Abstract
Purpose
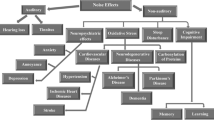
Noise is one of the major environmental health problems and is defined as any unpleasant sound. It was shown that prolonged exposure to noise was associated with progress of diseases. There is no study evaluating the effect of noise on the oxidative parameters of Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC), Total Oxidant Status (TOS) and DNA damage.
Aim
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of noise on TOS, TAC and DNA damage.
Methods
In this study, we included 100 textile factory workers affected by noise as a noise group, and 56 healthy volunteers employed as office workers in our hospital who were not exposed to noise as the control group. Blood samples were obtained from both the groups. Oxidative Stress (OS) was measured by Oxidative stress index (OSI), TOS and TAC. The DNA damage level was measured by 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG).
Results
8-OHdG (21.8 ± 12.0 vs. 14.7 ± 5.6 pg/ml, p = 0.001),TOS (14.1 ± 2.5 vs. 10.9 ± 1.5 mol H2O2 equivalent/l, p < 0.001), TAC (0.96 ± 0.19 vs. 1.54 ± 0.28 Trolox equivalent/l, p < 0.001) and OSI (1.52 ± 0.37, etc. 0.76 ± 0.35 arbitrary units, p < 0.001) were significantly higher in noise group compared to control group. Linear regression analysis showed that noise was the independent predictor of DNA damage (β = 0.310, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In this study, we showed that TOS and DNA damage were significantly higher in subjects exposed to noise when compared with subjects of the control group. Noise was the only independent predictor of the DNA damage. Therefore, early detection of DNA damage and increased OS, early corrective measures may delay the development and progression of diseases such as hypertension, arrhythmias.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atmaca E, Aksoy A (2009) Oxidative DNA damage and its chromatographic determination. YYU Vet FakDerg 20(2):79–83
Beydemir IMS (2019) Ache mRNA expression as a possible novel biomarker for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and Alzheimer’s disease, and its association with oxidative stress. Arch Physiol Biochem 14:1–8
Birben E, Şahiner UM, Sackesen C et al (2012) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J 5:9–19
De Martinis BS, Bianchi DLP, M, (2002) Methodology for urinary 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine analysis by hplc with electrochemical detection. Pharmacol Res 46(2):129–131
Demirbag R, Yilmaz R, Kocyigit A (2005) Relationship between DNA damage, total antioxidant capacity and coronary artery disease. Mutat Res 2:197–203
Dhalla NS, Temsah RM, Netticadan T (2000) Role of oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. J Hypertens 18:655–673
Doğan H, Çataltepe ÖA (2018) The effect of the noise on human health. JHSS 1(1-2–3):29–38
Erel O (2004) A novel automated direct measurement method for total antioxidant capacity using a new generation, more stable ABTS radical cation. Clin Biochem 37:277–285
Erel O (2005) A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem 38(12):1103–1111
FetonıAr GM, Rallı M et al (2009) The monitoring role of otoacoustic emissions and oxidative stress markers in the protective effects of antioxidant administration in noise exposed subjects: a pilot study. Med SciMonit 15(11):1–8
Frenzilli G, Lenzi P, Scarcelli V et al (2004) Effects of loud noise exposure on DNA integrity in rat adrenal gland. Environ Health Perspect 112:1671–1672
Işık M, Beydemir Ş, Yılmaz A et al (2017) Oxidative stress and mRNA expression of acetylcholinesterase in the leukocytes of ischemic patients. Biomed Pharmacother 87:561–567
Jayawardana TSS, Perera MYA, Wijesena GHD (2014) Analysis and control of noise in a textile factory. Int J Scient Res Public 4(12):1–7
KašparováS BV, Valko M et al (2005) Study of the oxidative stress in a rat model of chronic brain hypoperfusion. NeurochemInt 46:601–611
Kempen EE, Kruize H, Boshuizen H et al (2002) The association between noise exposure and blood pressure and ischemic heart disease: A meta-analysis. Environ Health Perspect 110:307–317
Lunec J, Blake D (1990). Oxygen free radicals: their relevance to disease processes. In: Cohen RD, Lewis B, Eds. The metabolic and molecular basis of acquired disease. London: Balliere Tindall, London. 189–212
McDorman KS, Pachkowski BF, Nakamura J (2005) Oxidative DNA damage from potassium bromate exposure in long-evans rats is not enhanced by a mixture of drinking water disinfection by-products. ChemBiol Interact 152(2–3):107–117
Medvedeva EA, Berezin II, Surkova EA et al (2016) Galectin-3 in patients with chronic heart failure: association with oxidative stress, inflammation, renal dysfunction and prognosis. Minerva Cardioangiol 64:595–602
Münzel T, Sorensen M, Schmidt E et al (2018) The adverse effects of environmental noise exposure on oxidative stress and cardiovascular risk. Antioxid Redox Signal 28(9):873–908
Muzet A (2007) Environmental noise, sleep and health. Sleep Med Rev 11:135–142
Nawaz SK, Hasnain S (2013) Occupational noise exposure may induce oxidative DNA damage. Pol J Environ Stud 22(5):1547–1551
Nordberg J, Arnér ES (2001) Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free Radical Biol Med 31(11):1287–1312
Ozcan O, Erdal H, Çakırca G et al (2015) Oxidative stress and its impact on intracellular lipids proteins and DNA. JCEI 6(3):331–336
Seidman M, Babu S, Tang W et al (2003) Effects of resveratrol on acoustic trauma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:463–470
Sies H (1991) Oxidative stress: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Med 91(3):31–38
Tascanov MB, Havlioglu S, Tanriverdi Z et al (2021a) Effect of noise on the electrocardiographic parameters. Int Arch Occup Environ Healthdoi. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01676-0
Tascanov MB, Tanriverdi Z, Gungoren F et al (2021b) Relationships between paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, total oxidant status, and DNA damage. Rev Port Cardiol 40(1):5–10
Toprak R, Aktürk N (2004). The negative effects of noise on human health. Turk Hij Den BiyolDerg 49–58
Valavanidis A, Vlachogianni T, FiotakisC, (2009) 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): a critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. J Environ Sci Health C Environ CarcinogEcotoxicol Rev 27:120–139
Vassalle C, Pratali L, Boni C et al (2008) An oxidative stress score as a combined measure of the pro-oxidant and anti-oxidant counterparts in patients with coronary artery disease. ClinBiochem 41:1162–1167
Vermeer W, Passchier W (2000) Noise exposure and public health. Environ Health Perspect 108:123
Yıldırım I, Kılınc M, Okur E et al (2007) The effects of noise on hearing and oxidative stress in textile workers. Ind Health 45(6):743–749
Zheng KC, Ariizumi M (2007) Modulations of immune functions and oxidative status induced by noise stress. J Occup Health 49(1):32–38
Funding
No funding source was used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have stated explicitly that there are no with this any financial support or relationships that may pose potential conflict of interest in this article.
Ethical considerations and disclosure
Ethics committee approval was obtained from the Noninvasive Clinic Ethical Committee of the Medical Faculty at Harran University (Decision dated 08.07.2019/No. 7).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Havlioglu, S., Tascanov, M.B., Koyuncu, I. et al. The relationship among noise, total oxidative status and DNA damage. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 95, 849–854 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01774-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01774-z