Abstract
Background
Excessive angiogenesis of the retina is a key component of irreversible causes of blindness in many ocular diseases. Pitavastatin is a cholesterol-lowering drug used to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Various studies have shown the effects of pitavastatin on angiogenesis but the conclusions are contradictory. The effects of pitavastatin on retinal angiogenesis have not been revealed. This study investigated the effects of pitavastatin at clinically relevant concentrations on retinal angiogenesis and its underlying mechanisms using retinal microvascular endothelial cells (RMECs).
Methods
The effects of pitavastatin on retinal angiogenesis were determined using in vitro model of retinal angiogenesis, endothelial cell migration, adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis assays. The mechanism studies were conducted using immunoblotting and stress fiber staining.
Results
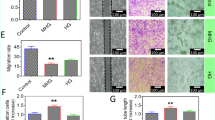
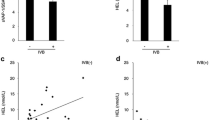
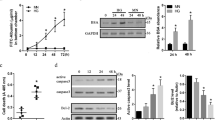
Pitavastatin stimulated capillary network formation of RMECs in a similar manner as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Pitavastatin also increased RMEC migration, adhesion to Matrigel, growth, and survival. The combination of pitavastatin with VEGF or LPS was more effective than VEGF or LPS alone in stimulating biological activities of RMECs, suggesting that pitavastatin can enhance the stimulatory effects of VEGF and LPS on retinal angiogenesis. Pitavastatin acted on RMECs in a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase-independent manner. In contrast, pitavastatin activated pro-angiogenic microenvironment via promoting the secretion of VEGF and stimulated retinal angiogenesis via multiple mechanisms including activation of RhoA-mediated pathways, induction of focal adhesion complex formation, and activation of ERK pathway.
Conclusion
Our work provides a preclinical evidence on the pro-angiogenic effect of pitavastatin in retina via multiple mechanisms that are irrelevant to mevalonate pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Puliafito CA, Wykoff CC (2020) New frontiers in retina: highlights of the 2020 angiogenesis, exudation and degeneration symposium. Int J Retina Vitreous 6:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40942-020-00221-4
Rubio RG, Adamis AP (2016) Ocular angiogenesis: vascular endothelial growth factor and other factors. Dev Ophthalmol 55:28–37. https://doi.org/10.1159/000431129
Eelen G, Treps L, Li X, Carmeliet P (2020) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis updated. Circ Res 127:310–329. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316851
Rezzola S, Loda A, Corsini M, Semeraro F, Annese T, Presta M, Ribatti D (2020) Angiogenesis-inflammation cross talk in diabetic retinopathy: novel insights from the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane/human vitreous platform. Front Immunol 11:581288. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.581288
Bharadwaj AS, Appukuttan B, Wilmarth PA, Pan Y, Stempel AJ, Chipps TJ, Benedetti EE, Zamora DO, Choi D, David LL, Smith JR (2013) Role of the retinal vascular endothelial cell in ocular disease. Prog Retin Eye Res 32:102–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.08.004
Bansal AB, Cassagnol M (2020) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL).
Chou R, Dana T, Blazina I, Daeges M, Jeanne TL (2016) Statins for prevention of cardiovascular disease in adults: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 316:2008–2024. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.15629
Vaughan CJ, Gotto AM Jr, Basson CT (2000) The evolving role of statins in the management of atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 35:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00525-2
Kajinami K, Koizumi J, Ueda K, Miyamoto S, Takegoshi T, Mabuchi H (2000) Effects of NK-104, a new hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme reductase inhibitor, on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Hokuriku NK-104 Study Group. Am J Cardiol 85:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9149(99)00656-6
Markle RA, Han J, Summers BD, Yokoyama T, Hajjar KA, Hajjar DP, Gotto AM Jr, Nicholson AC (2003) Pitavastatin alters the expression of thrombotic and fibrinolytic proteins in human vascular cells. J Cell Biochem 90:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.10602
Kikuchi R, Takeshita K, Uchida Y, Kondo M, Cheng XW, Nakayama T, Yamamoto K, Matsushita T, Liao JK, Murohara T (2011) Pitavastatin-induced angiogenesis and arteriogenesis is mediated by Notch1 in a murine hindlimb ischemia model without induction of VEGF. Lab Invest 91:691–703. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2011.5
Chen LW, Lin CS, Tsai MC, Shih SF, Lim ZW, Chen SJ, Tsui PF, Ho LJ, Lai JH, Liou JT (2019) Pitavastatin exerts potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects via the suppression of AP-1 signal transduction in human T cells. International journal of molecular sciences 20 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143534
Hu T, Shen H, Huang H, Yang Z, Zhou Y, Zhao G (2020) Cholesterol-lowering drug pitavastatin targets lung cancer and angiogenesis via suppressing prenylation-dependent Ras/Raf/MEK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Anticancer Drugs 31:377–384. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000000885
Li Z, Li Q, Wang G, Huang Y, Mao X, Zhang Y, Wang X (2017) Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin by anthelmintic drug niclosamide effectively targets growth, survival, and angiogenesis of retinoblastoma. American journal of translational research 9:3776–3786
Wang G, Li Z, Li Z, Huang Y, Mao X, Xu C, Cui S (2017) Targeting eIF4E inhibits growth, survival and angiogenesis in retinoblastoma and enhances efficacy of chemotherapy. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 96: 750–756 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.034
Luo Z, Zhang Y, Gu J, Feng P, Wang Y (2015) Pharmacokinetic properties of single- and multiple-dose pitavastatin calcium tablets in healthy Chinese volunteers. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 77:52–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2015.02.001
Melincovici CS, Bosca AB, Susman S, Marginean M, Mihu C, Istrate M, Moldovan IM, Roman AL, Mihu CM (2018) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Romanian journal of morphology and embryology = Revue roumaine de morphologie et embryologie 59: 455–467
Kajinami K, Takekoshi N, Saito Y (2003) Pitavastatin: efficacy and safety profiles of a novel synthetic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 21:199–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00116.x
Tan Q, Yu D, Song L (2020) Atorvastatin disrupts primary human brain microvascular endothelial cell functions via prenylation-dependent mitochondrial inhibition and oxidative stress. Fundamental & clinical pharmacology https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12615
Barlow HR, Cleaver O (2019) Building blood vessels-one Rho GTPase at a time. Cells 8 https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060545
Tojkander S, Gateva G, Lappalainen P (2012) Actin stress fibers–assembly, dynamics and biological roles. J Cell Sci 125:1855–1864. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.098087
Oesterle A, Laufs U, Liao JK (2017) Pleiotropic effects of statins on the cardiovascular system. Circ Res 120:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308537
Sandhu K, Mamas M, Butler R (2017) Endothelial progenitor cells: exploring the pleiotropic effects of statins. World J Cardiol 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i1.1
Landmesser U, Bahlmann F, Mueller M, Spiekermann S, Kirchhoff N, Schulz S, Manes C, Fischer D, de Groot K, Fliser D, Fauler G, Marz W, Drexler H (2005) Simvastatin versus ezetimibe: pleiotropic and lipid-lowering effects on endothelial function in humans. Circulation 111:2356–2363. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000164260.82417.3F
Weis M, Heeschen C, Glassford AJ, Cooke JP (2002) Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis. Circulation 105:739–745
Hu K, Wan Q (2019) Biphasic influence of pravastatin on human cardiac microvascular endothelial cell functions under pathological and physiological conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 511:476–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.090
Katsumoto M, Shingu T, Kuwashima R, Nakata A, Nomura S, Chayama K (2005) Biphasic effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, pitavastatin, on vascular endothelial cells and angiogenesis. Circ J 69:1547–1555
Dayang EZ, Plantinga J, Ter Ellen B, van Meurs M, Molema G, Moser J (2019) Identification of LPS-activated endothelial subpopulations with distinct inflammatory phenotypes and regulatory signaling mechanisms. Front Immunol 10:1169. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01169
Frick M, Dulak J, Cisowski J, Jozkowicz A, Zwick R, Alber H, Dichtl W, Schwarzacher SP, Pachinger O, Weidinger F (2003) Statins differentially regulate vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis 170:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9150(03)00299-5
Abdullah MI, Abed MN, Richardson A (2017) Inhibition of the mevalonate pathway augments the activity of pitavastatin against ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep 7:8090. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08649-9
Kojima Y, Ishida T, Sun L, Yasuda T, Toh R, Rikitake Y, Fukuda A, Kume N, Koshiyama H, Taniguchi A, Hirata K (2010) Pitavastatin decreases the expression of endothelial lipase both in vitro and in vivo. Cardiovasc Res 87:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvp419
Matsumoto T, Yamashita S, Yoshino S, Kurose S, Morisaki K, Nakano K, Koga JI, Furuyama T, Mori M, Egashira K (2020) Therapeutic arteriogenesis/angiogenesis for peripheral arterial disease by nanoparticle-mediated delivery of pitavastatin into vascular endothelial cells. Ann Vasc Dis 13:4–12. https://doi.org/10.3400/avd.ra.19-00130
Kubo M, Egashira K, Inoue T, Koga J, Oda S, Chen L, Nakano K, Matoba T, Kawashima Y, Hara K, Tsujimoto H, Sueishi K, Tominaga R, Sunagawa K (2009) Therapeutic neovascularization by nanotechnology-mediated cell-selective delivery of pitavastatin into the vascular endothelium. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:796–801. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.182584
Funding
Hubei Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission Youth Talent Project (WJ2017Q039) provided financial support in the form of research funding. The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhi Li, Jing Zhang and Yanni Xue have contributed equally to this work and are co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Zhang, J., Xue, Y. et al. Pitavastatin stimulates retinal angiogenesis via HMG-CoA reductase-independent activation of RhoA-mediated pathways and focal adhesion. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 259, 2707–2716 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05328-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05328-4