Abstract
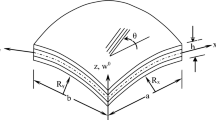
In the present study, the dynamic characterization of the glass fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP)-laminated composite cylindrical open shallow shell panels is explored with the experimental and numerical approach. In the finite element modeling (FEM), the governing equilibrium equation of the cylindrical shell panel is developed with higher-order shear deformation theory by considering the nine-noded rectangular elements. The convergence and validation study of the present FEM is accomplished with the available literature. The cylindrical laminated composite shallow shell panels are fabricated with a curvature radius of 0.8 m, and the experimentation on the free vibration investigation is performed with various boundary conditions; then, the experimental outcomes are compared with the present FEM to verify the effectiveness. The detailed parametric investigation is executed to explore the impact of curvature radius (R), boundary conditions, thickness ratio, aspect ratio (L/B), and stacking sequence on the structural response of the cylindrical laminated composite shallow shell panel. Transverse vibration response of the GFRP cylindrical laminated composite shallow shell panel is also performed with the various curvature ratios at clamped at all end conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy, J.N.: Exact solutions of moderately thick laminated shells. J. Eng. Mech. ASCE 110(5), 794–809 (1984)
Lim, C.W., Liew, K.M.: A higher order theory for vibration of shear deformable cylindrical shallow shells. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 37(3), 277–295 (1995)
Qatu, M.S., Leissa, A.W.: Natural frequencies for cantilevered doubly-curved laminated composite shallow shells. Compos. Struct. 7(3), 227–255 (1991)
Qatu, M.S., Asadi, E.: Vibration of doubly curved shallow shells with arbitrary boundaries. Appl. Acoust. 73(1), 21–27 (2012)
Qatu, M.S.: Vibration studies on completely free shallow shells having triangular and trapezoidal planforms. Appl. Acoust. 44(3), 215–231 (1995)
Bardell, N.S., Dunsdon, J.M., Langley, R.S.: On the free vibration of completely free, open, cylindrically curved isotropic shell panels. J. Sound Vib. 207(5), 647–669 (1997)
Messina, A., Soldatos, K.P.: Vibration of completely free composite plates and cylindrical shell panels by a higher-order theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 41(8), 891–918 (1999)
Zhao, X., Ng, T.Y., Liew, K.M.: Free vibration of two-side simply-supported laminated cylindrical panels via the mesh-free kp-Ritz method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 46(1), 123–142 (2004)
Shakeri, M., Alibeigloo, A.: Dynamic analysis of orthotropic laminated cylindrical panels. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 12(1), 67–75 (2005)
Bespalova, E.I.: Solving stationary problems for shallow shells by a generalized Kantorovich–Vlasov method. Int. Appl. Mech. 44(11), 1283–1293 (2008)
Albuquerque, E.L., Aliabadi, M.H.: (2010) A boundary element analysis of symmetric laminated composite shallow shells. Comput. Method Appl. Mech. 199(41–44), 2663–2668 (2010)
Liu, B., Xing, Y.F., Qatu, M.S., et al.: Exact characteristic equations for free vibrations of thin orthotropic circular cylindrical shells. Compos. Struct. 94(2), 484–493 (2012)
Asadi, E., Qatu, M.S.: Static analysis of thick laminated shells with different boundary conditions using GDQ. Thin Wall Struct. 51, 76–81 (2012)
Qu, Y., Hua, H., Meng, G.: A domain decomposition approach for vibration analysis of isotropic and composite cylindrical shells with arbitrary boundaries. Compos. Struct. 95, 307–321 (2013)
Yiotis, A.J., Katsikadelis, J.T.: Analysis of cylindrical shell panels. A meshless solution. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 37(6), 928–935 (2013)
Jin, G., Ye, T., Ma, X., et al.: A unified approach for the vibration analysis of moderately thick composite laminated cylindrical shells with arbitrary boundary conditions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 75, 357–376 (2013)
Jin, G., Ye, T., Chen, Y., et al.: An exact solution for the free vibration analysis of laminated composite cylindrical shells with general elastic boundary conditions. Compos. Struct. 106, 114–127 (2013)
Useche, J.: Vibration analysis of shear deformable shallow shells using the boundary element method. Eng. Struct. 62, 65–74 (2014)
Tornabene, F., Brischetto, S., Fantuzzi, N., et al.: Viola, numerical and exact models for free vibration analysis of cylindrical and spherical shell panels. Compos. Part B Eng. 81, 231–250 (2015)
Tang, D., Sun, L., Yao, X., et al.: Free vibration analysis of open circular cylindrical shells by the method of reverberation-ray matrix. Adv. Mech. Eng. 8(3), 1687814016638979 (2016)
Wang, Q., Shao, D., Qin, B.: A simple first-order shear deformation shell theory for vibration analysis of composite laminated open cylindrical shells with general boundary conditions. Compos. Struct. 184, 211–232 (2018)
Okhovat, R., Bostrom, A.: Dynamic equations for an orthotropic cylindrical shell. Compos. Struct. 184, 1197–1203 (2018)
Kumari, P., Kar, S.: Static behavior of arbitrarily supported composite laminated cylindrical shell panels: an analytical 3D elasticity approach. Compos. Struct. 207, 949–965 (2019)
Tong, B., Li, Y., Zhu, X., et al.: Three-dimensional vibration analysis of arbitrary angle-ply laminated cylindrical shells using differential quadrature method. Appl. Acoust. 146, 390–397 (2019)
Li, R., Zheng, X., Yang, Y., et al.: Hamiltonian system-based new analytic free vibration solutions of cylindrical shell panels. Appl. Math. Model. 76, 900–917 (2019)
Sheikholeslami, M., Farshad, S.A., Shafee, A., et al.: Numerical modeling for nanomaterial behavior in a solar unit analyzing entropy generation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 112, 271–285 (2020)
Sheikholeslami, M., Jafaryar, M., Shafee, A., et al.: Acceleration of discharge process of clean energy storage unit with insertion of porous foam considering nanoparticle enhanced paraffin. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 121206 (2020)
Sheikholeslami, M., Jafaryar, A.E., et al.: Energy and entropy evaluation and two-phase simulation of nanoparticles within a solar unit with impose of new turbulator. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 39, 100727 (2020)
Reddy, J.N.: Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells: Theory and Analysis, 2nd edn. CRC Press, London (2003)
Reddy, J.N., Liu, C.F.: A higher-order shear deformation theory of laminated elastic shells. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 23(3), 319–330 (1985)
Garg, A.K., Khare, R.K., Kant, T.: Higher-order closed-form solutions for free vibration of laminated composite and sandwich shells. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 8(3), 205–235 (2006)
Berthelot, J.M.: Composite Materials—Mechanical Behavior and Structural Analysis. Springer, New York (1999)
Jeyaraj, P., Ganesan, N., Padmanabhan, C.: Vibration and acoustic response of a composite plate with inherent material damping in a thermal environment. J. Sound Vib. 320(1–2), 322–338 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, Manoharan Ramamoorthy declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
In the present FEM, a nine-noded rectangular element is considered and the respective shape function is given as
Axial distortion strain–displacement field matrix \(B_{{{{\mathrm{cs}}} }}^{1} (x,y)\) of the cylindrical shell panel
Strain–displacement matrix \(B_{{{{\mathrm{cs}}} }}^{2} (x,y)\) of the cylindrical shell panel in concerning with the transverse deformation.
For the orthotropic cylindrical laminated composite shell panel, the inertia matrix is given as
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subramani, M., Ramamoorthy, M. Assessment on dynamic characterization of the cylindrical laminated composite shallow shell panel through experimental and numerical approach. Arch Appl Mech 91, 1925–1943 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01862-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01862-5