Abstract
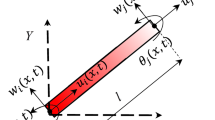
Periodic truss materials can be regarded as a kind of phononic crystals, which have both excellent elastic wave band gap properties and good design ability. By reasonably changing the parameters of truss materials, the dispersion relationship of regular distribution can be achieved, so as to realize the tuning of different phases. Due to the variety of microstructure configurations of truss materials, it provides a broad space for the design of acoustic/elastic metasurfaces. In this paper, we design a new type of lattice truss material metasurfaces, which can adjust the phase 0–2π range of flexural wave by adjusting the vertex angle of single-cell without changing the external size of phononic crystal. According to the Generalized Snell's Law, the abnormal refraction, beam focusing and non-paraxial self-acceleration of flexural waves can be realized by reasonable arrangement of truss materials with different vertex angles. Moreover, the operating frequency domain of metasurfaces can be widened and adjusted by increasing or decreasing the number of truss material microstructure arrays. This provides more possibilities for the design of elastic wave metasurfaces.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen, J., et al.: Exploration of amphoteric and negative refraction imaging of acoustic sources via active metamaterials. Phys. Lett. A 337(34–36), 2199–2206 (2013)
Ruan, Y., et al.: Reflective elastic metasurface for flexural wave based on surface impedance model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 212, 106859 (2021)
Assouar, B., Liang, B., Ying, Wu., Li, Y., Cheng, J.-C., Jing, Y.: Acoustic metasurfaces. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3(12), 460–472 (2018)
Yu, N., et al.: Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction. Science 334(6054), 333–337 (2011)
Ahn, B., et al.: Topology optimization of metasurfaces for anomalous reflection of longitudinal elastic waves. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 357 (2019)
Zhu, H., et al.: Experimental study of vibration isolation in thin-walled structural assemblies with embedded total-internal-reflection metasurfaces. J. Sound Vib. 456 (2019)
Ruan, Y., et al.: Retroreflection of flexural wave by using elastic metasurface. J. Appl. Phys. 128(4), 045116 (2020)
Li, P., et al.: Stepped acoustic metasurface with simultaneous modulations of phase and amplitude. Appl. Phys. Express. 14(12) (2021)
Rong, J., et al.: Multifunctional elastic metasurface design with topology optimization. Acta Mater. 185, 382–399 (2020)
Lee, S.W., et al.: Broad-angle refractive transmodal elastic metasurface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117(21) (2020)
Jin, Y., et al.: Elastic metasurfaces for deep and robust subwavelength focusing and imaging. Phys. Rev. Appl. 15(2), 024005 (2021)
Su, X., et al.: Elastic metasurfaces for splitting SV- and P-waves in elastic solids. J. Appl. Phys. 123(9), 091701 (2018)
Zhao, S., et al.: Delivering sound energy along an arbitrary convex trajectory. Sci. Rep. 4(1) (2015)
Hu, Y., et al.: Dielectric metasurface zone plate for the generation of focusing vortex beams. PhotoniX 2(1) (2021)
Yaw, Z., et al.: Stiffness Tuning a functional-switchable active coding elastic metasurface. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 207(80), 106654 (2021)
Lin, Z., et al.: Elastic metasurfaces for low-frequency flexural wavefront control. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2020 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. 2020. 7(32nd Conference on Mechanical Vibration and Noise).
Zhao, T., et al.: Reflected flexural wave manipulation based on ultra-thin elastic metasurface. In: 2020 15th SPAWDA (2021)
Kim, M.S., et al.: Elastic wave energy entrapment for reflectionless metasurface. Phys. Rev. Appl. 12(5), 054036 (2020)
Wang, W., et al.: Experimental realization of a pillared metasurface for flexural wave focusing. APL Mater. 9(5), 051125 (2021)
Rong, J., et al.: Frequency-coded passive multifunctional elastic metasurfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(50), 2005285 (2020)
Cao, L., et al.: Disordered elastic metasurfaces. Phys. Rev. Appl. 13(1), 014054 (2021)
Zhang, J., et al.: Metasurface constituted by thin composite beams to steer flexural waves in thin plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 162, 14–20 (2019)
Lin, Z., et al.: Elastic metasurfaces for full wavefront control and low-frequency energy harvesting. J. Vib. Acoust. 143(6), 1–22 (2021)
Xu, W., et al.: Anomalous refraction control of mode-converted elastic wave using compact notch-structured metasurface. Mater. Res. Express 6(6), 065802 (2019)
Xu, W., et al.: Anomalous refraction manipulation of Lamb waves using single-groove metasurfaces. Phys. Scripta 94(10), 105807 (2019)
Lin, Z., et al.: Modular elastic metasurfaces with mass oscillators for transmitted flexural wave manipulation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 54(25) (2021)
Xuan, C., et al.: Broadband tunable elastic metastructure based on one-dimensional phononic crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 129, 245102 (2021)
Lin, Z., et al.: Modulation and research of ultra wideband acoustic vortex device. J. Shenyang Aerosp. Univ. 38(03), 7–13 (2021). ((In Chinese))
Lin, Z., et al.: Gradient folding metasurfaces with simultaneous phase and amplitude modulation. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 35(12) 2021
Zhang, W., Ma, Z., Hu, P.: Mechanical properties of a cellular vehicle body structure with negative Poisson’s ratio and enhanced strength. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 33(4), 342–349 (2013)
Gong, X., Huang, J., Scarpa, F., et al.: Zero Poisson’s ratio cellular structure for two-dimensional morphing applications. Compos. Struct. 134(15), 384–392 (2015)
Wei, K., et al.: Planar lattices with tailorable coefficient of thermal expansion and high stiffness based on dual-material triangle unit. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 86, 173–191 (2016)
Zhang, Y.C., et al.: A new design of dual-constituent triangular lattice metamaterial with unbounded thermal expansion. Acta. Mech. Sin. 035(003), 507–517 (2019)
Huang, Y., Liu, S., Zhao, J.: Optimal design of two-dimensional band-gap materials for uni-directional wave propagation. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48(3), 487–499 (2013)
Lv, S., Weikai, Xu., Bai, L., Qi, W., Wang, W.: Thermal tuning of band gap properties in planar stretch-dominated lattices with tailorable coefficient of thermal expansion. Appl. Phys. A 127, 425 (2021)
Weikai, Xu., Lv, S., Liu, C., Qi, W., Wang, W.: Multifunctional design of triangular lattice metamaterials with customizable thermal expansion and tunable band gap properties. J. Appl. Phys. 130(8), 085106 (2021)
Hang, Xu., Farag, A., Pasini, D.: Multilevel hierarchy in bi-material lattices with high specific stiffness and unbounded thermal expansion. Acta Mater. 134, 155–166 (2017)
Chen, J., Wentao, Xu., Wei, Z., Wei, K., Yang, X.: Stiffness characteristics for a series of lightweight mechanical metamaterials with programmable thermal expansion. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 202–203, 106527 (2021)
Chen, J., Wang, H., Wang, K., Wei, Z., Wentao, Xu., Wei, K.: Mechanical performances and coupling design for the mechanical metamaterials with tailorable thermal expansion. Mech. Mater. 165, 104176 (2022)
Yuan, S., et al.: Switchable multifunctional fish-bone elastic metasurface for transmitted plate wave modulation. J. Sound Vib. 470, 115168 (2020)
Su, X., et al.: Focusing, refraction, and asymmetric transmission of elastic waves in solid metamaterials with aligned parallel gaps. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 139(6), 3386–3394 (2016)
Zhu, H., et al.: Anomalous refraction of acoustic guided waves in solids with geometrically tapered metasurfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1171, 034302 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11502149, 11302135), Natural Science Foundation of Suqian City (No. K202124), Scientific Research Foundation of Suqian University. The financial contributions are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Yang, Z., Wang, W. et al. Design of elastic wave metasurfaces based on lattice truss material. Arch Appl Mech 92, 2137–2149 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02166-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02166-6