Abstract
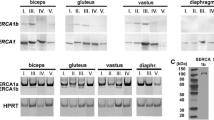
The sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) is a membrane protein that plays a crucial role in muscle relaxation by transporting cytosolic Ca2+ into the lumen of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum. In this study, the presence of SERCA1 and SERCA2 was investigated in human intrafusal fibers by immunocytochemistry. Nuclear bag1 fibers contained both SERCA1 and SERCA2 isoforms, with predominant staining seen with SERCA2 in the A and B regions. Most nuclear bag2 fibers also contained SERCA1 and SERCA2 isoforms and their coexistence frequently occurred in the A region. SERCA1 was present whereas SERCA2 was generally absent in the nuclear chain fibers. The staining intensity seen with the SERCA1 monoclonal antibody varied in the order of chain>bag1>bag2. The expression of SERCA1 isoform was found to correlate with the presence of fast myosin heavy chain (MyHC) isoform in nuclear chain fibers, whereas for nuclear bag fibers there was no such apparent correlation between patterns of expression of SERCA and MyHC isoforms. The phenotype revealed for the human bag fibers was very sophisticated and adapted to attain a very wide range of contraction and relaxation velocities.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awede B, Berquin A, Wuytack F, Lebacq J (1999) Adaptation of mouse skeletal muscle to a novel functional overload test: changes in myosin heavy chains and SERCA and physiological consequences. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 80:519–526
Barker D, Banks RW (1994) The muscle spindle. In: Engel AG, Franzini-Armstrong C (eds) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 333–360
Bigard AX, Zoll J, Ribera F, Mateo P, Sanchez H, Serrurier B, Ventura-Clapier R (2001) Influence of overload on phenotypic remodeling in regenerated skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1686–C1694
Bottinelli R, Reggiani C (2000) Human skeletal muscle fibres: molecular and functional diversity. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 73:195–262
Boyd IA (1980) The isolated mammalian muscle spindle. Trends Neurosci 3:258–265
Boyd IA (1981) The muscle spindle controversy. Sci Prog 67:205–221
Brandl CJ, Green NM, Korczak B, MacLennan DH (1986) Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell 44:597–607
Brandl CJ, deLeon S, Martin DR, MacLennan DH (1987) Adult forms of the Ca2+ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Expression in developing skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 262:3768–3774
Burk SE, Lytton J, MacLennan DH, Shull GE (1989) cDNA cloning, functional expression, and mRNA tissue distribution of a third organellar Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem 264:18561–18568
Close RI (1967) Properties of motor units in fast and slow skeletal muscle of the rat. J Physiol 193:45–55
Dubowitz V (1985) Muscle biopsy: a practical approach, 2nd edn. Bailliere Tindall, London
Dux L (1993) Muscle relaxation and sarcoplasmic reticulum function in different muscle types. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 122:69–147
Eriksson PO, Butler-Browne GS, Thornell LE (1994) Immunohistochemical characterization of human masseter muscle spindles. Muscle Nerve 17:31–41
Gelebart P, Martin V, Enouf J, Papp B (2003) Identification of a new SERCA2 splice variant regulated during monocytic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:676–684
Hamalainen N, Pette D (1997) Coordinated fast-to-slow transitions of myosin and SERCA isoforms in chronically stimulated muscles of euthyroid and hyperthyroid rabbits. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 18:545–554
Hamalainen N, Pette D (2001) Myosin and SERCA isoform expression in denervated slow-twitch muscle of euthyroid and hyperthyroid rabbits. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 22:453–457
Hughes SM, Cho M, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Travis M, Silberstein L, Leinwand LA, Blau HM (1993) Three slow myosin heavy chains sequentially expressed in developing mammalian skeletal muscle. Dev Biol 158:183–199
Jacoby J, Ko K (1993) Sarcoplasmic reticulum fast Ca(2+)-pump and myosin heavy chain expression in extraocular muscles. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 34:2848–2858
Kjellgren D, Ryan M, Ohlendieck K, Thornell LE, Pedrosa-Domellöf F (2003) Sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA1 and 2) in human extraocular muscles. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci (in press)
Larsson L, Moss RL (1993) Maximum velocity of shortening in relation to myosin isoform composition in single fibres from human skeletal muscles. J Physiol Lond 472:595–614
Liu JX, Eriksson PO, Thornell LE, Pedrosa-Domellof F (2002) Myosin heavy chain composition of muscle spindles in human biceps brachii. J Histochem Cytochem 50:171–184
Liu JX, Thornell LE, Pedrosa-Domellof F (2003) Muscle spindles in the deep muscles of the human neck. A morphological and immunocytochemical study. J Histochem Cytochem 51:175–186
Lompre A-M (1998) The sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPases in the cardiovascular system during growth and proliferation. Trends Cardiovasc Med 8:75–82
MacLennan DH, Brandl CJ, Korczak B, Green NM (1985) Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature 316:696–700
Maier A, Leberer E, Pette D (1988) Distribution of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase and of calsequestrin at the polar regions of rat, rabbit and cat intrafusal fibers. Histochemistry 88:273–276
Martin V, Bredoux R, Corvazier E, Van Gorp R, Kovacs T, Gelebart P, Enouf J (2002) Three novel sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) 3 isoforms. Expression, regulation, and function of the membranes of the SERCA3 family. J Biol Chem 277:24442–24452
Martonosi A (1994) Regulation of calcium by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. In: Engel AG, Franzini-Armstrong C (eds) Myology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 553–606
Matthews PB (1981) Evolving views on the internal operation and functional role of the muscle spindle. J Physiol 320:1–30
Moller JV, Juul B, le Maire M (1996) Structural organization, ion transport, and energy transduction of P-type ATPases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1286:1–51
Molnar E, Seidler NW, Jona I, Martonosi AN (1990) The binding of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum: effects on interactions between ATPase molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta 1023:147–167
Moss RL, Diffee GM, Greaser ML (1995) Contractile properties of skeletal muscle fibers in relation to myofibrillar protein isoforms. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 126:1–63
Ogata T, Yamasaki Y (1991) Ultra-high-resolution scanning electron microscopic studies on the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of the rat intrafusal muscle fibers, part I. The capsular sleeve region. Arch Histol Cytol 54:471–490
Ogata T, Yamasaki Y (1992) Ultra-high-resolution scanning electron microscopic studies on the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of the rat intrafusal muscle fibers, part II. The extracapsular region. Arch Histol Cytol 55:117–124
Ogata T, Yamasaki Y (1993) Ultra-high resolution scanning electron microscopic studies on the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in various muscles: a review. Scanning Microsc 7:145–156
Ovalle WK Jr (1971) Fine structure of rat intrafusal muscle fibers. The polar region. J Cell Biol 51:83–103
Ovalle WK Jr (1972) Fine structure of rat intrafusal muscle fibers. The equatorial region. J Cell Biol 52:382–396
Ovalle WK, Smith RS (1972) Histochemical identification of three types of intrafusal muscle fibers in the cat and monkey based on the myosin ATPase reaction. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 50:195–202
Pedrosa Domellof F, Thornell LE (1994) Expression of myosin heavy chain isoforms in developing human muscle spindles. J Histochem Cytochem 42:77–88
Pette D (1985) Metabolic heterogeneity of muscle fibres. J Exp Biol 115:179–189
Pette D, Staron RS (1990) Cellular and molecular diversities of mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 116:1–76
Quiroz-Rothe E, Rivero JL (2001) Co-ordinated expression of contractile and non-contractile features of control equine muscle fibre types characterised by immunostaining of myosin heavy chains. Histochem Cell Biol 116:299–312
Sawchak JA, Leung B, Shafiq SA (1985) Characterization of a monoclonal antibody to myosin specific for mammalian and human type II muscle fibers. J Neurol Sci 69:247–254
Schiaffino S, Reggiani C (1996) Molecular diversity of myofibrillar proteins: gene regulation and functional significance. Physiol Rev 76:371–423
Shull GE (2000) Gene knockout studies of Ca2+-transporting ATPases. Eur J Biochem 267:5284–5290
Sohn A, Kaidoh T, Inoue T (1999) Scanning electron microscopic observation on the equatorial region of the rat intrafusal muscle fibres, especially on the subsarcolemmal sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 48:659–663
Sternberger L (1979) Immunohistochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Talmadge RJ, Roy RR, Chalmers GR, Edgerton VR (1996) MHC and sarcoplasmic reticulum protein isoforms in functionally overloaded cat plantaris muscle fibers. J Appl Physiol 80:1296–1303
Wu KD, Lee WS, Wey J, Bungard D, Lytton J (1995) Localization and quantification of endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase isoform transcripts. Am J Physiol 269:C775–C784
Zhang KM, Hu P, Wang SW, Wright LD, Wechsler AS, Spratt JA, Briggs FN (1997) Fast- and slow-twitch isoforms (SERCA1 and SERCA2a) of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase are expressed simultaneously in chronically stimulated muscle fibers. Pflugers Arch 433:766–772
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Donald A. Fischman for kindly providing antibody ALD 19. This work was supported by grants from the Medical Faculty of Umeå University and by the Swedish Research Council (12X-03934).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, JX., Thornell, LE. & Pedrosa-Domellöf, F. Distribution of SERCA isoforms in human intrafusal fibers. Histochem Cell Biol 120, 299–306 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0569-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0569-5