Abstract
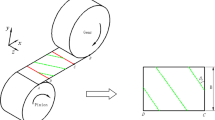
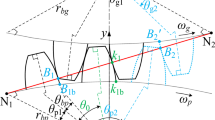
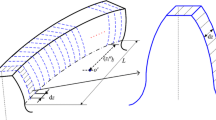
Helical gear teeth are subject to spalling, pitting and other failures under prolonged operation, which can contribute to a reduction in the time-varying meshing stiffness (TVMS) of the gear. The shape of the depression formed by the absence of the gear tooth surface is irregular in practice. Firstly, an irregular-shaped pitting model is constructed by the slicing method. On the premise of improving the transition curve, the TVMS calculation equations under the irregular pitting model are derived considering the effect of axial stiffness. Then, a randomly distributed tooth surface pitting evolution model was established by the random pitting generation function, and the effects of three different failure degrees from slight to severe pitting on the TVMS are evaluated. Eventually, the faulty helical gear pairs are constructed in Solidworks and simulated by the finite element method (FEM), verifying that the irregular pitting evolution model and calculation method proposed in this paper are effective.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, R.-B., Yang, Z.-B., Gryllias, K., Chen, X.-F.: Cyclostationary modeling for local fault diagnosis of planetary gear vibration signals. J. Sound Vib. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2020.115175
Kumar, A., Gandhi, C.P., Zhou, Y., Kumar, R., Xiang, J.: Latest developments in gear defect diagnosis and prognosis: a review. Measurement (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.107735
Sun, R.-B., Yang, Z.-B., Yang, L.-D., Qiao, B.-J., Chen, X.-F., Gryllias, K.: Planetary gearbox spectral modeling based on the hybrid method of dynamics and LSTM. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106611
Mohammed, O.D., Rantatalo, M.: Gear fault models and dynamics-based modelling for gear fault detection – a review. Eng. Fail. Anal. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104798
Huangfu, Y., Zeng, J., Ma, H., Dong, X., Han, H., Zhao, Z.: A flexible-helical-geared rotor dynamic model based on hybrid beam-shell elements. J. Sound Vibr. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2021.116361
Chaari, F., Baccar, W., Abbes, M.S., Haddar, M.: Effect of spalling or tooth breakage on gearmesh stiffness and dynamic response of a one-stage spur gear transmission. Eur. J. Mech. A. Solids 27, 691–705 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2007.11.005
Chen, Z., Shao, Y.: Mesh stiffness calculation of a spur gear pair with tooth profile modification and tooth root crack. Mech. Mach. Theory 62, 63–74 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2012.10.012
Chen, W., Lei, Y., Fu, Y., Hou, L.: A study of effects of tooth surface wear on time-varying mesh stiffness of external spur gear considering wear evolution process. Mech. Mach. Theory (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2020.104055
Chen, K., Huangfu, Y., Zhao, Z., Ma, H., Dong, X.: Dynamic modeling of the gear-rotor systems with spatial propagation crack and complicated foundation structure. Mech. Mach. Theory (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2022.104827
Liang, X., Zhang, H., Zuo, M.J., Qin, Y.: Three new models for evaluation of standard involute spur gear mesh stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 101, 424–434 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.09.005
Chen, Z., Zhai, W., Shao, Y., Wang, K., Sun, G.: Analytical model for mesh stiffness calculation of spur gear pair with non-uniformly distributed tooth root crack. Eng. Fail. Anal. 66, 502–514 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.05.006
Xie, C., Shu, X.: A new mesh stiffness model for modified spur gears with coupling tooth and body flexibility effects. Appl. Math. Model. 91, 1194–1210 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2020.11.003
Wang, Q., Chen, K., Zhao, B., Ma, H., Kong, X.: An analytical-finite-element method for calculating mesh stiffness of spur gear pairs with complicated foundation and crack. Eng. Fail. Anal. 94, 339–353 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.08.013
Natali, C., Battarra, M., Dalpiaz, G., Mucchi, E.: A critical review on FE-based methods for mesh stiffness estimation in spur gears. Mech. Mach. Theory. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2021.104319
Jia, S., Howard, I.: Comparison of localised spalling and crack damage from dynamic modelling of spur gear vibrations. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 20, 332–349 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.02.009
Ma, H., Li, Z., Feng, M., Feng, R., Wen, B.: Time-varying mesh stiffness calculation of spur gears with spalling defect. Eng. Fail. Anal. 66, 166–176 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.04.025
Chen, Z., Zhang, J., Zhai, W., Wang, Y., Liu, J.: Improved analytical methods for calculation of gear tooth fillet-foundation stiffness with tooth root crack. Eng. Fail. Anal. 82, 72–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.08.028
Liang, X., Zuo, M.J., Pandey, M.: Analytically evaluating the influence of crack on the mesh stiffness of a planetary gear set. Mech. Mach. Theory 76, 20–38 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2014.02.001
Liu, Y., Shi, Z., Shen, G., Zhen, D., Wang, F., Gu, F.: Evaluation model of mesh stiffness for spur gear with tooth tip chipping fault. Mech. Mach. Theory. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2020.104238
Jiang, H., Shao, Y., Mechefske, C.K.: Dynamic characteristics of helical gears under sliding friction with spalling defect. Eng. Fail. Anal. 39, 92–107 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.01.008
Liang, X., Zhang, H., Liu, L., Zuo, M.J.: The influence of tooth pitting on the mesh stiffness of a pair of external spur gears. Mech. Mach. Theory 106, 1–15 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2016.08.005
Saxena, A., Parey, A., Chouksey, M.: Time varying mesh stiffness calculation of spur gear pair considering sliding friction and spalling defects. Eng. Fail. Anal. 70, 200–211 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.09.003
Luo, Y., Baddour, N., Han, G., Jiang, F., Liang, M.: Evaluation of the time-varying mesh stiffness for gears with tooth spalls with curved-bottom features. Eng. Fail. Anal. 92, 430–442 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.06.010
Luo, Y., Baddour, N., Liang, M.: A shape-independent approach to modelling gear tooth spalls for time varying mesh stiffness evaluation of a spur gear pair. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 120, 836–852 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.11.008
Lei, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, D., Yang, X., Liu, H., Lin, J.: A probability distribution model of tooth pits for evaluating time-varying mesh stiffness of pitting gears. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 106, 355–366 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.01.005
Chen, T., Wang, Y., Chen, Z.: A novel distribution model of multiple teeth pits for evaluating time-varying mesh stiffness of external spur gears. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 129, 479–501 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.04.029
Meng, Z., Wang, F., Shi, G.: A novel evolution model of pitting failure and effect on time -varying meshing stiffness of spur gears. Eng. Fail. Anal. 120, 105068 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.105068
El Yousfi, B., Soualhi, A., Medjaher, K., Guillet, F.: New approach for gear mesh stiffness evaluation of spur gears with surface defects. Eng. Fail. Anal. 116, 104740 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104740
Sun, R., Song, C., Zhu, C., Yang, X., Li, X.: Computational study of pitting defect influence on mesh stiffness for straight beveloid gear. Eng. Fail. Anal. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104971
Huangfu, Y., Chen, K., Ma, H., Che, L., Li, Z., Wen, B.: Deformation and meshing stiffness analysis of cracked helical gear pairs. Eng. Fail. Anal. 95, 30–46 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.08.028
Chen, K., Ma, H., Che, L., Li, Z., Wen, B.: Comparison of meshing characteristics of helical gears with spalling fault using analytical and finite-element methods. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 121, 279–298 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.11.023
Wang, S., Zhu, R.: An improved mesh stiffness calculation model for cracked helical gear pair with spatial crack propagation path. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 172, 108989 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2022.108989
Wu, X., Luo, Y., Li, Q., Shi, J.: A new analytical model for evaluating the time-varying mesh stiffness of helical gears in healthy and spalling cases. Eng. Fail. Analysis. 131, 105842 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105842
Li, S., Kahraman, A.: A micro-pitting model for spur gear contacts. Int. J. Fatigue 59, 224–233 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2013.08.015
Tan, C.K., Irving, P., Mba, D.: A comparative experimental study on the diagnostic and prognostic capabilities of acoustics emission, vibration and spectrometric oil analysis for spur gears. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 21, 208–233 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.09.015
Piegl, L., Tiller, W.: The NURBS Book. Springer (1996)
Xie, C., Hua, L., Han, X., Lan, J., Wan, X., Xiong, X.: Analytical formulas for gear body-induced tooth deflections of spur gears considering structure coupling effect. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 148, 174–190 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.08.022
Chen, Z., Zhou, Z., Zhai, W., Wang, K.: Improved analytical calculation model of spur gear mesh excitations with tooth profile deviations. Mech. Mach. Theory. 149, 103838 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2020.103838
Wei, J., Zhang, A., Wang, G., Qin, D., Lim, T.C., Wang, Y., Lin, T.: A study of nonlinear excitation modeling of helical gears with modification: theoretical analysis and experiments. Mech. Mach. Theory 128, 314–335 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2018.06.005
Ma, H., Zeng, J., Feng, R., Pang, X., Wang, Q., Wen, B.: Review on dynamics of cracked gear systems. Eng. Fail. Anal. 55, 224–245 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.06.004
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 52075470, in part by the Central government guides local science and technology development Foundation under Grant 206Z4301G, in part by the introduction of foreign intellectual project of Hebei Province, in part by the Cultivation Project for Basic Research and Innovation of Yanshan University under Grant 2021LGZD006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial or personal interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Z., Pang, X., Hao, G. et al. A novel analytical model for evaluating the time-varying meshing stiffness of helical gears under irregular pitting failure. Arch Appl Mech 93, 3775–3795 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-023-02460-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-023-02460-x