Abstract
Objectives
Sensitive and easily applicable methods are needed for early detection of central nervous system adverse effects related to occupational solvent exposure. The present study evaluates how symptom screening works in practice.
Methods
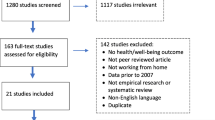
A cross-sectional questionnaire survey was conducted on 2,000 construction workers, including painters and carpenters, in Finland. Scores were calculated for symptoms relevant for chronic solvent encephalopathy (CSE). Responses on exposure and health were compared between subjects with high score (N = 28) and all other respondents. The respondents with the highest scores, regardless of their occupation and exposure, were invited for clinical examination to investigate the aetiologies of the symptoms. If the examination resulted in a suspicion of CSE, a multidisciplinary differential diagnostic follow-up procedure was performed.
Results
The respondents with highest symptom scores were more exposed to solvents than those with lower scores (P < 0.001) and reported more often physician-diagnosed diseases, especially psychiatric disorders (P < 0.001). They also consumed more alcohol (P = 0.005) and were more often unemployed or unable to work (P < 0.001). In the clinical examination, sleep disturbances, somatic disorders, depression, unemployment, and alcohol use were commonly found in addition to considerable solvent exposure history and clinical neurological findings. Further examinations and a diagnostic follow-up verified three cases of encephalopathy. One case was a CSE, an occupational disease. The other two encephalopathy cases had multifactorial aetiology including solvents.
Conclusions
Screening in active workforce for symptoms of cognitive dysfunction identifies highly solvent-exposed workers and also reveals occupational and non-occupational cases of encephalopathy. Evaluation of differential diagnostic conditions is essential in the detection of CSE. A stepwise model is proposed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akila R, Muller K, Kaukiainen A, Sainio M (2006) Memory performance profile in occupational chronic solvent encephalopathy suggests working memory dysfunction. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 28:1307–1326. doi:10.1080/13803390500477515
Arlien-Soborg P, Bruhn P, Gyldensted C, Melgaard B (1979) Chronic painters’ syndrome. Chronic toxic encephalopathy in house painters. Acta Neurol Scand 60:149–156
Attia JR, D’Este C, Schofield PW, Brown AM, Gibson R, Tavener M et al (2006) Mental health in F-111 maintenance workers: the study of Health Outcomes in Aircraft Maintenance Personnel (SHOAMP) general health and medical study. J Occup Environ Med 48:682–691. doi:10.1097/01.jom.0000205985.00559.84
Banno K, Kryger MH (2007) Sleep apnea: clinical investigations in humans. Sleep Med 8:400–426. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2007.03.003
Beck AT, Steer RA, Garbin MG (1988) Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: twenty-five years of evaluation. Clin Psychol Rev 8:77–100. doi:10.1016/0272-7358(88)90050-5
Bush K, Kivlahan DR, McDonell MB, Fihn SD, Bradley KA (1998) The AUDIT alcohol consumption questions (AUDIT-C): an effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Ambulatory Care Quality Improvement Project (ACQUIP). Alcohol use disorders identification test. Arch Intern Med 158:1789–1795. doi:10.1001/archinte.158.16.1789
Caldwell DJ, Armstrong TW, Barone NJ, Suder JA, Evans MJ (2000) Hydrocarbon solvent exposure data: compilation and analysis of the literature. AIHAJ 61:881–894. doi:10.1080/15298660008984602
Carter N, Iregren A, Söderman E, Olson BA, Karlson B, Lindelöf B et al (2002) EUROQUEST—a questionnaire for solvent related symptoms: factor structure, item analysis and predictive validity. Neurotoxicology 23:711–717. doi:10.1016/S0161-813X(02)00039-6
Chouaniere D, Cassitto MG, Spurgeon A, Verdier A, Gilioli R (1997) An international questionnaire to explore neurotoxic symptoms. Environ Res 73:70–72. doi:10.1006/enrs.1997.3701
Chouaniere D, Wild P, Fontana JM, Hery M, Fournier M, Baudin V et al (2002) Neurobehavioral disturbances arising from occupational toluene exposure. Am J Ind Med 41:77–88. doi:10.1002/ajim.10030
CIOMS (2002) International ethical guidelines for biomedical research involving human subjects. Geneva, The Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (CIOMS)
Cranmer JM, Goldberg L (1987) Human aspects of solvent neurobehavioral effects. Report of the workshop session on clinical and epidemiological topics. In: Proceedings of the work-shop on neuro-behavioral effect of solvents. Neurotoxicology 7:45–56
Daniell WE, Claypoole KH, Checkoway H, Smith-Weller T, Dager SR, Townes BD et al (1999) Neuropsychological function in retired workers with previous long-term occupational exposure to solvents. Occup Environ Med 56:93–105
Decopaint (2000). Study on the potential for reducing emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOC) due to the use of decorative paints and varnishes for professional and non-professional use. EC DG Environment Tender E1/ETU/980084. Final report, Contributors Chemiewinkel Enterprise Ireland WIMM http://www.europa.eu.int/comm/environment/air/pdf/decopaint.pdf
Deschamps D, Geraud C, Dally S (2001) Cognitive functions in workers exposed to toluene: evaluation at least 48 hours after removal from exposure. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 74:285–288. doi:10.1007/PL00007945
Dick F, Semple S, Chen R, Seaton A (2000) Neurological deficits in solvent-exposed painters: a syndrome including impaired colour vision, cognitive defects, tremor and loss of vibration sensation. QJM 93:655–661. doi:10.1093/qjmed/93.10.655
Dick F, Semple S, Osborne A, Soutar A, Seaton A, Cherrie JW et al (2002) Organic solvent exposure, genes, and risk of neuropsychological impairment. QJM 95:379–387. doi:10.1093/qjmed/95.6.379
Dick FD (2006) Solvent neurotoxicity. Occup Environ Med 63: 221–226, 179
Edling C, Ekberg K, Ahlborg G Jr, Alexandersson R, Barregård L, Ekenvall L et al (1990) Long-term follow up of workers exposed to solvents. Br J Ind Med 47:75–82
Friis L, Norback D, Edling C (1997) Occurrence of neuropsychiatric symptoms at low levels of occupational exposure to organic solvents and relationships to health, lifestyle, and stress. Int J Occup Environ Health 3:184–189
Heiskel H, Gunzenhäuser D, Seidler A, Volk S, Pflug B, Kauppinen T et al (2002) Sleep apnea and occupational exposure to solvents. Scand J Work Environ Health 28:249–255
Ihrig A, Triebig G, Dietz MC (2001) Evaluation of a modified German version of the Q16 questionnaire for neurotoxic symptoms in workers exposed to solvents. Occup Environ Med 58:19–23. doi:10.1136/oem.58.1.19
Juntunen J (1993) Neurotoxic syndromes and occupational exposure to solvents. Environ Res 60:98–111. doi:10.1006/enrs.1993.1019
Karlson B, Österberg K, Orbaek P (2000) Euroquest: the validity of a new symptom questionnaire. Neurotoxicology 21:783–789
Kaukiainen A, Riala R, Martikainen R, Akila R, Reijula K, Sainio M (2004a) Solvent-related health effects among construction painters with decreasing exposure. Am J Ind Med 46:627–636. doi:10.1002/ajim.20107
Kaukiainen A, Vehmas T, Rantala K, Nurminen M, Martikainen R, Taskinen H (2004b) Results of common laboratory tests in solvent-exposed workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 77:39–46. doi:10.1007/s00420-003-0476-z
Kaukiainen A, Riala R, Martikainen R, Reijula K, Riihimäki H, Tammilehto L (2005) Respiratory symptoms and diseases among construction painters. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 78:452–458. doi:10.1007/s00420-004-0600-8
Kezic S, Calkoen F, Wenker MA, Jacobs JJ, Verberk MM (2006) Genetic polymorphism of metabolic enzymes modifies the risk of chronic solvent-induced encephalopathy. Toxicol Ind Health 22:281–289. doi:10.1177/0748233706070287
Kiesswetter E, Sietmann B, Seeber A (1997) Standardization of a questionnaire for neurotoxic symptoms. Environ Res 73:73–80. doi:10.1006/enrs.1997.3716
Leira HL, Myhr G, Nilsen G, Dale LG (1992) Cerebral magnetic resonance imaging and cerebral computerized tomography for patients with solvent-induced encephalopathy. Scand J Work Environ Health 18:68–70
Lundberg I, Högberg M, Michelsen H, Nise G, Hogstedt C (1997) Evaluation of the Q16 questionnaire on neurotoxic symptoms and a review of its use. Occup Environ Med 54:343–350
Lundberg I, Michelsen H, Nise G, Hogstedt C, Högberg M, Alfredsson L et al (1995) Neuropsychiatric function of housepainters with previous long-term heavy exposure to organic solvents. Scand J Work Environ Health 21(Suppl 1):1–44
Mikkelsen S (1997) Epidemiological update on solvent neurotoxicity. Environ Res 73:101–112. doi:10.1006/enrs.1997.3706
Mikkelsen S, Jorgensen M, Browne E, Gyldensted C (1988) Mixed solvent exposure and organic brain damage. A study of painters. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 118:1–143
Morrow LA, Gibson C, Bagovich GR, Stein L, Condray R, Scott A (2000) Increased incidence of anxiety and depressive disorders in persons with organic solvent exposure. Psychosom Med 62:746–750
Nasterlack M, Dietz MC, Frank KH, Hacke W, Scherg H, Schmittner H et al (1999) A multidisciplinary cross-sectional study on solvent-related health effects in painters compared with construction workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 72:205–214. doi:10.1007/s004200050363
Nordling Nilson L, Barregård L, Sällsten G, Hagberg S (2007) Self-reported symptoms and their effects on cognitive functioning in workers with past exposure to solvent-based glues: an 18-year follow-up. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 81:69–79. doi:10.1007/s00420-007-0192-1
Parkinson DK, Bromet EJ, Cohen S, Dunn LO, Dew MA, Ryan C et al (1990) Health effects of long-term solvent exposure among women in blue-collar occupations. Am J Ind Med 17:661–675. doi:10.1002/ajim.4700170602
Päällysaho J, Näsänen R, Mäntyjärvi M, Kaukiainen A, Sainio M (2007) Colour vision defects in occupational chronic solvent encephalopathy. Hum Exp Toxicol 26:375–383. doi:10.1177/0960327107076820
Riala R, Kalliokoski P, Pyy L, Wickström G (1984) Solvent exposure in construction and maintenance painting. Scand J Work Environ Health 10:263–266
Ridgway P, Nixon TE, Leach JP (2003) Occupational exposure to organic solvents and long-term nervous system damage detectable by brain imaging, neurophysiology or histopathology. Food Chem Toxicol 41:153–187. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(02)00214-4
Riihimäki H, Kurppa K, Karjalainen A, Palo L, Jolanki R, Keskinen H et al (2004) Occupational diseases in Finland in 2002 New cases of occupational diseases reported to the Finnish Register of Occupational Diseases. Helsinki, Finnish Institute Of Occupational Health
Rouch I, Wild P, Fontana JM, Chouaniere D (2003) Evaluation of the French version of EUROQUEST: a questionnaire for neurotoxic symptoms. Neurotoxicology 24:541–546. doi:10.1016/S0161-813X(03)00075-5
Rutchik JS, Wittman RI (2004) Neurologic issues with solvents. Clin Occup Environ Med 4:621–656. v–vi. doi:10.1016/j.coem.2004.03.010
Saddik B, Williamson A, Nuwayhid I, Black D (2005) The effects of solvent exposure on memory and motor dexterity in working children. Public Health Rep 120:657–663
Schofield PW, Gibson R, Tavener M, Attia JR, D’Este C, Guest M et al (2006) Neuropsychological health in F-111 aircraft maintenance workers. Neurotoxicology 27:852–860. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2006.02.002
Semple S (2004) Dermal exposure to chemicals in the workplace: just how important is skin absorption? Occup Environ Med 61:376–382. doi:10.1136/oem.2003.010645
Siebert U, Rothenbacher D, Daniel U, Brenner H (2001) Demonstration of the healthy worker survivor effect in a cohort of workers in the construction industry. Occup Environ Med 58:774–779. doi:10.1136/oem.58.12.774
Spurgeon A (2006) Watching paint dry: organic solvent syndrome in late-twentieth-century Britain. Med Hist 50:167–188
Triebig G, Hallermann J (2001) Survey of solvent related chronic encephalopathy as an occupational disease in European countries. Occup Environ Med 58:575–581. doi:10.1136/oem.58.9.575
van der Hoek JA, Verberk MM, Hageman G (2000) Criteria for solvent-induced chronic toxic encephalopathy: a systematic review. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 73:362–368. doi:10.1007/s004200000119
van der Hoek JA, Verberk MM, van der Laan G, Hageman G (2001) Routine diagnostic procedures for chronic encephalopathy induced by solvents: survey of experts. Occup Environ Med 58:382–385. doi:10.1136/oem.58.6.382
van Hout MS, Schmand B, Wekking EM, Deelman BG (2006) Cognitive functioning in patients with suspected chronic toxic encephalopathy: evidence for neuropsychological disturbances after controlling for insufficient effort. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:296–303. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.047167
van Thriel C, Kiesswetter E, Schaper M, Blaszkewicz M, Golka K, Juran S et al (2007) From neurotoxic to chemosensory effects: new insights on acute solvent neurotoxicity exemplified by acute effects of 2-ethylhexanol. Neurotoxicology 28:347–355. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2006.03.008
WHO (1985) Chronic effects of organic solvents on the central nervous system and diagnostic criteria. Copenhagen, WHO
WHO (2005) ICD-10. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision. Geneva, WHO
Viaene MK, Pauwels W, Veulemans H, Roels HA, Masschelein R (2001) Neurobehavioural changes and persistence of complaints in workers exposed to styrene in a polyester boat building plant: influence of exposure characteristics and microsomal epoxide hydrolase phenotype. Occup Environ Med 58:103–112. doi:10.1136/oem.58.2.103
Williamson A (2007) Using self-report measures in neurobehavioural toxicology: can they be trusted? Neurotoxicology 28:227–234. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2006.03.009
Acknowledgments
This study was carried out at the Finnish Institute of Occupational Health (FIOH) in co-operation with the Federation of Painting and Decoration Contractors in Finland, the Finnish Construction Trade Union, and the Finnish Association of Paint Manufacturers. Financial support was received from the Finnish Work Environment Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaukiainen, A., Akila, R., Martikainen, R. et al. Symptom screening in detection of occupational solvent-related encephalopathy. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 82, 343–355 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0341-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-008-0341-1