (2013) Bahia: Simões Filho. https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/. Accessed 11 Aug 2020
Jalili C, Kazemi M, Cheng H, Mohammadi H, Babaei A, Taheri E, Moradi S (2021) Associations between exposure to heavy metals and the risk of chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Toxicol 51:165–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2021.1891196
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives Meeting and World Health Organization (2011) Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants: seventy-third report of the joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives, vol, 73. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44813. Accessed 11 Aug 2020
Kubier A, Wilkin RT, Pichler T (2019) Cadmium in soils and groundwater: a review. Appl Geochem 108:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/japgeochem2019104388
Kummrow F, Silva FF, Kuno R, Souza AL, Oliveira PV (2008) Biomonitoring method for the simultaneous determination of cadmium and lead in whole blood by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for assessment of environmental exposure. Talanta 75:246–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/jtalanta200711003
Maciel CJ, Miranda GM, de Oliveira DP, de Siqueira MEP, Silveira JN, Leite EMA, da Silva JBB (2003) Determination of cadmium in human urine by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 491:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00820-1
Martins AC, Urbano MR, Lopes ACBA, Carvalho MFH, Buzzo ML, Docea AO, Mesas AE, Aschner M, Silva AMR, Silbergeld EK, Paoliello MMB (2020) Blood cadmium levels and sources of exposure in an adult urban population in Southern Brazil. Environ Res 187:109618. https://doi.org/10.1016/jenvres2020109618
Menezes-Filho JA, Paes CR, Pontes AMC, Moreira JC, Sarcinelli PN, Mergler D (2009) High levels of hair manganese in children living in the vicinity of a ferro-manganese alloy production plant. Neurotoxicology 30:1207–1213. https://doi.org/10.1016/jneuro200904005
Menezes-Filho JA, de Sousa Viana GF, Paes CR (2012) Determinants of lead exposure in children on the outskirts of Salvador Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 184:2593–2603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2137-0
Nordberg G, Jin T, Wu X, Lu J, Chen L, Liang Y, Lei L, Feng H, Bergdahl IA, Nordberg M (2012) Kidney dysfunction and cadmium exposure–factors influencing dose–response relationships. J Trace Elem Med Biol 26:197–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjtemb201203007
Olmedo P, Pla A, Hernández AF, Barbier F, Ayouni L, Gil F (2013) Determination of toxic elements (mercury, cadmium, lead, tin and arsenic) in fish and shellfish samples Risk assessment for the consumers. Environ Int 59:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/jenvint201305005
Orr SE, Bridges CC (2017) Chronic kidney disease and exposure to nephrotoxic. Metals Int J Mol Sci 18:1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051039
Osorio-Yañez C, Gelaye B, Miller RS, Enquobahrie DA, Baccarelli AA, Qiu C, Williams MA (2016) Associations of maternal urinary cadmium with trimester-specific blood pressure in pregnancy: role of dietary intake of micronutrients. Biol Trace Elem Res 174:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0705-4
Pereira AB, Nishida SK, Kirstajn GM (2006) Como avaliar o ritmo de filtração glomerular. J Bras Nefrol 28:S15–S18
Price RG, Taylor SA, Chivers I, Arce-Tomas M, Crutcher E, Franchini I, Alinovi R, Cavazzini S, Bergamaschi E, Mutti A, Vettori MV, Lauwerys R, Bernad A, Kabanda A, Roels H, Thielemans N, Hotz M, De Broe ME, Elseviers MM, Nuyts GD, Gelpi E, Hotter G, Rosello J, Ramis I, Stolte H (1996) Development and validation of new screening tests for nephrotoxic effects. Hum Exp Toxicol 15:S10–S19
Rahimzadeh MR, Rahimzadeh MR, Kazemi S, Moghadamnia AA (2017) Cadmium toxicity and treatment: an update Caspian. J Intern Med 8:135. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim83135
Rodrigues JL, Araújo CFS, Santos NR, Bandeira MJ, Anjos ALS, Carvalho CF, Lima CS, Abreu JNS, Mergler D, Menezes-Filho JA (2018) Airborne manganese exposure and neurobehavior in school-aged children living near a ferro-manganese alloy plant. Environ Res 167:66–77
Sánchez-González C, López-Chaves C, Gómez-Aracena J, Galindo P, Aranda P, Lopis J (2015) Association of plasma manganese levels with chronic renal failure. J Trace Elem Med Biol 31:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/jjtemb201504001
Satarug S (2018) Dietary cadmium intake and its effects on kidneys. Toxics 6:15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6010015
Satarug S, Swaddiwudhipong W, Ruangyuttikarn W, Nishijo M, Ruiz P (2013) Modeling cadmium exposures in low-and high-exposure areas in Thailand. Environ Health Perspect 121:531–536. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp1104769
Satarug S, Ruangyuttikarn W, Nishijo M, Ruiz P (2018) Urinary cadmium threshold to prevent kidney disease development. Toxics 6:26. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6020026
Satarug S, Boonprasert K, Gobe GC, Ruenweerayut R, Johnson DW, Na-Bangchang K, Vesey DA (2019) Chronic exposure to cadmium is associated with a marked reduction in glomerular filtration rate. Clin Kidney J 12:468–475. https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfy113
Sociedade Brasileira de Cardiologia; Sociedade Brasileira de Hipertensão; Sociedade Brasileira de Nefrologia (2010) VI Diretrizes Brasileiras de Hipertensão. http://www.rio.rj.gov.br/dlstatic/10112/4446958/4111920/diretriz.pdf. Accessed 11 Aug 2020
Song Y, Wang Y, Mao W, Sui H, Yong L, Yang D, Jiang D, Zhang L, Gong Y (2017) Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 12:e0177978. https://doi.org/10.1371/journalpone0177978
Storelli MM, Normanno G, Barone G, Dambrosio A, Errico L, Garofalo R, Giacominelli-Stuffler R (2012) Toxic metals (Hg, Cd, and Pb) in fishery products imported into Italy: suitability for human consumption. J Food Prot 75:189–194. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028XJFP-11-212
Sun H, Wang D, Zhou Z, Ding Z, Chen X, Xu Y, Huang L, Tang D (2016) Association of cadmium in urine and blood with age in a general population with low environmental exposure. Chemosphere 156:392–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/jchemosphere201605013
Tinkov AA, Filippini T, Ajsuvakova OP, Skalnaya MG, Aaseth J, Bjørklund G, Gatiatulina ER, Popova EV, Nemereshina ON, Huang P, Vinceti M, Skalny AV (2018) Cadmium and atherosclerosis: a review of toxicological mechanisms and a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Environ Res 162:240–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/jenvres201801008
Vacchi-Suzzi C, Kruse D, Harrington J, Levine K, Meliker JR (2016) Is urinary cadmium a biomarker of long-term exposure in humans? A review. Curr Environ Health Rep 3:450–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-016-0107-y
Vallée A, Gabet A, Grave C, Blacher J, Olié V (2020) Associations between urinary cadmium levels, blood pressure, and hypertension: the ESTEBAN survey. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:10748–10756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07249-6
Viana GF, de Carvalho CF, Nunes LS, Rodrigues JL, Ribeiro NS, de Almeida DA, Ferreira JRD, Abreu N, Menezes-Filho JA (2014) Noninvasive biomarkers of manganese exposure and neuropsychological effects in environmentally exposed adults in Brazil. Toxicol Lett 231:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/jtoxlet201406018
Wang X, Cui W, Wang M, Liang Y, Zhu G, Jin T, Chen X (2021) The association between life-time dietary cadmium intake from rice and chronic kidney disease. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111933
Watanabe Y, Nogawa K, Nishijo M, Sakurai M, Ishizaki M, Morikawa Y, Kido T, Nakagawa H, Suwazono Y (2020) Relationship between cancer mortality and environmental cadmium exposure in the general Japanese population in cadmium non-polluted areas. Int J Hyg Environ Health 223:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/jijheh201910005
Wu H, Liao Q, Chillrud SN, Yang Q, Huang L, Bi J, Yan B (2016) Environmental exposure to cadmium: health risk assessment and its associations with hypertension and impaired kidney function. Sci Rep 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29989
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the inhabitants of Santa Luzia and Cotegipe village for their patient collaboration as volunteers or supporters (teachers and community leaders) with this investigation
Funding
This investigation was partially funded by research grant numbers PROPCI-PROPG 02/2011, UFBA and PP047/2011 from Fundação de Apoio a Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia, Brazil (FAPESB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, JAM-F; methodology, JAM-F, GSV and LSN; validation JAM-F and LSN; formal analysis, VOM; investigation, LSN and NRdS; resources, JAM-F; data curation, JAM-F; writing—original draft preparation, VOM; writing—review and editing, JAM-F, NRdS and GSV; visualization, JAM-F; supervision JAM-F; project administration, JAM-F; funding acquisition, JAM-F.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
The project, entitled ‘Exposure to heavy metals and its effects on human health in a vulnerable population’ was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Climério de Oliveira Hospital of the Federal University of Bahia, Report Number 054/2011.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, V.O., Nunes, L.S., Viana, G.S. et al. Biomarkers of cadmium exposure and renal function in estuarine adult villagers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 95, 981–992 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01815-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01815-7