Abstract
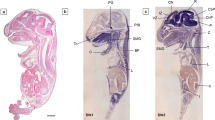
Notch and Delta signaling regulates cell-fate decisions in a variety of tissues in diverse organisms through cell-to-cell interactions. In this study we isolated a 696 bp fragment of chick Delta-like 4 (Dll4) cDNA and analyzed its expression pattern during chick development by in situ hybridization. We report a detailed description of cDll4 expression from HH-stage 8–30. Expression is seen in extraembryonic tissues and in the dorsal aorta throughout development but is absent from venules. Dll4 is expressed in the embryonic blood vessels, heart, somites, neural tube, limb, pharyngeal arches, esophagus, and in the developing eye. In accordance with the report from mice, cDll4 is a marker of the arterial type of endothelial cells. These analyses show that Dll4 is expressed in a wide range of tissues and organs suggesting its role in vascular development during chick embryogenesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999). Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284:770–776
Benedito R, Duarte A (2005). Expression of Dll4 during mouse embryogenesis suggests multiple developmental roles. Gene Expr Patterns 5:750–755
Bettenhausen B, Gossler A. 1995. Efficient isolation of novel mouse genes differentially expressed in early postimplantation embryos. Genomics 28:436–441
Boardman PE, Sanz-Ezquerro J, Overton IM, Burt DW, Bosch E, Fong WT, Tickle C, Brown WR, Wilson SA, Hubbard SJ (2002) A comprehensive collection of chicken cDNAs. Curr Biol 12:1965–1969
Claxton S, Fruttiger M (2004) Periodic Delta-like 4 expression in developing retinal arteries. Gene Expr Patterns 5:123–127
Cuadros MA, Martin C, Coltey P, Almendros A, Navascues J (1993) First appearance, distribution and origin of macrophages in the early development of the avain central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 330:113–129
Diez H, Fischer A, Winkler A, Hu CJ, Hatzopoulos AK, Breier G, Gessler M (2007) Hypoxia-mediated activation of Dll4-Notch-Hey2 signaling in endothelial progenitor cells and adoption of arterial cell fate. Exp Cell Res 313:1–9
Dorsch M, Zheng G, Yowe D, Rao P, Wang Y, Shen Q, Murphy C, Xiong X, Shi Q, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Fraser C, Villeval JL (2002) Ectopic expression of Delta4 impairs hematopoietic development and leads to lymphoproliferative disease. Blood 100:2046–2055
Dunwoodie SL, Henrique D, Harrison SM, Beddington RS (1997) Mouse Dll3: a novel divergent Delta gene which may complement the function of other Delta homologues during early pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development 124:3065–3076
Duarte A, Hirashima M, Benedito R, Trindade A, Diniz P, Bekman E, Costa L, Henrique D, Rossant J (2004) Dosage-sensitive requirement for mouse Dll4 in artery development. Genes Dev 18:2474–2478
Ellisen LW, Bird J, West DC, Soreng AL, Reynolds TC, Smith SD, Sklar J (1991) TAN−1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell 66:649–661
Fischer A, Schumacher N, Maier M, Sendtner M, Gessler M (2004) The Notch target genes Hey1 and Hey2 are required for embryonic vascular development. Genes Dev 18:901–911
Gale NW, Yancopoulos GD (1999) Growth factors acting via endothelial cell-specific receptor tyrosine kinases: VEGFs, angiopoietins, and ephrins in vascular development. Genes Dev 13:1055–1066
Gale NW, Dominguez MG, Noguera I, Pan L, Hughes V, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Adams NC, Lin HC, Holash J, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD (2004) Haploinsufficiency of delta-like 4 ligand results in embryonic lethality due to major defects in arterial and vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15949–15954
Greenwald I (1998) LIN−12/Notch signaling: lessons from worms and flies. Genes Dev 12:1751–1762
Gridley T (1997) Notch signaling in vertebrate development and disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 9:103–108
Hamburger V, Hamilton HL (1951) A series of normal stages in the development of chick embryo. J Morphol. 88:49–92
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, Shutter JR, Maguire M, Sundberg JP, Gallahan D, Closson V, Kitajewski J, Callahan R, Smith GH, Stark KL, Gridley T (2000) Notch signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes Dev 14:1343–1352
Krebs LT, Shutter JR, Tanigaki K, Honjo T, Stark KL, Gridley T (2004) Haploinsufficient lethality and formation of arteriovenous malformations in Notch pathway mutants. Genes Dev 18:2469–2473
Kurz H, Gärtner T, Eggli PS, Christ B (1996) First blood vessels in the avian neural tube are formed by a combination of dorsal angioblast immigration and ventral sprouting of endothelial cells. Dev Biol 173:133–147
Kurz H, Christ B (1998) Embryonic CNS macrophages and microglia do not stem from circulating, but from extravascular precursors. Glia 22:98–102
Kurz H, Korn J, Eggli PS, Huang R, Christ B (2001) Embryonic central nervous system angiogenesis does not involve blood-borne endothelial progenitors. J Comp Neurol 436:263–274
Lawson ND, Weinstein BM (2002) Arteries and veins: making a difference with zebrafish. Nat Rev Genet 3:674–682
Lawson ND, Scheer N, Pham VN, Kim CH, Chitnis AB, Campos-Ortega JA, Weinstein BM (2001) Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular development. Development 128:3675–3683
Lawson ND, Mugford JW, Diamond BA, Weinstein BM (2003) phospholipase C gamma-1 is required downstream of vascular endothelial growth factor during arterial development. Genes Dev 17:1346–1351
Lardelli M, Dahlstrand J, Lendahl U (1994) The novel Notch homologue mouse Notch 3 lacks specific epidermal growth factor-repeats and is expressed in proliferating neuroepithelium. Mech Dev 46:123–136
Licht AH, Muller-Holtkamp F, Flamme I, Breier G (2006) Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor activity in endothelial cells disrupts embryonic cardiovascular development. Blood 107:584–590
Lindsell CE, Shawber CJ, Boulter J, Weinmaster G (1995) Jagged: a mammalian ligand that activates Notch1. Cell 80:909–917
Liu ZJ, Shirakawa T, Li Y, Soma A, Oka M, Dotto GP, Fairman RM, Velazquez OC, Herlyn M (2003) Regulation of Notch1 and Dll4 by vascular endothelial growth factor in arterial endothelial cells: implications for modulating arteriogenesis and angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 23:14–25
Mailhos C, Modlich U, Lewis J, Harris A, Bicknell R, Ish-Horowicz D (2001) Delta4, an endothelial specific notch ligand expressed at sites of physiological and tumor angiogenesis. Differentiation 69:135–144
Nieto MA, Patel K, Wilkinson DG (1996) In situ hybridization analysis of chick embryos in whole mount and tissue sections. Methods Cell Biol 51:219–235
Nye JS, Kopan R (1995) Developmental signaling vertebrate ligands for Notch. Curr Biol 5:966–969
Noguera-Troise I, Daly C, Papadopoulos NJ, Coetzee S, Boland P, Gale NW, Lin HC, Yancopoulas GD, Thurston G (2006) Blockade of Dll4 inhibits tumour growth by promoting non-productive angiogenesis. Nature 444:1032–1037
Pardanaud L, Yassine F, Dieterlen-Lievre F (1989) Relationship between vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and haemopoiesis during avian ontogeny. Development 105:473–485
Patel NS, Dobbie MS, Rochester M, Steers G, Poulsom R, Le Monnier K, Cranston DW, Li JL, Harris AL (2006) Up-regulation of endothelial delta-like 4 expression correlates with vessel maturation in bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:4836–4844
Ridgway J, Zhang G, Wu Y, Stawicki S, Liang WC, Chanthery Y, Kowalski J, Watts RJ, Callahan C, Kasman I, Singh M, Chein M, Tan c, Hongo JA, de Sauvage F, Plowman G, Yan M (2006) Inhibition of Dll4 signalling inhibits tumour growth by deregulating angiogenesis. Nature 444:1083–1087
Rossant J, Howard L (2002) Signaling pathways in vascular development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:541–573
Scehnet JS, Jiang W, Ram Kumar S, Krasnoperov V, Trindade A, Benedito R, Djokovic D, Borges C, Ley EJ, Duarte A, Gill PS (2007) Inhibition of Dll4-mediated signaling induces proliferation of immature vessels and results in poor tissue perfusion. Blood 109:4753–4760
Shawber C, Boulter J, Lindsell CE, Weinmaster G (1996) Jagged2: a serrate-like gene expressed during rat embryogenesis. Dev Biol 180:370–376
Shawber CJ, Das I, Francisco E, Kitajewski J (2003) Notch signaling in primary endothelial cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 995:162–170
Shutter JR, Scully S, Fan W, Richards WG, Kitajewski J, Deblandre GA, Kintner CR, Stark KL (2000) Dll4, a novel Notch ligand expressed in arterial endothelium. Genes Dev 14:1313–1318
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature 359:843–845
Uyttendaele H, Marazzi G, Wu G, Yan Q, Sassoon D, Kitajewski J (1996) Notch4/int−3, a mammary proto-oncogene, is an endothelial cell-specific mammalian Notch gene. Development 122:2251–2259
Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ (1998) Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell 93:741–753
Weinmaster G (1997) The ins and outs of notch signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci 9:91–102
Weinmaster G, Roberts VJ, Lemke G (1992) Notch2: a second mammalian Notch gene. Development 116:931–941
Williams CK, Li JL, Murga M, Harris AL, Tosato G (2006) Up-regulation of the Notch ligand Delta-like 4 inhibits VEGF-induced endothelial cell function. Blood 107:931–939
Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J (2000) Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature 407:242–248
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Ulrike Pein, Diana Schätzle-Wangler for their excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Hu 792/2) to RH and (SFB−592, A1 to B.C and M.S).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nimmagadda, S., Geetha-Loganathan, P., Pröls, F. et al. Expression pattern of Dll4 during chick embryogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol 128, 147–152 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-007-0306-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-007-0306-6