Abstract
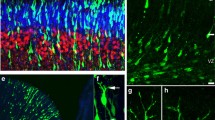
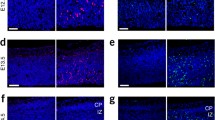
De novo synthesis of the nucleotide CTP is catalyzed by the essential pyrimidine biosynthesis enzyme CTP synthase (CTPs), which forms large-scale filamentous structures consisting of CTPs termed cytoophidia in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes. Recent studies have shown that cytoophidia are abundant in neuroepithelial stem cells in Drosophila optic lobes and that overexpression of CTPs impairs optic lobe development. Whether CTPs and cytoophidia also play a role in the development of the mammalian cortex remains elusive. Here, we show that overexpression of CTPs by in utero electroporation in the embryonic mouse brain induces formation of cytoophidia in developing cortical neurons and impairs neuronal migration. In addition, the increase of cytoophidia accelerates neuronal differentiation and inhibits neural progenitor cell proliferation by reducing their mitotic activity. Furthermore, we discovered that the cytoophidia diffused during the early G1-phase of the cell cycle. Together, our findings show, for the first time, that CTPs play a significant role in the development of the mammalian cortex.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronow B, Ullman B (1987) In situ regulation of mammalian CTP synthetase by allosteric inhibition. J Biol Chem 262:5106–5112
Aughey GN et al (2014) Nucleotide synthesis is regulated by cytoophidium formation during neurodevelopment and adaptive metabolism. Biol Open 3:1045–1056. doi:10.1242/bio.201410165
Aughey GN, Grice SJ, Liu JL (2016) The interplay between Myc and CTP synthase in Drosophila. PLoS Genet 12:e1005867. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005867
Azzam G, Liu JL (2013) Only one isoform of Drosophila melanogaster CTP synthase forms the cytoophidium. PLoS Genet 9:e1003256. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003256
Barry RM et al (2014) Large-scale filament formation inhibits the activity of CTP synthetase. Elife 16:03638
Berry M, Rogers AW (1965) The migration of neuroblasts in the developing cerebral cortex. J Anat 99:691–709
Carcamo WC et al (2011) Induction of cytoplasmic rods and rings structures by inhibition of the CTP and GTP synthetic pathway in mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 6:e29690. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029690
Chen K, Zhang J, Tastan OY, Deussen ZA, Siswick MY, Liu JL (2011) Glutamine analogs promote cytoophidium assembly in human and Drosophila cells. J Genet Genom 38:391–402. doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2011.08.004
Cunningham JJ, Roussel MF (2001) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in the development of the central nervous system. Cell Growth Differ 12:387–396
Endrizzi JA, Kim H, Anderson PM, Baldwin EP (2005) Mechanisms of product feedback regulation and drug resistance in cytidine triphosphate synthetases from the structure of a CTP-inhibited complex. Biochemistry 44:13491–13499
Farkas LM, Huttner WB (2008) The cell biology of neural stem and progenitor cells and its significance for their proliferation versus differentiation during mammalian brain development. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:707–715. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2008.09.008
Florio M, Huttner WB (2014) Neural progenitors, neurogenesis and the evolution of the neocortex. Development 141:2182–2194. doi:10.1242/dev.090571
Franco SJ, Gil-Sanz C, Martinez-Garay I, Espinosa A, Harkins-Perry SR, Ramos C, Muller U (2012) Fate-restricted neural progenitors in the mammalian cerebral cortex. Science 337:746–749. doi:10.1126/science.1223616
Haubensak W, Attardo A, Denk W, Huttner WB (2004) Neurons arise in the basal neuroepithelium of the early mammalian telencephalon: a major site of neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:3196–3201
Ingerson-Mahar M, Briegel A, Werner JN, Jensen GJ, Gitai Z (2010) The metabolic enzyme CTP synthase forms cytoskeletal filaments. Nat Cell Biol 12:739–746. doi:10.1038/ncb2087
Kriegstein AR (2005) Constructing circuits: neurogenesis and migration in the developing neocortex. Epilepsia 7:15–21
Kuzniecky RI (2006) Malformations of cortical development and epilepsy, part 1: diagnosis and classification scheme. Rev Neurol Dis 3:151–162
Liu JL (2010) Intracellular compartmentation of CTP synthase in Drosophila. J Genet Genom 37:281–296. doi:10.1016/S1673-8527(09)60046-1
Liu JL (2011) The enigmatic cytoophidium: compartmentation of CTP synthase via filament formation. BioEssays 33:159–164. doi:10.1002/bies.201000129
McEvilly RJ, de Diaz MO, Schonemann MD, Hooshmand F, Rosenfeld MG (2002) Transcriptional regulation of cortical neuron migration by POU domain factors. Science 295:1528–1532
Miyata T, Kawaguchi A, Saito K, Kawano M, Muto T, Ogawa M (2004) Asymmetric production of surface-dividing and non-surface-dividing cortical progenitor cells. Development 131:3133–3145
Molyneaux BJ, Arlotta P, Menezes JR, Macklis JD (2007) Neuronal subtype specification in the cerebral cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:427–437
Noctor SC, Martinez-Cerdeno V, Ivic L, Kriegstein AR (2004) Cortical neurons arise in symmetric and asymmetric division zones and migrate through specific phases. Nat Neurosci 7:136–144
Noree C, Sato BK, Broyer RM, Wilhelm JE (2010) Identification of novel filament-forming proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol 190:541–551. doi:10.1083/jcb.201003001
Noree C, Monfort E, Shiau AK, Wilhelm JE (2014) Common regulatory control of CTP synthase enzyme activity and filament formation. Mol Biol Cell 25:2282–2290. doi:10.1091/mbc.E14-04-0912
Petrovska I et al (2014) Filament formation by metabolic enzymes is a specific adaptation to an advanced state of cellular starvation. Elife 25:02409
Polleux F, Dehay C, Kennedy H (1997a) The timetable of laminar neurogenesis contributes to the specification of cortical areas in mouse isocortex. J Comp Neurol 385:95–116
Polleux F, Dehay C, Moraillon B, Kennedy H (1997b) Regulation of neuroblast cell-cycle kinetics plays a crucial role in the generation of unique features of neocortical areas. J Neurosci 17:7763–7783
Pontious A, Kowalczyk T, Englund C, Hevner RF (2008) Role of intermediate progenitor cells in cerebral cortex development. Dev Neurosci 30:24–32
Rakic P (1972) Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol 145:61–83
Rakic P (1978) Neuronal migration and contact guidance in the primate telencephalon. Postgrad Med J 1:25–40
Rakic P (2009) Evolution of the neocortex: a perspective from developmental biology. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:724–735. doi:10.1038/nrn2719
Rakic P, Lombroso PJ (1998) Development of the cerebral cortex: I. Forming the cortical structure. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 37:116–117
Sidman RL, Miale IL, Feder N (1959) Cell proliferation and migration in the primitive ependymal zone: an autoradiographic study of histogenesis in the nervous system. Exp Neurol 1:322–333
Strochlic TI, Stavrides KP, Thomas SV, Nicolas E, O’Reilly AM, Peterson JR (2014) Ack kinase regulates CTP synthase filaments during Drosophila oogenesis. EMBO Rep 15:1184–1191. doi:10.15252/embr.201438688
Sugitani Y et al (2002) Brn-1 and Brn-2 share crucial roles in the production and positioning of mouse neocortical neurons. Genes Dev 16:1760–1765
Tabata H, Nakajima K (2001) Efficient in utero gene transfer system to the developing mouse brain using electroporation: visualization of neuronal migration in the developing cortex. Neuroscience 103:865–872
Takahashi T, Nowakowski RS, Caviness VS Jr (1995) The cell cycle of the pseudostratified ventricular epithelium of the embryonic murine cerebral wall. J Neurosci 15:6046–6057
Tastan OY, Liu JL (2015) CTP synthase is required for optic lobe homeostasis in Drosophila. J Genet Genom 42:261–274. doi:10.1016/j.jgg.2015.04.006
Wang JT et al (2015) Src controls neuronal migration by regulating the activity of FAK and cofilin. Neuroscience 292:90–100
Xie J et al (2016) Aberrant expression of LIMK1 impairs neuronal migration during neocortex development. Histochem Cell Biol. doi:10.1007/s00418-016-1514-8
Yang WL, McDonough VM, Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O, Adeline MT, Flocco MT, Carman GM (1994) Purification and characterization of CTP synthetase, the product of the URA7 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry 33:10785–10793
Zecevic N, Chen Y, Filipovic R (2005) Contributions of cortical subventricular zone to the development of the human cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol 491:109–122
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572477). We thank the Life Science Research Core Services (LSRCS) in Northwest A&F University for supplying the Leica TCS SP8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript and the manuscript was approved by all authors for publication. The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Xie, J., Hei, M. et al. High level of CTP synthase induces formation of cytoophidia in cortical neurons and impairs corticogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol 149, 61–73 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-017-1612-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-017-1612-2