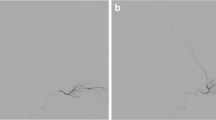
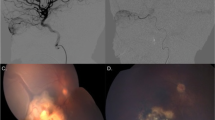
Abstract
Purpose
To identify the specific clinical and angiographic variables that determine the success of intra-arterial chemotherapy (IAC) in a patient with retinoblastoma.
Methods
Medical records from patients undergoing intra-arterial chemotherapy for the treatment of retinoblastoma between January 2015 and June 2020 within a large academic ocular oncology practice were retrospectively reviewed. Demographics were recorded together with clinical, ocular, and angiographic variables such as the diameter of the ophthalmic artery (OA), angle of ophthalmic artery takeoff, and branching pattern of ophthalmic vasculature.
Results
Forty-four eyes from 33 patients with retinoblastoma treated with IAC were identified. Over the total 32 mean months of follow-up, these patients received 144 total catheterizations and a mean of 3.2 IAC cycles for each eye. The number of IAC cycles and the chemotherapeutic agent used did not vary significantly with worsening International Classification of Retinoblastoma (ICRB) groups (P > 0.1). Cumulative dose did not vary with the ICRB group for eyes treated with melphalan, topotecan, or carboplatin (P > 0.1). A higher ICRB group was associated with a smaller mean ophthalmic artery diameter across all procedures (P = 0.016), and femoral artery diameter did not vary significantly between ICRB groups (P = 0.906). A higher cumulative dose of IAC was significantly associated with a smaller takeoff angle of the OA (melphalan, P = 0.011; topotecan, P = 0.009; carboplatin, P = 0.031) in patients who underwent successful IAC procedures. Ophthalmic artery diameter and femoral artery diameter did not have a significant association (P > 0.1) with higher IAC doses in successful IACs. Cumulative IAC dose was not significantly associated with ophthalmic vasculature branching pattern, presence of choroidal blush, temporary OA vasospasm reported during the procedure, and OA occlusion upon microcatheter placement.
Conclusion
In this study, neurosurgical angioanatomy appeared to influence the cumulative dose of chemotherapy needed during IAC for retinoblastoma. In the future, these anatomic variables may be used to guide the frequency of monitoring, dosing, and estimation of recurrence risk.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grigorovski N, Lucena E, Mattosinho C et al (2014) Use of intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: results of a survey. Int J Ophthalmol 7(4):726–730
Francis JH, Levin AM, Zabor EC, Gobin YP, Abramson DH (2018) Ten-year experience with ophthalmic artery chemosurgery: ocular and recurrence-free survival. PLoS One 13(5):e0197081
Chen Q, Zhang B, Dong Y et al (2018) Comparison between intravenous chemotherapy and intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 18:486
Biancotto C, Shields CL, Iturralde JC, Sarici A, Jabbour P, Shields JA (2012) Fluorescein angiographic findings after intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 119(4):843–849
Reddy MA, Naeem Z, Duncan C et al (2017) Reduction of severe visual loss and complications following intra-arterial chemotherapy (IAC) for refractory retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol 101(12):1704–1708
Yamane T, Kaneko A, Mohri M (2004) The technique of ophthalmic arterial infusion therapy for patients with intraocular retinoblastoma. Int J Clin Oncol 9(2):69–73
Suzuki S, Kaneko A (2004) Management of intraocular retinoblastoma and ocular prognosis. Int J Clin Oncol 9(1):1–615162819
Abramson DH, Dunkel IJ, Brodie SE, Kim JW, Gobin YP (2008) A phase I/II study of direct intraarterial (ophthalmic artery) chemotherapy with melphalan for intraocular retinoblastoma initial results. Ophthalmology 115(8):1398–404, 1404.e1
Abramson DH, Dunkel IJ, Brodie SE, Marr B, Gobin YP (2010) Superselective ophthalmic artery chemotherapy as primary treatment for retinoblastoma (chemosurgery). Ophthalmology 117(8):1623–1629
Shields CL, Bianciotto CG, Jabbour P et al (2011) Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: report No. 1, control of retinal tumors, subretinal seeds, and vitreous seeds. Arch Ophthalmol 129(11):1399–406
Shields CL, Kaliki S, Shah SU et al (2012) Minimal exposure (one or two cycles) of intra-arterial chemotherapy in the management of retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 119(1):188–192
Yousef YA, Soliman SE, Astudillo PPP et al (2016) Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: a systematic review. JAMA Ophthalmol 134(5):584–591
Shields CL, Manjandavida FP, Lally SE et al (2014) Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma in 70 eyes: outcomes based on the international classification of retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology 121(7):1453–1460
Abramson DH, Marr BP, Dunkel IJ et al (2012) Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma in eyes with vitreous and/or subretinal seeding: 2-year results. Br J Ophthalmol 96:499–502
Marr BP, Hung C, Gobin YP, Dunkel IJ, Brodie SE, Abramson DH (2012) Success of intra-arterial chemotherapy (chemosurgery) for retinoblastoma: effect of orbitovascular anatomy. Arch Ophthalmol 130(2):180–185
Francis JH, Levin AM, Zabor EC et al (2018) Ten-year experience with ophthalmic artery chemosurgery: ocular and recurrence-free survival. PLoS ONE 13:e0197081
Stenzel E, Göricke S, Temming P et al (2019) Feasibility of intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: experiences in a large single center cohort study. Neuroradiology 61:351–357
Area C, Yen CJ, Chevez-Barrios P et al (2019) Technical and anatomical factors affecting intra-arterial chemotherapy fluoroscopy time and radiation dose for intraocular retinoblastoma. J NeuroInterv Surg 11:1273–1276
Sweid A, Hammoud B, Weinberg JH et al (2020) Ophthalmic artery catheterization for retinoblastoma treatment: does reflux affect tumor response? J NeuroInterv Surg 12:915–920
Sweid A, El Naamani K, Sajja KC et al (2021) Incidence and predictors of ophthalmic artery occlusion in intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. J NeuroInterv Surg 13:652–656
Zhou M, Wen X, Jia S et al (2022) Risk factors for ophthalmic artery stenosis and occlusion in patients with retinoblastoma treated with intra-arterial chemotherapy. Br J Ophthalmol 106:1581–1586
Kim RS, Dannenbaum MJ, Lin MW, Bretana ME, Brown DL, Schefler AC (2018) Use of femoral artery ultrasound during intraarterial chemotherapy for children under 10 kg with retinoblastoma. Retina 38(7):1420–1426
Klufas MA, Gobin YP, Marr B et al (2012) Intra-arterial chemotherapy as a treatment for intraocular retinoblastoma: alternatives to direct ophthalmic artery catheterization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1608–1614
Bertelli E, Leonini S, Galimberti D et al (2016) Hemodynamic and anatomic variations require an adaptable approach during intra-arterial chemotherapy for intraocular retinoblastoma: alternative routes, strategies, and follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:1289–1295
Gobin YP, Dunkel IJ, Marr BP et al (2011) Intra-arterial chemotherapy for the management of retinoblastoma: four-year experience. Arch Ophthalmol 129:732–737
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by AR, MN, BZ, and MB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AR and AS. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical compliance
Institutional review board (Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas; University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston) approval for chart review was obtained. All study procedures adhered to the tenets set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rusakevich, A.M., Nahhas, M.I., Zhou, B. et al. Angiographic characteristics and treatment approach in patients undergoing intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 262, 1321–1328 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-023-06279-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-023-06279-8