Abstract
Purpose
To compare the postoperative alignment, degree of improvement of abduction, and complications of the Hummelsheim procedure to the Jensen procedure in chronic sixth nerve palsy, and to calculate the dose-response of both procedures.
Methods
A retrospective study was done on patients who either had Hummelsheim or Jensen procedure for chronic sixth nerve palsy. Demographic characteristics, details of surgical procedure, ductions, versions, and angles of misalignment before and after surgery were analyzed.
Results
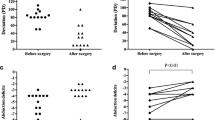
A total of 79 patients were identified: 38 Jensen and 41 Hummelsheim. There were no statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics of both groups. Medial rectus recession was performed in 35 patients in the Jensen group and in 30 patients in the Hummelsheim group. Success defined as orthotropia within 8 PD was achieved in 25 (66%) patients in the Jensen group and in 24 (59%) patients in the Hummelsheim group (P = 0.51). The mean improvement in the angle of deviation in the primary position was 42 ± 12 PD in the Jensen group and 42 ± 16 PD in the Hummelsheim group (P = 0.89). The mean improvement in abduction was slightly better in the Hummelsheim group (1.8 vs 1.5, P = 0.32). A new vertical deviation occurred in three patients in the Jensen group and in 4 patients in the Hummelsheim group. Anterior segment ischemia occurred in one patient in the Jensen group.
Conclusions
There was no difference in the success rate between the Hummelsheim and Jensen procedures in cases of chronic sixth nerve palsy. Strabismus surgeons can choose between the two procedures according to their preference.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Full data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Nelson LB (1991) Strabismus disorders. In: Nelson LB, Calhoun JH, Harley RD (eds) Pediatric ophthalmology, 3rd edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 149–168
Rush JA, Younge BR (1981) Paralysis of cranial nerves III, IV, and VI: cause and prognosis in 1000 cases. Arch Ophthalmol 99(1):76–79
Von Noorden GK, Campos EC (2002) Paralytic strabismus. In: Von Noorden GK, Campos EC (eds) Binocular vision and ocular motility, 6th edn. CV Mosby, New York, pp 414–457
King AJ, Stacey E, Stephenson G, Trimble RB (1995) Spontaneous recovery rates for unilateral sixth nerve palsies. Eye 9(Pt 4):476–478
Hummelsheim E (1908) Weitere Ertahrungen mit partieller Sehnenüberpflanzung an den Augenmuskein. Arch Augenheilkd 1908–1909:62–71
Jensen CD (1964) Rectus muscle union: a new operation for paralysis of the rectus muscles. Trans Pac Coast Otoophthalmol Soc 45:359–87
Gunton KB (2015) Vertical rectus transpositions in sixth nerve palsies. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 26(5):366–370
Nowakowska O, Loba P, Broniarczyk-Loba A (2011) The efficacy of vertical rectus transposition and its modalities in patients with abducens nerve palsy. Eur J Ophthalmol 21(3):223–227
Foster RS (1997) Vertical muscle transposition augmented with lateral fixation. J AAPOS. 1(1):20–30
Brooks SE, Olitsky SE, Ribeiro GD (2000) Augmented Hummelsheim procedure for paralytic strabismus. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 37(4):189
Schillinder RJ (1959) A new type of tendon transplant operation for abducens paralysis. J Int Coll Surg 31(5):593–600
Sen S, Dhiman R, Saxena D, Phuljhele S, Sharma P (2019) Vertical rectus transposition procedures for lateral rectus palsy: a systematic review. Indian J Ophthalmol 67(11):1793–1799
Scott AB. Lateral rectus palsy. In: 5º Congresso do Conselho Latinoamericano de Estrabismo. Anais. Guarujá, Brasil, October 16–20, 1976.
Ejzenbaum F, Pinto JR, Souza-Dias CR, Goldchmit M (2007) Treatment outcomes in VI nerve palsy corrected by Carlson & Jampolsky technique. Arq Bras Oftalmol 70(6):967–70
Laby DM, Rosenbaum AL (1994) Adjustable vertical rectus muscle transposition surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 31(2):75–78
Holmes JM, Hatt SR, Leske DA (2012) Intraoperative monitoring of torsion to prevent vertical deviations during augmented vertical rectus transposition surgery. J AAPOS 16(2):136–140
Struck MC (2009) Augmented vertical rectus transposition surgery with single posterior fixation suture: modification of foster technique. JAAPOS 13(4):343–349
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SA analyzed the data, did the statistical analysis, and wrote the manuscript. MA performed the literature review, tabulated the data, and drafted the manuscript. ZA contributed to the collection of the clinical data. AA contributed to the study design, cleaned and analyzed the data, did the statistical analysis, performed the surgeries, and revised the paper. He is the guarantor. MK and AE performed the surgeries, contributed to data collection, and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (Cairo University, Alexandria University, and Mansoura University Research Ethics Committee) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from the participants or the guardians of all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Additional informed consent was obtained from the participants or the guardians of all individual participants for whom identifying information is included in this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
E-Supplement 1
Summary of the data of the patients in the Jensen Group (PDF 32 kb)
E-Supplement 2
Summary of the data of the patients in the Hummelsheim Group (PDF 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arfeen, S., Azzab, M., Saad, Z. et al. Comparison between Hummelsheim and Jensen procedures in the management of chronic sixth nerve palsy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 260, 363–369 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05352-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05352-4