Abstract
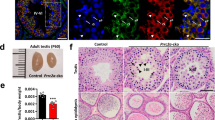
Nanos and pumilio bind each other to regulate translation of specific mRNAs in germ cells of model organisms, such as D. melanogaster or C. elegans. Recently described human homologues NANOS1 and PUMILIO2 form a complex similar to their ancestors. This study was aimed to identify the proteins interacting with NANOS1-PUMILIO2 complex in the human spermatogenic cells. Here, using the yeast two-hybrid system we found that NANOS1 and PUMILIO2 proteins interact with RNA DEAD-box helicase GEMIN3, a microRNA biogenesis factor. Moreover, GEMIN3 coimmunoprecipitates with NANOS1 and PUMILIO2 in transfected mammalian cells. By double immunofluorescence staining, we observed that complexes built of NANOS1, PUMILIO2 and GEMIN3 are located within cytoplasmic region of germ cells. These proteins condense to form a compact aggregate in the round spermatids of the human and mouse germ cells. This aggregate was reminiscent of the chromatoid body (CB), a perinuclear structure present in the mammalian male germ line. This structure is considered evolutionary remnant of germ plasm, a hallmark structure of germ cells in lower metazoan. Using a CB marker VASA protein, we demonstrated that CBs are present in the human round spermatids, as they are in the mouse. Moreover, NANOS1, PUMILIO2 and GEMIN3 colocalize with VASA protein. We demonstrated for the first time that a mammalian Nanos-Pumilio complex functions within CB, a center of RNA storing and processing, involving microRNAs. NANOS1-PUMILIO2 complex, together with GEMIN3 and small noncoding RNAs, possibly regulate mRNA translation within CB of the human germ cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asaoka-Taguchi M, Yamada M, Nakamura A, Hanyu K, Kobayashi S (1999) Maternal Pumilio acts together with Nanos in germline development in Drosophila embryos. Nat Cell Biol 1:431–437
Cauchi RJ, Davies KE, Liu JL (2008) A motor function for the DEAD-box RNA helicase, Gemin3, in Drosophila. Plos Genet 4:e1000265
Chemes HE, Fawcett DW, Dym M (1978) Unusual features of the nuclear envelope in human spermatogenic cells. Anat Rec 192:493–513
de Moor CH, Meijer H, Lissenden S (2005) Mechanisms of translational control by the 3′ UTR in development and differentiation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:49–58
Farrar MA, Johnston HM, Grattan-Smith P, Turner A, Kiernan MC (2009) Spinal muscular atrophy: molecular mechanisms. Curr Mol Med 9:851–862
Galgano A, Forrer M, Jaskiewicz L, Kanitz A, Zavolan M, Gerber AP (2008) Comparative analysis of mRNA targets for human PUF-family proteins suggests extensive interaction with the miRNA regulatory system. PLOS One 3:e3164
Ginter-Matuszewska B, Spik A, Rembiszewska A, Koyias C, Kupryjanczyk J, Jaruzelska J (2009) The SNARE-associated component SNAPIN binds PUMILIO2 and NANOS1 proteins in human male germ cells. Mol Hum Reprod 15:173–179
Grundhoff AT, Kremmer E, Türeci O, Glieden A, Gindorf C, Atz J, Mueller-Lantzsch N, Schubach WH, Grässer FA (1999) Characterization of DP103, a novel DEAD box protein that binds to the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins EBNA2 and EBNA3C. J Biol Chem 2:19136–19144
Jaruzelska J, Kotecki M, Kusz K, Spik A, Firpo M, Reijo Pera RA (2003) Conservation of a Pumilio-Nanos complex from Drosophila germ plasm to human germ cells. Dev Genes Evol 213:120–126
Kadyrova LY, Habara Y, Lee TH, Wharton RP (2007) Translational control of maternal Cyclin B mRNA by Nanos in the Drosophila germline. Development 134:1519–1527
Kotaja N, Sassone-Corsi P (2007) The chromatoid body: a germ-cell-specific RNA-processing centre. Mol Cell Biol 8:85–90
Kupryjanczyk J, Szymanska T, Madry R, Timorek A, Stelmachow J, Karpinska G, Rembiszewska A, Ziołkowska I, Kraszewska E, Debniak J et al (2003) Evaluation of clinical significance of TP53, BCL-2, BAX and MEK1 expression in 229 ovarian carcinomas treated with platinum-based regimen. Br J Cancer 88:848–854
Meister G, Bühler D, Laggerbauer B, Zobawa M, Lottspeich F, Fischer U (2000) Characterization of a nuclear 20S complex containing the survival of motor neurons (SMN) protein and a specific subset of spliceosomal Sm proteins. Hum Mol Genet 12:1977–1986
Moore FL, Jaruzelska J, Fox MS, Urano J, Firpo MT, Turek PJ, Dorfman DM, Pera RA (2003) Human Pumilio-2 is expressed in embryonic stem cells and germ cells and interacts with DAZ (Deleted in AZoospermia) and DAZ-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:538–543
Morris AR, Mukherjee N, Keene JD (2008) Ribonomic analysis of human Pum1 reveals cis-trans conservation across species despite evolution of diverse mRNA target sets. Mol Cell Biol 28:4093–4103
Mouillet JF, Yan X, Ou X, Jin L, Muglia LJ, Crawford PA, Sadovsky Y (2008) DEAD-box protein-103 (DP103, Ddx20) is essential for early embryonic development and modulates ovarian morphology and function. Endocrinology 149:2168–2175
Mourelatos Z, Dostie J, Paushkin S, Sharma A, Charroux B, Abel L, Rappsilber J, Mann M, Dreyfuss G (2002) miRNPs: a novel class of ribonucleoproteins containing numerous microRNAs. Genes Dev 16:720–728
Nagamori I, Sassone-Corsi P (2008) The chromatoid body of male germ cells: epigenetic control and miRNA pathway. Cell Cycle 7:3503–3508
Nelson PT, Hatzigeorgiou AG, Mourelatos Z (2004) miRNP:mRNA association in polyribosomes in a human neuronal cell line. RNA 10:387–394
Nolde MJ, Saka N, Reinert KL, Slack FJ (2007) The Caenorhabditis elegans pumilio homolog, puf-9, is required for the 3′UTR-mediated repression of the let-7 microRNA target gene, hbl-1. Dev Biol 15:551–563
O’Carroll D, Mecklenbrauker I, Das PP, Santana A, Koenig U, Enright AJ, Miska EA, Tarakhovsky A (2007) A slicer-independent role for Argonaute 2 in hematopoiesis and the microRNA pathway. Genes Dev 15:1999–2004
Parvinen M (2005) The chromatoid body in spermatogenesis. Int J Androl 28:189–201
Parvinen M, Parvinen LM (1979) Active movements of the chromatoid body. A possible transport mechanism for haploid gene products. J Cell Biol 80:621–628
Shpargel KB, Matera AG (2005) Gemin proteins are required for efficient assembly of Sm-class ribonucleoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:17372–17377
Spassov DS, Jurecic R (2002) Cloning and comparative sequence analysis of PUM1 and PUM2 genes, human members of the Pumilio family of RNA-binding proteins. Gene 16:195–204
Verrotti AC, Wharton RP (2000) Nanos interacts with cup in the female germline of Drosophila. Development 127:5225–5232
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Robert P Erickson and the members of Jaruzelska lab for comments on the manuscript, Aleksander Ratajczyk and Marcin Kujawa from laboratory of confocal microscopy at Adam Mickiewicz University for assistance while analyzing fluoroimmunohistochemical reactions, Dr. Krzysztof Deregowski for providing us with prenatal testis tissue sections and Dr. Friedrich A Grässer with anti-GEMIN3 antibodies. This work was supported by Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education (grant numbers N401129 32/2581 and N N401280833 to J.J., 6PO5E 001 21 and 3PO5E 013 25 to K.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ginter-Matuszewska, B., Kusz, K., Spik, A. et al. NANOS1 and PUMILIO2 bind microRNA biogenesis factor GEMIN3, within chromatoid body in human germ cells. Histochem Cell Biol 136, 279–287 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-011-0842-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-011-0842-y