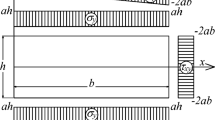
Abstract
The traditional Saint-Venant problem of three-dimensional viscoelasticity is discussed under the Hamiltonia system with the use of the Laplace integral transformation, and the original problem is transformed into finding eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the Hamiltonia operator matrix. Since local effect near the boundary is usually neglected, all solutions of Saint-Venant problems can be obtained directly by the combinations of zero eigenvectors. Moreover, the adjoint relationships of the symplectic orthogonality of zero eigenvectors in the Laplace domain are generalized to the time domain. Therefore the problem can be discussed directly in the eigenvector space of the time domain, and the iterative application of Laplace transformation is not needed. Simply by applying the adjoint relationships of the symplectic orthogonality, an effective method for boundary condition is given. Based on this method, some typical examples are discussed, in which the whole character of total creep and relaxation of viscoelasticity is clearly revealed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danyluk M.J., Geubelle P.H., Hilton H.H.: Two-dimensional and three-dimensional fracture in viscoelastic materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 35, 3831–3853 (1998)
Ashish O., Ray V.J., Roderic S.L.: Generalized solution for predicting relaxation from creep in soft tissue: application to ligament. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 48, 662–673 (2006)
Vinogradov V., Milton G.W.: The total creep of viscoelastic composites under hydrostatic or antiplane loading. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53, 1248–1279 (2005)
De Chant L.J.: Impulsive displacement of a quasi-linear viscoelastic material through accurate numerical inversion of the laplace transform. Comput. Math. Appl. 43, 1161–1170 (2002)
Temel B. et al.: Quasi-static and dynamic response of viscoelastic helical rods. J. Sound Vib. 271, 921–935 (2004)
Huang Y., Crouch S.L. et al.: A time domain direct boundary integral method for a viscoelastic plane with circular holes and elastic inclusions. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 29, 725–737 (2005)
Schanz M., Antes H. et al.: Convolution quadrature boundary element method for quasi-static visco- and poroelastic continua. Comput. Struct. 83, 673–684 (2005)
Syngellakis S.: Boundary element methods for polymer analysis. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 27, 125–135 (2003)
Schanz M., Antes H.: A new visco- and elastodynamic time domain boundary element formulation. Comput. Mech. 20, 452–45 (1997)
Yun H., Sofia G.M. et al.: Complex variable boundary integral method for linear viscoelasticity: Part I—basic formulations. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 30, 1049–1056 (2006)
Mesquita A.D., Coda H.B.: A boundary element methodology for viscoelastic analysis: Part I with cells. Appl. Math. Model. 31, 1149–1170 (2007)
Saint-Venant B.: Memoire sur la torsion des prismes. Paris Memoires des Savants etrangers 14, 233–560 (1856)
Saint-Venant B.: Memoire sur la flexion des prismes. J. Math. Pures. Appl. 1, 89–189 (1856)
Chirita, S., Iasi R.: Saint-Venant problem and semi-inverse solutions in linear viscoelasticity 94, 221–232 (1992)
Chirita S., Ciarletta M., Fabrizio M.: Saint-Venant’s principle in linear viscoelasticity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 35, 1221–123 (1997)
Zhong W.X.: Duality System in Applied Mechanics and Optimal Control. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York (2004)
Xu X.S., Zhang W.X. et al.: An application of the symplectic system in two-dimensional viscoelasticity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 44, 897–914 (2006)
Stephen N.G., Wang M.Z.: Decay rates for the hollow circular cylinder. J. Appl. Mech. 59, 747–753 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W. Saint-Venant problem of three-dimensional linear viscoelasticity in the Hamiltonian system. Arch Appl Mech 79, 793–806 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-008-0253-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-008-0253-2