Abstract
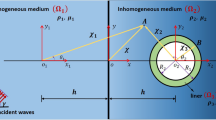
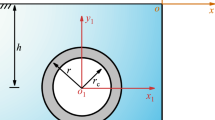
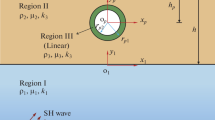
As an important underground structure, reinforced concrete lining tunnel is widely used in transportation and urban underground drainage. Reinforced concrete has orthogonal anisotropy. Therefore, the wave equation of SH wave in orthotropic lining in cylindrical coordinate system is studied. In this paper, the expression of standing wave in lining is given based on the separated variable method, and the expression of the scattering wave of the lining in the homogeneous half space is given by using the mirror image method. The unknown coefficients in the wave field expression are determined according to the boundary conditions. Finally, a numerical example is given to analyze the scattering of SH waves by a pair of identical orthotropic subsurface lining, the influence of incident angle and wave number of SH waves, lining thickness, spacing between two lining and two shear modulus ratio parameters on dynamic stress concentration factor and surface displacement amplitude of lining and its adjacent surface are studied.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsaur, D., Hsu, M.: SH waves scattering from a partially filled semi-elliptic alluvial valley. Geophys. J. Int. 194(1), 499–511 (2013)
Tsaur, D., Chang, K.: SH-waves scattering from a partially filled semi-circular alluvial valley. Geophys. J. Int. 173(1), 157–167 (2008)
Yang, Z., Xu, H., Hei, B., Zhang, J.: Antiplane response of two scalene triangular hills and a semi-cylindrical canyon by incident SH-waves. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vibr. 13(4), 569–581 (2014)
Zhang, C., Liu, Q., Deng, P.: Antiplane scattering of SH waves by a trapezoidal valley with a circular-arc alluvium in an elastic half space. J. Earthq. Tsunami 09(03), 1550008 (2015)
Zhang, N., Gao, Y., Pak, R.Y.S.: Soil and topographic effects on ground motion of a surficially inhomogeneous semi-cylindrical canyon under oblique incident SH waves. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 95, 17–28 (2017)
Sohrabibidar, A., Kamalian, M.: Effects of three-dimensionality on seismic response of Gaussian-shaped hills for simple incident pulses. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 52, 1–12 (2013)
Ba, Z., Liang, J., Mei, X.: 3D scattering of obliquely incident plane SV waves by an alluvial valley embedded in a fluid-saturated, poroelastic layered half-space. Earthq. Sci. 26(2), 107–116 (2013)
Alielahi, H., Kamalian, M., Adampira, M.: A BEM investigation on the influence of underground cavities on the seismic response of canyons. Acta Geotech. 11(2), 391–413 (2016)
Ducellier, A., Aochi, H.: Interactions between topographic irregularities and seismic ground motion investigated using a hybrid FD-FE method. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 10(3), 773–792 (2012)
Zhu, C., Thambiratnam, D.P.: Interaction of geometry and mechanical property of trapezoidal sedimentary basins with incident SH waves. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 14(11), 2977–3002 (2016)
Chen, J., Chen, P., Chen, C.: Surface motion of multiple alluvial valleys for incident plane SH-waves by using a semi-analytical approach. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 28(1), 58–72 (2008)
Chen, J., Lee, J., Shyu, W.: SH-wave scattering by a semi-elliptical hill using a null-field boundary integral equation method and a hybrid method. Geophys. J. Int. 188(1), 177–194 (2012)
Liu, G., Chen, H., Liu, D., Khoo, B.C.: Surface motion of a half-space with triangular and semicircular hills under incident SH waves. B Seismol. Soc. Am. 100(3), 1306–1319 (2010)
Shyu, W., Teng, T., Chou, C.: Anti-plane response induced by an irregular alluvial valley using a hybrid method with modified transfinite interpolation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 90, 250–264 (2016)
Shyu, W.S., Teng, T.J.: Hybrid method combines transfinite interpolation with series expansion to simulate the anti-plane response of a surface irregularity. J. Mech. 30(04), 349–360 (2014)
Hashash, Y.M.A., Hook, J.J., Schmidt, B., Yao, I.C.: Seismic design and analysis of underground structures. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 16(4), 247–293 (2001)
Henrych, J., Abrahamson, G.R.: The Dynamics of Explosion and Its Use, p. 218. Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co. (1979)
Hamhaber, U., Grieshaber, F.A., Nagel, J.H., Klose, U.: Comparison of quantitative shear wave MR-elastography with mechanical compression tests. Magn. Reson. Med. 49(1), 71–77 (2003)
Bayly, P.V., Massouros, P.G., Christoforou, E., Sabet, A., Genin, G.M.: Magnetic resonance measurement of transient shear wave propagation in a viscoelastic gel cylinder. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56(5), 2036 (2008)
Pao, Y.H., Mow, C.C., Achenbach, J.D.: Diffraction of elastic waves and dynamic stress concentrations. J. Appl. Mech. 40(4), 213–219 (1973)
Liu, D., Gai, B., Tao, G.: Applications of the method of complex function to dynamic stress concentration. Wave Motion 4(3), 293–304 (1982)
Balendra, T., Thambiratnam, D.P., Chan, G.K., Lee, S.L.: Dynamic response of twin circular tunnels due to incident SH-waves. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 12(2), 181–201 (1984)
Lee, V.W., Trifunac, M.D.: Response of tunnels to incident SH waves. J. Eng. Mech. 105(4), 643–659 (1979)
Li, Y.S., Li, T.B., Zhang, X.: Response of shallow-buried circular lining tunnel to incident P wave. Appl. Mech. Mat. 160, 331–336 (2012)
Xu, H., Li, T., Xu, J., Wang, Y.: Dynamic response of underground circular lining tunnels subjected to incident P waves. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014(4), 1–11 (2014)
Kara, H.F.: A note on response of tunnels to incident SH-waves near hillsides. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 90, 138–146 (2016)
Amornwongpaibun, A., Luo, H., Lee, V.W.: Scattering of anti-plane (SH) waves by a shallow semi-elliptical hill with a concentric elliptical tunnel. J. Earthq. Eng. 20(3), 363–382 (2015)
Liu, Q., Wang, R.: Dynamic response of twin closely-spaced circular tunnels to harmonic plane waves in a full space. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 32(6), 212–220 (2012)
Hei, B., Yang, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, D.: Dynamic analysis of elastic waves by an arbitrary cavity in an inhomogeneous medium with density variation. Math. Mech. Solids 21(8), 931–940 (2014)
Yang, Z., Hei, B., Wang, Y.: Scattering by circular cavity in radially inhomogeneous medium with wave velocity variation. Appl. Math. Mech. 6(5), 599–608 (2015)
Han, F., Liu, D.: Scattering of plane SH-waves on semi-canyon topography of arbitrary shape with linging in anisotropic media. Appl. Math. Mech. 8(8), 807–816 (1997)
Fang, X.Q., Zhang, T.F., Li, H.Y.: Elastic-slip interface effect on dynamic response of a lined tunnel in a semi-infinite alluvial valley under SH waves. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 74, 96–106 (2018)
Hasheminejad, S.M., Kazemirad, S.: Dynamic response of an eccentrically lined circular tunnel in poroelastic soil under seismic excitation. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 28(4), 277–292 (2008)
Hasheminejad, S.M., Miri, A.K.: Seismic isolation effect of lined circular tunnels with damping treatments. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vibr. 7(3), 305–319 (2008)
Hasheminejad, S.M., Avazmohammadi, R.: Dynamic stress concentrations in lined twin tunnels within fluid-saturated soil. J. Eng. Mech. 134(7), 542–554 (2008)
Liao, W.I., Yeh, C.-S., Teng, T.-J.: Scattering of elastic waves by a buried tunnel under obliquely incident waves using T matrix. J. Mech. 24(4), 405–418 (2008)
Zhou, X.L., Wang, J.H., Jiang, L.F.: Dynamic response of a pair of elliptic tunnels embedded in a poroelastic medium. J. Sound Vibr. 325(4), 816–834 (2009)
Fang, X.Q., Yang, S.P., Liu, J.X., Feng, W.J.: Dynamic interaction between two fluid-filled circular pipelines in saturated poroelastic medium subjected to harmonic waves. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 137(1), 011305 (2015)
Wang, Y., Gao, G.Y., Yang, J., Bai, X.Y.: Transient dynamic response of a shallow buried lined tunnel in saturated soil. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 94, 13–17 (2017)
Esmaeili, M., Vahdani, S., Noorzad, A.: Dynamic response of lined circular tunnel to plane harmonic waves. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 21(5), 511–519 (2005)
Manolis, G.D., Parvanova, S.L., Makra, K., Dineva, P.S.: Seismic response of buried metro tunnels by a hybrid FDM-BEM approach. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 13(7), 1953–1977 (2015)
Lin, K.C., Hung, H.H., Yang, J.P., Yang, Y.B.: Seismic analysis of underground tunnels by the 2.5D finite/infinite element approach. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 85, 31–43 (2016)
Panji, M., Ansari, B.: Transient SH-wave scattering by the lined tunnels embedded in an elastic half-plane. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 84, 220–230 (2017)
Huang, J., Zhao, M., Du, X.: Non-linear seismic responses of tunnels within normal fault ground under obliquely incident P waves. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 61, 26–39 (2017)
Vosoughifar, H., Madadi, F., Rabiefar, A.: Modified dynamic stress concentration factor for twin tunnels using a novel approach of FEM-scattering. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 70, 30–41 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 12072085); the Opening Fund of Acoustics Science and Technology Laboratory (Grant No. SSKF2020011); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3072021CF0206); the “Young Talents” Project of Northeast Agricultural University (17QC12) and the Research Team Project of Heilongjiang Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.TD2020A001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Yang, Zl., Yang, Y. et al. Scattering of SH waves by orthotropic lining groups in half space. Arch Appl Mech 92, 691–712 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02067-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02067-0