Abstract
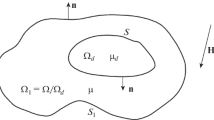
In this paper, exact solutions for the primary field variables and their first derivatives are derived for the coupled magneto-mechanical problem of a circular inclusion embedded in an infinite surrounding. Both material domains possess linear and isotropic material properties. The assumed planarity of all fields enables and recommends the description with analytic functions depending on the complex variable z. The well-known technique of a complex stress potential satisfying the bipotential equation is used and adapted to coupled magneto-mechanical problems. The provided analytic expressions are of special interest for the validation of numeric solutions of coupled magneto-mechanical boundary value problems. In this contribution, they are applied to analyze the convergence behavior of an extended finite element formulation for coupled magneto-mechanical problems. Based on the analytic results, proper boundary conditions are prescribed to the numeric model. The convergence in terms of polynomial degree and mesh refinement of the implemented element formulation is proved by computing the L2 and the energy norm which requires the knowledge of the exact solution. The generality of the proposed formulas allows for the deduction of some other kind of problems, e.g., the pure mechanical displacement and stress field of a bimaterial setting or the stress concentration around a circular hole.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardzokas D.I., Filshtinsky M.L., Filshtinsky L.A.: Mathematical Methods in Electro-Magneto-Elasticity. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Belytschko T., Moës N., Usui S., Parimi C.: Arbitrary discontinuities in finite elements. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 50(4), 993–1013 (2001)
Bender P., Tschöpe A., Birringer R.: Determination of the shear modulus of gelatine hydrogels by magnetization measurements using dispersed nickel nanorods as mechanical probes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 346, 152–160 (2013)
Bustamante, R.: Mathematical modelling of non-linear magneto- and electro-active rubber-like materials. Ph.D. thesis, University of Glasgow (2007)
Cheng K.W., Fries T.P.: Higher-order XFEM for curved strong and weak discontinuities. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 82(5), 564–590 (2010)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: Nonlinear magnetoelastic deformations. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 57(4), 599–622 (2004)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: Nonlinear Theory of Electroelastic and Magnetoelastic Interactions. Springer, New York (2014)
Engel A., Friedrichs R.: On the electromagnetic force on a polarizable body. Am. J. Phys. 70(4), 428–432 (2002)
Eringen A.C., Maugin G.A.: Electrodynamics of Continua I. Springer, New York (1990)
Fish J., Belytschko T.: A First Course in Finite Elements. Wiley, Chichester (2007)
Galipeau E., Ponte Castañeda P.: A finite-strain constitutive model for magnetorheological elastomers: magnetic torques and fiber rotations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 61(4), 1065–1090 (2013)
Galipeau E., Ponte Castañeda P.: Giant field-induced strains in magnetoactive elastomer composites. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. 469(2158), 20130385 (2013)
de Groot S.R., Suttorp L.G.: Foundations of Electrodynamics. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam (1972)
Hutter K., van de Ven A.A.F., Ursescu A.: Electromagnetic Field Matter Interactions in Thermoelastic Solids and Viscous Fluids. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Jackson J.D.: Klassische Elektrodynamik. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin (2006)
Javili A., Chatzigeorgiou G., Steinmann P.: Computational homogenization in magneto-mechanics. Int. J. Solids Struct. 50(25–26), 4197–4216 (2013)
Kästner M., Müller S., Goldmann J., Spieler C., Brummund J., Ulbricht V.: Higher-order extended FEM for weak discontinuities—level set representation, quadrature and application to magneto-mechanical problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 93(13), 1403–1424 (2013)
Landau L.D., Lifschitz E.M.: Lehrbuch der theoretischen Physik VIII—Elektrodynamik der Kontinua. Akademie-Verlag, Berlin (1974)
Miehe C., Kiefer B., Rosato D.: An incremental variational formulation of dissipative magnetostriction at the macroscopic continuum level. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48(13), 1846–1866 (2011)
Moës N., Dolbow J., Belytschko T.: A finite element method for crack growth without remeshing. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 46(1), 131–150 (1999)
Moës N., Cloirec M., Cartraud P., Remacle J.F.: A computational approach to handle complex microstructure geometries. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 192(28–30), 3163–3177 (2003)
Moon F.C.: Magneto-Solid Mechanics. Wiley, New York (1984)
Mußchelischwili N.I.: Einige Grundaufgaben zur mathematischen Elastizitästheorie. VEB Fachbuchverlag, Leipzig (1971)
Miyata K., Miya K.: Magnetic field and stress analysis of saturated steel. IEEE Trans. Magn. 24(1), 230–233 (1988)
Ogden, R.W., Steigmann, D.J. (eds.): Mechanics and Electrodynamics of Magneto- and Electro-elastic Materials. Springer, Wien (2011)
Paria G.: Magneto-elasticity and magneto-thermo-elasticity. Adv. Appl. Mech. 10, 73–112 (1966)
Ponte Castañeda P., Galipeau E.: Homogenization-based constitutive models for magnetorheological elastomers at finite strain. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 59(2), 194–215 (2011)
Roeder L., Bender P., Tschöpe A., Birringer R., Schmidt A.M.: Shear modulus determination in model hydrogels by means of elongated magnetic nanoprobes. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 50(24), 1772–1781 (2012)
Sawin G.N.: Spannungsüberhöhung am Rande von Löchern. VEB Verlag Technik, Berlin (1956)
Siboni M.H., Ponte Castañeda P.: A magnetically anisotropic, ellipsoidal inclusion subjected to a non-aligned magnetic field in an elastic medium. C. R. Mécanique 340(4–5), 205–218 (2012)
Spieler C., Kästner M., Goldmann J., Brummund J., Ulbricht V.: XFEM modeling and homogenization of magnetoactive composites. Acta Mech. 224(11), 2453–2469 (2013)
Spieler C., Metsch P., Kästner M., Ulbricht V.: Microscale modeling of magnetoactive composites undergoing large deformations. Tech. Mech. 34(1), 39–50 (2014)
Sukumar N., Chopp D.L., Moës N., Belytschko T.: Modeling holes and inclusions by level sets in the extended finite-element method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190(46–47), 6183–6200 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spieler, C., Kästner, M. & Ulbricht, V. Analytic and numeric solution of a magneto-mechanical inclusion problem. Arch Appl Mech 85, 1483–1497 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-014-0952-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-014-0952-9