Abstract
Purpose
Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) is an important cytokine released after ocular surface injury to promote wound healing. However, its persistence at the injury site triggers a fibrotic response that leads to corneal scarring and opacity. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are synthetic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) ligands used to regulate glucose and lipid metabolism in the management of type 2 diabetes. Studies have also showed TZDs have antifibrotic effect. In this study, we investigated the antifibrotic effect of the TZD lobeglitazone on TGF-β1-induced fibrosis in corneal fibroblasts.
Methods
Human primary corneal fibroblasts were cultivated and treated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) to induce fibrosis, with or without pre-treatments with different concentrations of lobeglitazone. Myofibroblast differentiation and extracellular matrix (ECM) protein expression was evaluated by western blotting, immunofluorescence, real-time PCR, and collagen gel contraction assay. The effect of lobeglitazone on TGF-β1-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation was evaluated by DCFDA–cellular ROS detection assay kit. Signaling proteins were evaluated by western blotting to determine the mechanism underlying the antifibrotic effect.
Results
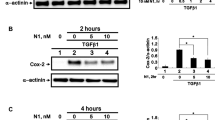
Our results showed lobeglitazone attenuated TGF-β1-induced ECM synthesis and myofibroblast differentiation of corneal fibroblasts. This antifibrotic effect appeared to be independent of PPAR signaling and rather due to the inhibition of the TGF-β1-induced Smad signaling. Lobeglitazone also blocked TGF-β1-induced ROS generation and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (Nox) 4 transcription.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that lobeglitazone may be a promising therapeutic agent for corneal scarring.
Key messages







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Yes
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Wilson SE (2019) Coordinated modulation of corneal Scarring by the epithelial basement membrane and Descemet’s basement membrane. J Refract Surg 35(8):506–516
Fini ME (1999) Keratocyte and fibroblast phenotypes in the repairing cornea. Prog. Retin. Eye Res 18:529–551
Friedlander M (2007) Fibrosis and diseases of the eye. J Clin Invest 117:576–586
Torricelli AA, Santhanam A, Wu J, Singh V, Wilson SE (2016) The corneal fibrosis response to epithelial-stromal injury. Exp. Eye Res 142:110–118
Saika S (2006) TGF-β pathobiology in the eye. Lab Investig 86:106–115
Tandon A, Tovey JC, Sharma A, Gupta R, Mohan RR (2010) Role of transforming growth factor Beta in corneal function, biology and pathology. Curr Mol Med 10:565–578
Wilson SE (2020) Corneal myofibroblasts and fibrosis. Exp Eye Res 201:108272
Louise M, Carrington JA, Anderson I, Kamma C, Boulton M (2006) Differential regulation of key stages in early corneal wound healing by TGF-β isoforms and their inhibitors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:1886–1894
Shu DY, Lovicu FJ (2017) Myofibroblast transdifferentiation: the dark force in ocular wound healing and fibrosis. Prog Retin Eye Res 60:44–65
Wilson SE (2012) Corneal myofibroblast biology and pathobiology: generation, persistence, and transparency. Exp Eye Res 99:78–88
Kaur H, Chaurasia SS, Agrawal V, Suto C, Wilson SE (2009) Corneal myofibroblast viability: opposing effects of IL-1 and TGF beta1. Exp Eye Res 89:152–158
Torricelli AA, Singh V, Santhiago MR, Wilson SE (2013) The corneal epithelial basement membrane: structure, function, and disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:6390–6400
Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, Kajimura S, Boström P, Laznik D, Ruas JL, Chalmers MJ, Kamenecka TM, Blüher M, Griffin PR, Spiegelman BM (2010) Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPAR-γ 3 by Cdk5. Nature. 466:451–456
Thangavel N, Al Bratty M, Javed SA, Ahsan W, Alhazmi HA (2017) Targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors using thiazolidinediones: strategy for design of novel antidiabetic drugs. Int J Med Chem 2017:1069718
Burgess HA, Daugherty LE, Thatcher TH, Lakatos HF, Ray DM, Redonnet M, Phipps RP, Sime PJ (2005) PPAR gamma agonists inhibit TGF-beta induced pulmonary myofibroblast differentiation and collagen production: implications for therapy of lung fibrosis. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 288:L1146–L1153
Ghosh AK, Bhattacharyya S, Lakos G, Chen SJ, Mori Y, Varga J (2004) Disruption of transforming growth factor beta signaling and profibrotic responses in normal skin fibroblasts by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Arthritis Rheum 50:1305–1318
Jeon K-I, Kulkarni A, Woeller CF, Phipps RP, Sime PJ, Hindman HB, Huxlin KR (2014) Inhibitory effects of PPARγ ligands on TGF-β1-induced corneal myofibroblast transformation. Am J Pathol 184:1429–1445
Kawai T, Masaki T, Doi S, Arakawa T, Yokoyama Y, Doi T, Kohno N, Yorioka N (2009) PPAR-gamma agonist attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis and inflammation through reduction of TGF-beta. Lab Investig 89:47–58
Liu Y, Dai B, Xu C, Fu L, Hua Z, Mei C (2011) Rosiglitazone inhibits transforming growth factor-beta 1 mediated fibrogenesis in ADPKD cyst-lining epithelial cells. PLoS One 6:e28915
Milam JE, Keshamouni VG, Phan SH, Hu B, Gangireddy SR, Hogaboam CM, Standiford TJ, Thannickal VJ, Reddy RC (2008) PPAR-γ agonists inhibit profibrotic phenotypes in human lung fibroblasts and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 294:L891–L901
Zheng F, Fornoni A, Elliot SJ, Guan Y, Breyer MD, Striker LJ, Striker GE (2002) Upregulation of type I collagen by TGF-beta in mesangial cells is blocked by PPAR gamma activation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol 282:F639–F648
Shi-wen X, Eastwood M, Stratton RJ, Denton CP, Leask A, Abraham DJ (2010) Rosiglitazone alleviates the persistent fibrotic phenotype of lesional skin scleroderma fibroblasts. Rheumatology 49:259–263
Saika S, Yamanaka O, Okada Y, Miyamoto T, Kitano A, Flanders KC, Ohnishi Y, Nakajima Y, Kao WWY, Ikeda K (2007) Effect of overexpression of PPAR gamma on the healing process of corneal alkali burn in mice. Am J Phys Cell Phys 293(1):C75–C86
Jang JY, Bae H, Lee YJ, Choi YI, Kim H-J, Park SB, Suh SW, Kim SW, Han BW (2018) Structural basis for the enhanced anti-diabetic efficacy of lobeglitazone on PPAR-γ. Sci Rep 8:31
Kroker AJ, Bruning JB (2015) Review of the structural and dynamic mechanisms of PPAR-γ partial agonism. PPAR Res 2015:816856
Lee MA, Tan L, Yang H, Im Y-G, Im YJ (2017) Structures of PPARγ complexed with lobeglitazone and pioglitazone reveal key determinants for the recognition of antidiabetic drugs. Sci Rep 7:16837
Nuwormegbe SA, Sohn JH, Kim SW (2017) A PPAR-gamma agonist rosiglitazone suppresses fibrotic response in human pterygium fibroblasts by modulating the p38 MAPK pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 58:5217–5226
Bruning JB, Chalmers MJ, Prasad S, Busby SA, Kamenecka TM, He Y, Nettles KW, Griffin PR (2007) Partial agonists activate PPARγ using a helix 12 independent mechanism. Structure 15:1258–1271
Jester JV, Huang J, Fisher S, Spiekerman J, Chang JH, Wright WE, Shay JW (2003) Myofibroblast differentiation of normal human keratocytes and hTERT, extended-life human corneal fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:1850–1858
Nuwormegbe SA, Kim SW (2020) AMPK activation by 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxamide riboside-1-β-D-ribofuranoside attenuates alkali injury-induced corneal fibrosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 61:43
Bickel PE, Tansey JT, Welte MA (2009) PAT proteins, an ancient family of lipid droplet proteins that regulate cellular lipid stores. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791:419–440
Liu RM, Desai LP (2015) Reciprocal regulation of TGF-β and reactive oxygen species: a perverse cycle for fibrosis. Redox Biol 6:565–577
Ahmadian M, Suh JM, Hah N, Liddle C, Atkins AR, Downes M, Evans RM (2013) PPARγ signaling and metabolism: the good, the bad and the future. Nat Med 19:557–566
Mangelsdorf DJ, Thummel C, Beato M, Herrlich P, Schütz G, Umesono K, Blumberg B, Kastner P, Mark M, Chambon P, Evans RM (1995) The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell 83:835–839
Wei J, Bhattacharyya S, Jain M, Varga J (2012) Regulation of matrix remodeling by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma: a novel link between metabolism and fibrogenesis. Open Rheumatol J 6:103–115
Huxlin KR, Hindman HB, Jeon K-I, Bühren J, MacRae S, DeMagistris M, Ciufo D, Sime PJ, Phipps RP (2013) Topical rosiglitazone is an effective anti-scarring agent in the cornea. PLoS One 8:e70785
Kuriyan AE, Lehmann GM, Kulkarni AA, Woeller CF, Feldon SE, Hindman HB, Sime PJ, Huxlind KR, Phipps RP (2012) Electrophilic PPAR gamma ligands inhibit corneal fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation in vitro: a potentially novel therapy for corneal scarring. Exp. Eye Res 94:136–145
Ferguson HE, Kulkarni A, Lehmann GM, Garcia-Bates TM, Thatcher TH, Huxlin KR, Phipps RP, Sime PJ (2009) Electrophilic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands have potent antifibrotic effects in human lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41:722–730
Hogan CM, Thatcher TH, Sapinoro RE, Gurell MN, Ferguson HE, Pollock SJ, Jones C, Phipps RP, Sime PJ, Drew P (2011) Electrophilic PPAR ligands attenuate IL-1 and silica-induced inflammatory mediator production in human lung fibroblasts via a PPAR-γ independent mechanism. PPAR Res 2011:318134
Hu H-H, Chen D-Q, Wang Y-N, Feng Y-L, Cao G, Vaziri ND, Zhao Y-Y (2018) New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact 292:76–83
Bae K-H, Seo JB, Seo H-Y, Kang SH, Jeon H-J, Lee JM, Lee S, Kim J-G, Lee I-K, Jung G-S, Park KG (2017) Lobeglitazone, a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonist, attenuates renal fibrosis caused by unilateral ureteral obstruction in mice. Endocrinol Metab 32:115–123
Jiang F, Liu G-S, Dusting GJ, Chan EC (2014) NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signaling in TGF-β-mediated fibrotic responses. Redox Biol 2:267–272
Yeh YH, Kuo CT, Chang GJ, Qi XY, Nattel S, Chen WJ (2013) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 mediates the differential responsiveness of atrial versus ventricular fibroblasts to transforming growth factor-beta. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 6:790–798
Bondi CD, Manickam N, Lee DY, Block K, Gorin Y, Abboud HE, Barnes JL (2010) NAD(P)H oxidase mediates TGF-β1–induced activation of kidney myofibroblasts. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:93–102
Brown KD, Shah MH, Liu GS, Chan EC, Crowston JG, Peshavariya HM (2017) Transforming growth factor β1-induced NADPH oxidase-4 expression and fibrotic response in conjunctival fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 58:3011–3017
Hakami NY, Dusting GJ, Chan EC, Shah MH, Peshavariya HM (2020) Wound healing after alkali burn injury of the cornea involves Nox4-type NADPH oxidase. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 61:20
Shah MH, Chan EC, Van Bergen NJ, Pandav SS, Ng S, Crowston JG, Peshavariya HM (2020) Nox4 facilitates TGF beta 1-induced fibrotic response in human tenon’s fibroblasts and promotes wound collagen accumulation in murine model of glaucoma filtration surgery. Antioxidants. 9:1126
Gong Y, Yang Y (2020) Activation of Nrf2/AREs-mediated antioxidant signalling, and suppression of profibrotic TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway: a promising therapeutic strategy for hepatic fibrosis—a review. Life Sci 256:117909
Li WQ, Qureshi HY, Liacini A, Dehnade F, Zafarullah M (2004) Transforming growth factor Beta 1 induction of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 3 in articular chondrocytes is mediated by reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 37(2):196–207
Inoue I, Katayama S, Takahashi K, Negishi K, Miyazaki T, Sonoda M et al (1997) Troglitazone has a scavenging effect on reactive oxygen species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 235:113–116
Lee YS, Park JS, Lee DH, Lee DK, Kwon SW, Lee BW, Bae SH (2018) The antidiabetic drug lobeglitazone protects mice from lipogenesis-induced liver injury via mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 inhibition. Front Endocrinol 9:539
Lee HW, Kim BY, Ahn JB, Kang SK, Lee JH, Shin JS, Ahn SK, Lee SJ, Yoon SS (2005) Molecular design, synthesis, and hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of novel pyrimidine derivatives having thiazolidinedione. Eur J Med Chem 40:862–874
Kim SG, Kim DM, Woo J-T, Jang HC, Chung CH, Ko KS, Park JH, Park YS, Kim SJ, Choi DS (2014) Efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus over 24-weeks: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo controlled trial. PLoS One 9:92843
Lee HS, Chang M, Lee J-E, Kim W, Hwang I-C, Kim D-H, Park H-K, Choi H-J, Jo W, Cha SW, Son WC (2014) Carcinogenicity study of CKD-501, a novel dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma agonist, following oral administration to Sprague Dawley rats for 94-101 weeks. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 69:207–216
Moon KS, Lee J-E, Lee HS, Hwang I-C, Kim D-H, Park H-K, Choi H-J, Jo W, Son W-C, Yun H-I (2014) CKD-501, a novel selective PPARgamma agonist, shows no carcinogenic potential in ICR mice following oral administration for 104 weeks. J Appl Toxicol 34:1271–1284
Walton KL, Johnson KE, Harrison CA (2017) Targeting TGF-β mediated SMAD signaling for the prevention of fibrosis. Front Pharmacol 8:461
Funding
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (2017R1D1A3B03036549 and 2020R1I1A3073515).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Sun Woong Kim; Funding acquisition, Sun Woong Kim; Supervision, Sun Woong Kim; Investigation, Selikem Nuwormegbe; Methodology, Selikem Nuwormegbe and Sun Woong Kim; Formal analysis, Selikem Nuwormegbe and Na-Young Park; Writing original draft, Selikem Nuwormegbe; Writing—review and editing, Na-Young Park and Sun Woong Kim
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplemental information
ESM 1
(DOC 227 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nuwormegbe, S., Park, NY. & Kim, S.W. Lobeglitazone attenuates fibrosis in corneal fibroblasts by interrupting TGF-beta-mediated Smad signaling. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 260, 149–162 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05370-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05370-2