Abstract
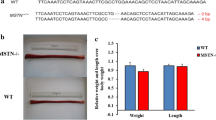
Collagen XIX is a nonfibrillar collagen that localizes in restricted tissues at very low amounts. A previous study on Col19a1 null mice revealed that collagen XIX is involved in esophageal muscle physiology and morphogenesis. Here, we use histological analysis to show that mice with a Col19a1 mutant lacking the NC3 domain and seven collagen triplets display abnormal transition of smooth to striated muscle in the abdominal segment of esophagus, and a widened esophagus with age. With two newly prepared antibodies, we analyzed the expression of collagen XIX in the mouse esophagus and show that collagen XIX colocalizes with α-smooth muscle actin. By immunoelectron microscopy, we confirmed the localization of collagen XIX in esophageal smooth muscle cells. Col19a1 mutant mice contained reduced levels of mutated Col19a1 mRNA. Interestingly, hepatocyte growth factor, which has an important role in esophageal striated muscle development, was reduced in the esophagus of the Col19a1 mutant mice. These findings suggest that collagen XIX may be critical for the function of esophageal smooth muscle cells as a scaffold for anteroposterior migration of esophagus-striated muscle cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study and the antibodies which generated for this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- LES:
-
Lower esophageal sphincter
- ESM:
-
Esophagus striated muscle
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- NC domain:
-
Noncollagenous domain
- ∆19 mice:
-
Col19a1 mutant mice that lack the NC3 domain and seven collagenous triplets
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- NGS:
-
Normal goat serum
References
Boudko SP, Engel J, Bächinger HP (2008) Trimerization and triple helix stabilization of the collagen XIX NC2 domain. J Biol Chem 283(49):34345–34351. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M806352200
Comai G, Heude E, Mella S, Paisant S, Pala F, Gallardo M, Langa F, Kardon G, Gopalakrishnan S, Tajbakhsh S (2019) A distinct cardiopharyngeal mesoderm genetic hierarchy establishes antero-posterior patterning of esophagus striated muscle. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47460
Gopalakrishnan S, Comai G, Sambasivan R, Francou A, Kelly RG, Tajbakhsh S (2015) A cranial mesoderm origin for esophagus striated muscles. Dev Cell 34(6):694–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2015.07.003
Litingtung Y, Lei L, Westphal H, Chiang C (1998) Sonic hedgehog is essential to foregut development. Nat Gene 20(1):58–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/1717
Myers JC, Li D, Bageris A, Abraham V, Dion AS, Amenta PS (1997) Biochemical and immunohistochemical characterization of human type XIX defines a novel class of basement membrane zone collagens. Am J Pathol 151(6):1729–1740
Myers JC, Li D, Rubinstein NA, Clark CC (1999) Up-regulation of type XIX collagen in rhabdomyosarcoma cells accompanies myogenic differentiation. Exp Cell Res 253(2):587–598. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1999.4642
Oudart JB, Monboisse JC, Maquart FX, Brassart B, Brassart-Pasco S, Ramont L (2017) Type XIX collagen: a new partner in the interactions between tumor cells and their microenvironment. Matrix Biol 57–58:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.010
Que J, Choi M, Ziel JW, Klingensmith J, Hogan BL (2006) Morphogenesis of the trachea and esophagus: current players and new roles for noggin and Bmps. Differentiation 74(7):422–437. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-0436.2006.00096.x
Rishniw M, Xin HB, Deng KY, Kotlikoff MI (2003) Skeletal myogenesis in the mouse esophagus does not occur through transdifferentiation. Genesis 36(2):81–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/gene.10198
Rishniw M, Fisher PW, Doran RM, Meadows E, Klein WH, Kotlikoff MI (2007) Smooth muscle persists in the muscularis externa of developing and adult mouse esophagus. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 28(2–3):153–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-007-9112-y
Rodriguez P, Da Silva S, Oxburgh L, Wang F, Hogan BL, Que J (2010) BMP signaling in the development of the mouse esophagus and forestomach. Development 137(24):4171–4176. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.056077
Rosas-Arellano A, Villalobos-González JB, Palma-Tirado L, Beltrán FA, Cárabez-Trejo A, Missirlis F, Castro MA (2016) A simple solution for antibody signal enhancement in immunofluorescence and triple immunogold assays. Histochem Cell Biol 146(4):421–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1447-2
Su J, Gorse K, Ramirez F, Fox MA (2010) Collagen XIX is expressed by interneurons and contributes to the formation of hippocampal synapses. J Comp Neurol 518(2):229–253. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.22228
Su J, Chen J, Lippold K, Monavarfeshani A, Carrillo GL, Jenkins R, Fox MA (2016) Collagen-derived matricryptins promote inhibitory nerve terminal formation in the developing neocortex. J Cell Biol 212(6):721–736. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201509085
Sumiyoshi H, Inoguchi K, Khaleduzzaman M, Ninomiya Y, Yoshioka H (1997) Ubiquitous expression of the alpha1(XIX) collagen gene (Col19a1) during mouse embryogenesis becomes restricted to a few tissues in the adult organism. J Biol Chem 272(27):17104–17111. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.27.17104
Sumiyoshi H, Laub F, Yoshioka H, Ramirez F (2001) Embryonic expression of type XIX collagen is transient and confined to muscle cells. Dev Dyn 220(2):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0177(2000)9999:9999%3c::aid-dvdy1099%3e3.0.co;2-w
Sumiyoshi H, Mor N, Lee SY, Doty S, Henderson S, Tanaka S, Yoshioka H, Rattan S, Ramirez F (2004) Esophageal muscle physiology and morphogenesis require assembly of a collagen XIX-rich basement membrane zone. J Cell Biol 166(4):591–600. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200402054
Talts JF, Sasaki T, Miosge N, Göhring W, Mann K, Mayne R, Timpl R (2000) Structural and functional analysis of the recombinant G domain of the laminin alpha4 chain and its proteolytic processing in tissues. J Biol CHem 275(45):35192–35199. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M003261200
Tillet E, Mann K, Nischt R, Pan TC, Chu ML, Timpl R (1995) Recombinant analysis of human alpha 1 (XVI) collagen. Evidence for processing of the N-terminal globular domain. Eur J Biochem 228(1):160–168. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20245.x
Timpl R (1982) Antibodies to collagens and procollagens. Meth Enzymol 82:472–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(82)82079-x (Pt A)
Veres-Székely A, Pap D, Sziksz E, Jávorszky E, Rokonay R, Lippai R, Tory K, Fekete A, Tulassay T, Szabó AJ, Vannay Á (2017) Selective measurement of α smooth muscle actin: why β-actin can not be used as a housekeeping gene when tissue fibrosis occurs. BMC Mol Biol 18(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12867-017-0089-9
Wörl J, Breuer C, Neuhuber WL (2009) Deletion of Pax7 changes the tunica muscularis of the mouse esophagus from an entirely striated into a mixed phenotype. Dev Dyn 238(4):864–874. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21898
Wuttke M, Müller S, Nitsche DP, Paulsson M, Hanisch FG, Maurer P (2001) Structural characterization of human recombinant and bone-derived bone sialoprotein. Functional implications for cell attachment and hydroxyapatite binding. J Biol Chem 276(39):36839–36848. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M105689200
Yano S, Kashima K, Daa T, Urabe S, Tsuji K, Nakayama I, Yokoyama S (2003) An antigen retrieval method using an alkaline solution allows immunoelectron microscopic identification of secretory granules in conventional epoxy-embedded tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 51(2):199–204. https://doi.org/10.1177/002215540305100208
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ai Uezono, a former master student in the department of Matrix Medicine for her contribution to the beginning of this study, Dr. Noritaka Matsuo for his support on this project and Dr. Boudko (Vanderbilt University Medical Center) for providing the expression plasmid and the cDNA of COL19A1. We are grateful to Professor Klaus von der Mark (University of Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany) for his valuable comments and editing the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS, KJ, HK, AY, SA, and TS performed experiments. SY analyzed using an electron microscopy. HK, HY, and TS designed the experiments, supervised the project, and wrote the manuscripts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the experimental protocols approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Oita University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, H., Jin, K., Yano, S. et al. Abnormalities in esophageal smooth muscle induced by mutations in collagen XIX. Histochem Cell Biol 157, 205–216 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-021-02059-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-021-02059-9