Abstract
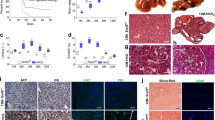
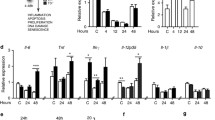
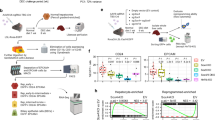
Both SULF1 and SULF2 enzymes are undetectable in normal adult liver tissue despite their high level expression during foetal development. Most hepatocellular carcinomas unlike the normal adult liver, however, express variable levels of these enzymes with a small proportion not expressing either SULF1 or SULF2. SULF1 expression, however, is not restricted to only foetal and tumour tissues but is also abundant in liver tissues undergoing injury-induced tissue regeneration as we observed during fatty liver degeneration, chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Unlike SULF1, the level of SULF2 activation during injury-induced regeneration, however, is much lower when compared to foetal or tumour growth. Although a small fraction of liver tumours and some liver tumour cell lines can grow in the absence of Sulf1 and/or Sulf2, the in vitro overexpression of these genes further confirms their growth-promoting effect while transient reduction in their levels by neutralisation antibodies reduces growth. Hedgehog signalling appeared to regulate the growth of both Hep3B and PRF5 cell lines since cyclopamine demonstrated a marked inhibitory effect while sonic hedgehog (SHH) overexpression promoted growth. All Sulf isoforms promoted SHH-induced growth although the level of increase in PRF5 cell line was higher with both Sulf2 variants than Sulf1. In addition to promoting growth, the Sulf variants, particularly the shorter Sulf2 variant, markedly promoted PRF5 cell migration in a scratch assay. The SULF1/SULF2 activation thus does not only promote regulated foetal growth and injury-induced liver regeneration but also dysregulated tumour growth.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai X, Do AT, Lozynska O, Kusche-Gullberg M, Lindahl U, Emerson CP Jr (2003) QSulf1 remodels the 6-O sulfation states of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans to promote Wnt signaling. J Cell Biol 162(2):341–351. doi:10.1083/jcb.200212083
Ai X, Kitazawa T, Do AT, Kusche-Gullberg M, Labosky PA, Emerson CP Jr (2007) SULF1 and SULF2 regulate heparan sulfate-mediated GDNF signaling for esophageal innervation. Development 134(18):3327–3338. doi:10.1242/dev.007674
Ashikari-Hada S, Habuchi H, Kariya Y, Itoh N, Reddi AH, Kimata K (2004) Characterization of growth factor-binding structures in heparin/heparan sulfate using an octasaccharide library. J Biol Chem 279(13):12346–12354
Barth H, Schafer C, Adah MI, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ, Toyoda H, Kinoshita-Toyoda A, Toida T, Van Kuppevelt TH, Depla E, Von Weizsacker F, Blum HE, Baumert TF (2003) Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J Biol Chem 278(42):41003–41012
Bret C, Moreaux J, Schved JF, Hose D, Klein B (2011) SULFs in human neoplasia: implication as progression and prognosis factors. J Transl Med 9:72. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-9-72
Dhoot GK (2012) Recent progress and related patents on the applications of SULF1/SULF2 enzymes in regenerative medicine and cancer therapies. Recent Pat Regen Med 2:137–145
Dhoot GK, Gustafsson MK, Ai X, Sun W, Standiford DM, Emerson CP Jr (2001) Regulation of Wnt signaling and embryo patterning by an extracellular sulfatase. Science 293(5535):1663–1666. doi:10.1126/science.293.5535.1663
Ford-Perriss M, Guimond SE, Greferath U, Kita M, Grobe K, Habuchi H, Kimata K, Esko JD, Murphy M, Turnbull JE (2002) Variant heparan sulfates synthesized in developing mouse brain differentially regulate FGF signaling. Glycobiology 12(11):721–727
Giakoustidis A, Giakoustidis D, Mudan S, Sklavos A, Williams R (2015) Molecular signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma: role of and crosstalk among WNT/ß-catenin, Sonic Hedgehog, Notch and Dickkopf-1. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29(4):209–217
Gill R, Hitchins L, Fletcher F, Dhoot GK (2010) Sulf1A and HGF regulate satellite-cell growth. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 11):1873–1883. doi:10.1242/jcs.061242
Gill RB, Day A, Barstow A, Liu H, Zaman G, Dhoot GK (2011) Sulf2 gene is alternatively spliced in mammalian developing and tumour tissues with functional implications. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414(3):468–473. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.088
Gill RB, Day A, Barstow A, Zaman G, Chenu C, Dhoot GK (2012) Mammalian Sulf1 RNA alternative splicing and its significance to tumour growth regulation. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med 33(5):1669–1680. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0423-2
Gill RM, Michael A, Westley L, Kocher HM, Murphy JI, Dhoot GK (2014) SULF1/SULF2 splice variants differentially regulate pancreatic tumour growth progression. Exp Cell Res 324(2):157–171. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.04.001
Hitchins L, Fletcher F, Allen S, Dhoot GK (2013) Role of Sulf1A in Wnt1- and Wnt6-induced growth regulation and myoblast hyper-elongation. FEBS Open Bio 3:30–34. doi:10.1016/j.fob.2012.11.007
Joy MT, Vrbova G, Dhoot GK, Anderson PN (2015) Sulf1 and Sulf2 expression in the nervous system and its role in limiting neurite outgrowth in vitro. Exp Neurol 263:150–160. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.10.011
Kroy DC, Beraza N, Tschaharganeh DF, Sander LE, Erschfeld S, Giebeler A, Liedtke C, Wasmuth HE, Trautwein C, Streetz KL (2010) Lack of interleukin-6/glycoprotein 130/signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 signaling in hepatocytes predisposes to liver steatosis and injury in mice. Hepatology 51(2):463–473. doi:10.1002/hep.23322
Kwon YC, Bose SK, Steele R, Meyer K, Di Bisceglie AM, Ray RB, Ray R (2015) Promotion of cancer stem-like cell properties in hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocytes. J Virol 89(22):11549–11556. doi:10.1128/JVI.01946-15
Lai J, Chien J, Staub J, Avula R, Greene EL, Matthews TA, Smith DI, Kaufmann SH, Roberts LR, Shridhar V (2003) Loss of HSulf-1 up-regulates heparin-binding growth factor signaling in cancer. J Biol Chem 278(25):23107–23117. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302203200
Lai JP, Yu C, Moser CD, Aderca I, Han T, Garvey TD, Murphy LM, Garrity-Park MM, Shridhar V, Adjei AA, Roberts LR (2006) SULF1 inhibits tumor growth and potentiates the effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 130(7):2130–2144. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.02.056
Lai JP, Sandhu DS, Shire AM, Roberts LR (2008a) The tumor suppressor function of human sulfatase 1 (SULF1) in carcinogenesis. J Gastrointest Cancer 39(1–4):149–158. doi:10.1007/s12029-009-9058-y
Lai JP, Thompson JR, Sandhu DS, Roberts LR (2008b) Heparin-degrading sulfatases in hepatocellular carcinoma: roles in pathogenesis and therapy targets. Future Oncol 4(6):803–814. doi:10.2217/14796694.4.6.803
Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, van Zante A, Singer MS, Xue Q, Wang YQ, Tsay D, He B, Jablons DM, Rosen SD (2010) Sulf-2, a heparan sulfate endosulfatase, promotes human lung carcinogenesis. Oncogene 29(5):635–646. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.365
Merry CL, Gallagher JT (2002) New insights into heparan sulphate biosynthesis from the study of mutant mice. Biochem Soc Symp 69:47–57
Meyers-Needham M, Lewis JA, Gencer S, Sentelle RD, Saddoughi SA, Clarke CJ, Hannun YA, Norell H, da Palma TM, Nishimura M, Kraveka JM, Khavandgar Z, Murshed M, Cevik MO, Ogretmen B (2012) Off-target function of the Sonic hedgehog inhibitor cyclopamine in mediating apoptosis via nitric oxide-dependent neutral sphingomyelinase 2/ceramide induction. Mol Cancer Ther 11(5):1092–1102. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0705
Morimoto-Tomita M, Uchimura K, Werb Z, Hemmerich S, Rosen SD (2002) Cloning and characterization of two extracellular heparin-degrading endosulfatases in mice and humans. J Biol Chem 277(51):49175–49185. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205131200
Nawroth R, van Zante A, Cervantes S, McManus M, Hebrok M, Rosen SD (2007) Extracellular sulfatases, elements of the Wnt signaling pathway, positively regulate growth and tumorigenicity of human pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One 2(4):e392. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000392
Rosen SD, Lemjabbar-Alaoui H (2010) Sulf-2: an extracellular modulator of cell signaling and a cancer target candidate. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14(9):935–949. doi:10.1517/14728222.2010.504718
Sahota AP, Dhoot GK (2009) A novel SULF1 splice variant inhibits Wnt signalling but enhances angiogenesis by opposing SULF1 activity. Exp Cell Res 315(16):2752–2764. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.06.029
Schulze A, Gripon P, Urban S (2007) Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology 46(6):1759–1768
Shukla D, Liu J, Blaiklock P, Shworak NW, Bai X, Esko J, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ, Rosenberg RD, Spear PG (1999) A novel role for 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate in herpes simplex virus 1 entry. Cell 99(1):13–22
Tarocchi M, Polvani S, Marroncini G, Galli A (2014) Molecular mechanism of hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 20(33):11630–11640. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i33.11630
Tátrai P, Egedi K, Somorácz A, van Kuppevelt TH, Ten Dam G, Lyon M, Deakin JA, Kiss A, Schaff Z et al (2010) Quantitative and qualitative alterations of heparan sulfate in fibrogenic liver diseases and hepatocellular cancer. J Histochem Cytochem 58(5):429–441. doi:10.1369/jhc.2010.955161
Tuo JWY, Cheng R, Li Y, Chen M, Qiu F, Qian H, Shen D, Penalva R, Xu H, Ma JX, Chan CC (2015) Wnt signaling in age-related macular degeneration: human macular tissue and mouse model. J Transl Med 13(1):330–342. doi:10.1186/s12967-015-0683-x
Uchimura K, Morimoto-Tomita M, Bistrup A, Li J, Lyon M, Gallagher J, Werb Z, Rosen SD (2006) HSulf-2, an extracellular endoglucosamine-6-sulfatase, selectively mobilizes heparin-bound growth factors and chemokines: effects on VEGF, FGF-1, and SDF-1. BMC Biochem 7:2. doi:10.1186/1471-2091-7-2
Wang S, Ai X, Freeman SD, Pownall ME, Lu Q, Kessler DS, Emerson CP Jr (2004) QSulf1, a heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatase, inhibits fibroblast growth factor signaling in mesoderm induction and angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(14):4833–4838. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401028101
Wang S, Jiang W, Chen X, Zhang C, Li H, Hou W, Liu Z, McNutt MA, Lu F, Gang L (2012) Alpha-fetoprotein acts as a novel signal molecule and mediates transcription of Fn14 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 57(2):322–329. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.029
Xu G, Ji W, Su Y, Xu Y, Yan Y, Shen S, Li X, Sun B, Qian H, Chen L, Fu X, Wu M, Su C (2014) Sulfatase 1 (hSulf-1) reverses basic fibroblast growth factor-stimulated signaling and inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in animal model. Oncotarget 5(13):5029–5039
Xu Y, Martinez P, Séron K, Luo G, Allain F, Dubuisson J, Belouzard S (2015) Characterization of hepatitis C virus interaction with heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Virol 89(7):3846–3858. doi:10.1128/JVI.03647-14
Zaman G, Staines K, Farquharson C, Newton PT, Dudhia J, Chenu C, Pitsillides A, Dhoot GK (2016) Expression of Sulf1 and Sulf2 in cartilage, bone and endochondral fracture healing. Histochem Cell Biol 145(1):67–79
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by RVC research studentships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graham, K., Murphy, J.I. & Dhoot, G.K. SULF1/SULF2 reactivation during liver damage and tumour growth. Histochem Cell Biol 146, 85–97 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1425-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-016-1425-8