Abstract
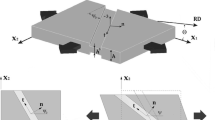
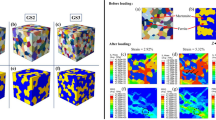
The mechanical behavior of automotive dual-phase steel (DP) is modeled by two different approaches: with a full-field representative volume element (RVE) and with a mean-field model. In the first part of this work, the full-field RVE is constituted by a crystal plasticity-based ferrite matrix with von Mises-type martensite inclusions. To isolate the martensite influence, the full-field DP results were compared to a full-field comparison RVE. In the comparison RVE, all martensite inclusions were replaced by a phase that exhibits the average ferrite behavior. A higher relative martensite grain boundary coverage facilitates an increased average dislocation density after quenching. However, for uniaxial deformations above ∼10%, the grain size-dependent relation reverses and exhibits slowed-down hardening. In the second part, we incorporate the main findings from the full-field simulations into a nonlinear mean-field model of Hashin–Shtrikman type. The dislocation density production parameter and the saturated dislocation density are modeled based on grain size and martensite coverage. The comparison of both approaches shows good agreement for both the overall and constituent averaged behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma M., Goutianos S., Hansen N., Winther G., Huang X.: Effect of hardness of martensite and ferrite on void formation in dual phase steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28(9), 1092–1100 (2012)
Bachmann, F., Hielscher, R., Schaeben, H.: Grain detection from 2d and 3d EBSD data-specification of the MTEX algorithm. Ultramicroscopy 111(12), 1720–33 (2011)
Balliger, N., Gladman, T.: Work hardening of dual-phase steels. Metal Sci. 15, 1–3 (1981)
Berbenni S., Favier V., Berveiller M.: Impact of the grain size distribution on the yield stress of heterogeneous materials. Int. J. Plast. 23(1), 114–142 (2007)
Böhlke T., Neumann R., Rieger F.: Two-scale modeling of grain size and phase transformation effects. Steel Res. Int. 85(6), 1018–1034 (2014)
Calcagnotto M., Ponge D., Demir E., Raabe D.: Orientation gradients and geometrically necessary dislocations in ultrafine grained dual-phase steels studied by 2D and 3D EBSD. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 527(10–11), 2738–2746 (2010)
Choi, S.-H., Kim, E., Woo, W., Han, S., Kwak, J.: The effect of crystallographic orientation on the micromechanical deformation and failure behaviors of DP980 steel during uniaxial tension. Int. J. Plast. 45, 85–102 (2013)
Danielsson M., Parks D.M., Boyce M.C.: Micromechanics, macromechanics and constitutive modeling of the elasto-viscoplastic deformation of rubber-toughened glassy polymers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55(3), 533–561 (2007)
Dederichs P.H., Zeller R.: Variational treatment of the elastic constants of disordered materials. Zeitschrift fuer Physik 259(2), 103–116 (1973)
Delincé M., Bréchet Y., Embury J., Geers M., Jacques P., Pardoen T.: Structure-property optimization of ultrafine-grained dual-phase steels using a microstructure-based strain hardening model. Acta Materialia 55(7), 2337–2350 (2007)
Dillien S., Seefeldt M., Allain S., Bouaziz O., Van Houtte P.: EBSD study of the substructure development with cold deformation of dual phase steel. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 527(4–5), 947–953 (2010)
Erdogan M., Tekeli S.: The effect of martensite particle size on tensile fracture of surface-carburised AISI 8620 steel with dual phase core microstructure. Mater. Des. 23(7), 597–604 (2002)
Gao S., Chen M., Chen S., Kamikawa N., Shibata A., Tsuji N.: Yielding behavior and its effect on uniform elongation of fine grained IF steel. Mater. Trans. 55(1), 73–77 (2014)
Gardey B., Bouvier S., Bacroix B.: Correlation between the macroscopic behavior and the microstructural evolutions during large plastic deformation of a dual-phase steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36, 2937–2945 (2005)
Ghassemi-Armaki H., Maaß R., Bhat S., Sriram S., Greer J., Kumar K.: Deformation response of ferrite and martensite in a dual-phase steel. Acta Materialia 62, 197–211 (2014)
Jiang Z., Guan Z., Lian J., Mechanics F.: Effects of microstructural variables on the deformation behaviour of dual-phase steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 190(1–2), 55–64 (1995)
Jöchen, K.: Homogenization of the Linear and Non-linear Mechanical Behavior of Polycrystals. Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT), KIT Scientific Publishing. http://uvka.ubka.uni-karlsruhe.de/shop/download/1000032289 (2013)
Jöchen K., Böhlke T.: Prediction of texture evolution in rolled sheet metals by using homogenization schemes. Key Eng. Mater. 504(506), 649–654 (2012)
Kadkhodapour J., Schmauder S., Raabe D., Ziaei-Rad S., Weber U., Calcagnotto M.: Experimental and numerical study on geometrically necessary dislocations and non-homogeneous mechanical properties of the ferrite phase in dual phase steels. Acta Materialia 59(11), 4387–4394 (2011)
Kang J., Ososkov Y., Embury J., Wilkinson D.: Digital image correlation studies for microscopic strain distribution and damage in dual phase steels. Scripta Materialia 56(11), 999–1002 (2007)
Kapp M., Hebesberger T., Kolednik O.: A micro-level strain analysis of a high-strength dual-phase steel. Int. J. Mater. Res. (formerly Zeitschrift fuer Metallkunde) 102(06), 687–691 (2011)
Kim S.A., Johnson W.L.: Elastic constants and internal friction of martensitic steel, ferritic–pearlitic steel, and α-iron. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 452(453), 633–639 (2007)
Kocks U.F., Mecking H.: Physics and phenomenology of strain hardening: the FCC case. Prog. Mater. Sci. 48, 171–273 (2003)
Koistinen D.P., Marburger R.E.: A general equation prescribing the extent of the austenite–martensite transformation in pure iron–carbon alloys and plain carbon steels. Acta Metallurgica 7(1), 59–60 (1959)
Korzekwa D., Matlock D., Procedure E.: Dislocation substructure as a function of strain in a dual-phase steel. Metall. Mater. 15, 1221–1228 (1984)
Kuziak R., Kawalla R., Waengler S.: Advanced high strength steels for automotive industry. Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 8(2), 103–117 (2008)
Larour P., Bäumer A., Dahmen K., Bleck W.: Influence of strain rate, temperature, plastic strain, and microstructure on the strain rate sensitivity of automotive sheet steels. Steel Res. Int. 84(5), 426–442 (2013)
Liedl U., Traint S., Werner E.: An unexpected feature of the stress–strain diagram of dual-phase steel. Comput. Mater. Sci. 25(1), 122–128 (2002)
Mecking H.: Work hardening of single-phase polycrystals. In: Buschow, K.J., Cahn, R.W., Flemings, M.C., Ilschner, B., Kramer, E.J., Mahajan, S. (eds.) Encyclopedia of Materials—Science and Technology, pp. 9785–9795. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2001)
Nadeau J., Ferrari M.: On optimal zeroth-order bounds with application to Hashin–Shtrikman bounds and anisotropy parameters. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38(44–45), 7945–7965 (2001)
Park K., Nishiyama M., Nakada N., Tsuchiyama T., Takaki S.: Effect of the martensite distribution on the strain hardening and ductile fracture behaviors in dual-phase steel. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 604, 135–141 (2014)
Ponte Castaneda, P., Suquet, P., Castaneda, P.P.: Nonlinear composites. In: van der Giessen E., Wu T.Y. (Eds.) Advances in Applied Mechanics, vol. 34 of Advances in Applied Mechanics. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p. 171.302 (1997)
Raeisinia B., Sinclair C.: A representative grain size for the mechanical response of polycrystals. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 525(1–2), 78–82 (2009)
Ramazani, A., Mukherjee, K., Quade, H., Prahl, U., Bleck, W.: Correlation between 2D and 3D flow curve modelling of DP steels using a microstructure-based RVE approach. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 560, 129–139 (2013a)
Ramazani, A., Mukherjee, K., Schwedt, A., Goravanchi, P., Prahl, U., Bleck, W.: Quantification of the effect of transformation-induced geometrically necessary dislocations on the flow-curve modelling of dual-phase steels. Int. J. Plast. 43, 128–152 (2013b)
Rauch E.F., Gracio J.J., Barlat F., Vincze G.: Modelling the plastic behaviour of metals under complex loading conditions. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 19(3), 035009 (2011)
Resende T.C., Bouvier S.: Dislocation-based model for the prediction of the behavior of bcc materials—grain size and strain path effects. Int. J. Plast. 47, 29–48 (2013)
Rodriguez R.-M., Gutiérrez I.: Unified formulation to predict the tensile curves of steels with different microstructures. Mater. Sci. Forum 426(432), 4525–4530 (2003)
Schreijäg, S.: Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Deep Drawing DC04 Steel at Different Length Scales. Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT), KIT Scientific Publishing, Karlsruhe (2013). http://uvka.ubka.uni-karlsruhe.de/shop/download/1000032165
Sodjit S., Uthaisangsuk V.: Microstructure based prediction of strain hardening behavior of dual phase steels. Mater. Des. 41, 370–379 (2012)
Tasan C.C., Hoefnagels J.J., Geers M.M.: Microstructural banding effects clarified through micrographic digital image correlation. Scripta Materialia 62(11), 835–838 (2010)
Thomser, C., Uthaisangsuk, V., Bleck, W.: Influence of martensite distribution on the mechanical properties of dual phase steels: experiments and simulation. Steel Res. Int. 80(8), 582–587 (2009)
Tsipouridis P., Koll L., Krempaszky C., Werner E.: On the strength of grain and phase boundaries in ferritic-martensitic dual-phase steels. Int. J. Mater. Res. (formerly Zeitschrift fuer Metallkunde) 102(06), 674–686 (2011)
Wasilkowska A., Petrov R., Kestens L., Werner E.A., Krempaszky C., Traint S., Pichler A.: Microstructure and texture changes in a low-alloyed TRIP-aided steel induced by small plastic deformation. ISIJ Int. 46(2), 302–309 (2006)
Wenk, M., Schreijäg, S.: Personal Communication (2013)
Willis J.: Bounds and self-consistent estimates for the overall properties of anisotropic composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 25(3), 185–202 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rieger, F., Böhlke, T. Microstructure based prediction and homogenization of the strain hardening behavior of dual-phase steel. Arch Appl Mech 85, 1439–1458 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-014-0974-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-014-0974-3