Abstract
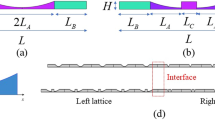
In the view of the potential for vibration control and energy harvesting of the acoustic black hole (ABH), the transfer matrix scheme combined with the finite element method is utilized to establish the governing equation of a one-dimensional ABH beams attached with a damping layer. According to the continuous condition of generalized forces and displacements between the two adjacent uniform sections, the transfer relationship is derived. The energy ratio is defined as the ratio of the edge part to the entire wedge, which illustrates the energy concentration effect. A damping layer is introduced for controlling the fluctuation. Numerical simulation is presented to illustrate the effectiveness of presented control method. The influences of physical parameters such as excitation frequency, power exponent and thickness of the damping layer on energy concentration are discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pekeris, C.L.: Theory of propagation of sound in a half-space of variable sound velocity under conditions of formation of a shadow zone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 18, 295–315 (1946)
Krylov, V.V.: Conditions for validity of the geometrical-acoustics approximation in application to waves in an acute-angle solid wedge. Soviet Phys. Acoust. 35(2), 176–180 (1989)
Krylov, V.V., Tilman, F.J.B.S.: Acoustic ‘black holes’ for flexural waves as effective vibration dampers. J. Sound Vib. 274(3–5), 605–619 (2004)
Krylov, V.V., Winward, R.E.T.B.: Experimental investigation of the acoustic black hole effect for flexural waves in tapered plates. J. Sound Vib. 300(1), 43–49 (2007)
Kralovic, V., Bowyer, E. P., Krylov, V. V., et al.: Experimental study on damping of flexural waves in rectangular plates by means of one-dimensional acoustic ‘black holes’ 14th International Acoustic Conference. (2009)
Denis, V., Pelat, A., Gautier, F., et al.: Modal overlap factor of a beam with an acoustic black hole termination. J. Sound Vib. 333(12), 2475–2488 (2014)
Bowyer, E.P., Krylov, V.V.: Sound radiation of rectangular plates containing tapered indentations of power-law profile. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 132(3), 2041 (2012)
Zhao, L., Conlon, S.C., Semperlotti, F.: Broadband energy harvesting using acoustic black hole structural tailoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(6), 5021 (2014)
Zhao, L., Conlon, S.C., Semperlotti, F.: An experimental study of vibration based energy harvesting in dynamically tailored structures with embedded acoustic black holes. Smart Mater. Struct. 24(6), 065039 (2015)
Bowyer, E.P., Nash, P., Krylov, V.V.: Damping of flexural vibrations in glass fibre composite plates and honeycomb sandwich panels containing indentations of power-law profile. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 132(3), 2041 (2012)
O’Boy, D.J., Krylov, V.V., Kralovic, V.: Damping of flexural vibrations in rectangular plates using the acoustic black hole effect. J. Sound Vib. 329(22), 4672–4688 (2010)
O’Boy, D.J., Krylov, V.V.: Damping of flexural vibrations in circular plates with tapered central holes. J. Sound Vib. 330(10), 2220–2236 (2011)
Lomonosov, A.M., Yan, S.L., Han, B., et al.: Orbital-type trapping of elastic Lamb waves. Ultrasonics 64, 58–61 (2016)
Huang, W., Ji, H.L., Qiu, J., et al.: Wave energy focalization in a plate with imperfect two-dimensional acoustic black hole indentation. J. Vib. Acoust. 138(6), 1004 (2016)
Torrent, D., Sánchez-Dehesa, J.: Acoustic metamaterials for new two-dimensional sonic devices. New J. Phys. 9(9), 323 (2007)
Zhang, S., Yin, L., Fang, N.: Focusing ultrasound with an acoustic metamaterial network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(19), 4301 (2009)
Dubois, M., Farhat, M., Bossy, E., et al.: Flat lens for pulse focusing of elastic waves in thin plates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(7), 1915 (2013)
Torrent, D., Pennec, Y., Djafari-Rouhani, B.: Omnidirectional refractive devices for flexural waves based on graded phononic crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 116(22), 4902-1-4902–8 (2014)
Climente, A., Torrent, D., Sánchez-Dehesa, J.: Gradient index lenses for flexural waves based on thickness variations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105(6), 4101-1-4101–4 (2014)
Krylov, V.V.: Surface properties of solids and surface acoustic waves: Application to chemical sensors and layer characterization. Appl. Phys. A 61(3), 229–236 (1995)
Krylov, V.V.: New type of vibration dampers utilising the effect of acoustic ‘black holes.’ Acta Acust. Acust. 90(5), 830–837 (2004)
Georgiev, V.B., Cuenca, J., Gautier, F., et al.: Damping of structural vibrations in beams and elliptical plates using the acoustic black hole effect. J. Sound Vib. 330(11), 2497–2508 (2011)
Tang, L., Cheng, L.: Loss of acoustic black hole effect in a structure of finite size. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109(1), 4102 (2016)
Tang, L., Cheng, L., Ji, H.L., et al.: Characterization of acoustic black hole effect using a one-dimensional fully-coupled and wavelet-decomposed semi-analytical model. J. Sound Vib. 374, 172–184 (2016)
Li, X., Ding, Q.: Analysis on vibration energy concentration of the one-dimensional wedge-shaped acoustic black hole structure. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 29(10), 2137–2148 (2018)
Li, X., Ding, Q.: Sound radiation of a beam with a wedge-shaped edge embedding acoustic black hole feature. J. Sound Vib. 439, 287–299 (2019)
He, M., Ding, Q.: Data-driven optimization of the periodic beam with multiple acoustic black holes. J. Sound Vib. 493, 115816 (2021)
Lyu, X., Ding, Q., Yang, T.: Merging phononic crystals and acoustic black holes. Appl. Math. Mech. English Ed. 41(5), 279–288 (2020)
Zeng, P., Zheng, L., Deng, J., et al.: Flexural wave concentration in tapered cylindrical beams and wedge-like rectangular beams with power-law thickness. J. Sound Vib. 452, 82–96 (2019)
Deng, J., Guasch, O., Zheng, L., et al.: Semi-analytical model of an acoustic black hole piezoelectric bimorph cantilever for energy harvesting. J. Sound Vib. 494, 115790 (2021)
Deng, J., Guasch, O., Maxit, L., et al.: A metamaterial consisting of an acoustic black hole plate with local resonators for broadband vibration reduction. J. Sound Vib. 526, 116803 (2022)
Park, S., Lee, J.Y., Jeon, W.: Vibration damping of plates using waveguide absorbers based on spiral acoustic black holes. J. Sound Vib. 521, 116685 (2022)
Li, H., Sécail-Géraud, M., Pelat, A., et al.: Experimental evidence of energy transfer and vibration mitigation in a vibro-impact acoustic black hole. Appl. Acoust. 182, 108168 (2021)
Li, H., Doaré, O., Touzé, C., et al.: Energy harvesting efficiency of unimorph piezoelectric acoustic black hole cantilever shunted by resistive and inductive circuits. Int. J. Solids Struct. 238, 111409 (2022)
Deng, J., Guasch, O., Maxit, L., et al.: Annular acoustic black holes to reduce sound radiation from cylindrical shells. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 158, 107722 (2021)
Chen, G., Nie, W.: Dynamic characteristics of a WPC-comparison of transfer matrix method and FE method. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2(2), 25–30 (2003)
Ece, M.C., Aydogdu, M., Taskin, V.: Vibration of a variable cross-section beam. Mech. Res. Commun. 34(1), 78–84 (2007)
Sun, Q.J.: Vibration and sound radiation of non-uniform beams. J. Sound Vib. 185(5), 827–843 (1995)
Uhrig, R.: The transfer matrix method seen as on method of structural analysis among others. J. Sound Vib. 4(2), 136–148 (1966)
Verdiere, K., Panneton, R., Elkoun, S.: Comparison between parallel transfer matrix method and admittance sum method. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 136(2), 90–95 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Tu, Z., Lu, T., et al.: A simplified transfer matrix of multi-layer piezoelectric stack. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 28(5), 595–603 (2017)
Chong, B.M.P., Tan, L.B., Lim, K.M., et al.: A review on acoustic black-holes (ABH) and the experimental and numerical study of ABH-featured 3D printed beams. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 9(6), 47 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11902001, 11875126). China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2018M641643), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 1908085QA13) and the Middle-aged Top-notch Talent and Innovative Team Support Program of Anhui Polytechnic University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhen, Y., Gu, T. & Tang, Y. Vibration control and energy accumulation of one-dimensional acoustic black hole structure with damping layer. Arch Appl Mech 92, 1777–1788 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02145-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-022-02145-x