Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to describe the initial experience, efficacy, and safety of ripasudil hydrochloride hydrate (ripasudil), a Rho-associated kinase inhibitor eye drop, for uveitic glaucoma.
Methods
In this retrospective case series, we retrieved the clinical data of 21 eyes from 19 patients with open-angle uveitic glaucoma who were treated with ripasudil at Kobe University Hospital. We analyzed the median intraocular pressure (IOP) reductions after ripasudil treatment and collected the information on the adverse events that were encountered during the course of this treatment period.
Results
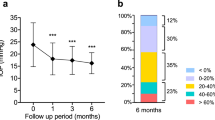
The causes of uveitis were sarcoidosis (29%), Behçet’s disease (14%), Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease (10%), others (15%), and unclassified (33%). Of total, 19 (90%) eyes were treated with topical, periocular, and/or systemic steroid therapies. The median number of glaucoma medications used before ripasudil treatment was 2, and the median follow-up time was 13 months. The median IOPs were 23 mmHg at baseline, 16 mmHg at 1 month, and 18 mmHg at 12 months with significant IOP reductions of − 3 mmHg at 1 month and − 2 mmHg at 12 months (P = 0.0050). Of total, 11 (52%) eyes with an IOP reduction ≥ 3 mmHg at 1 month (responders) showed a significant median IOP decrease at 12 months compared with non-responders (− 5 versus 0 mmHg, P = 0.0242). Two adverse events were observed: rashes on the back and transient conjunctival hyperemia.
Conclusions
Ripasudil appears to be safe and substantially reduce IOP in eyes with uveitic glaucoma if the eye is a responder. Ripasudil could be an option for the treatment of uveitic glaucoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panek WC, Holland GN, Lee DA, Christensen RE (1990) Glaucoma in patients with uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 74(4):223–227
Herbert HM, Viswanathan A, Jackson H, Lightman SL (2004) Risk factors for elevated intraocular pressure in uveitis. J Glaucoma 13(2):96–99
Heinz C, Koch JM, Zurek-Imhoff B, Heiligenhaus A (2009) Prevalence of uveitic secondary glaucoma and success of nonsurgical treatment in adults and children in a tertiary referral center. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 17(4):243–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/09273940902913035
Kanda T, Shibata M, Taguchi M, Ishikawa S, Harimoto K, Takeuchi M (2014) Prevalence and aetiology of ocular hypertension in acute and chronic uveitis. Br J Ophthalmol 98(7):932–936. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-304416
Siddique SS, Suelves AM, Baheti U, Foster CS (2013) Glaucoma and uveitis. Surv Ophthalmol 58(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.survophthal.2012.04.006
Hamanaka T, Takei A, Takemura T, Oritsu M (2002) Pathological study of cases with secondary open-angle glaucoma due to sarcoidosis. Am J Ophthalmol 134(1):17–26
Tektas OY, Heinz C, Heiligenhaus A, Hammer CM, Luetjen-Drecoll E (2011) Morphological changes of trabeculectomy specimens in different kinds of uveitic glaucoma. Curr Eye Res 36(5):442–448. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713683.2011.566409
Lu Z, Zhang Y, Freddo TF, Gong H (2011) Similar hydrodynamic and morphological changes in the aqueous humor outflow pathway after washout and Y27632 treatment in monkey eyes. Exp Eye Res 93(4):397–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2011.05.012
Kameda T, Inoue T, Inatani M, Fujimoto T, Honjo M, Kasaoka N, Inoue-Mochita M, Yoshimura N, Tanihara H (2012) The effect of Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor on monkey Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53(6):3092–3103. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.11-8018
Kaneko Y, Ohta M, Inoue T, Mizuno K, Isobe T, Tanabe S, Tanihara H (2016) Effects of K-115 (Ripasudil), a novel ROCK inhibitor, on trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells. Sci Rep 6:19640. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19640
Tanihara H, Inoue T, Yamamoto T, Kuwayama Y, Abe H, Fukushima A, Suganami H, Araie M, Group KCS (2016) One-year clinical evaluation of 0.4% ripasudil (K-115) in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Acta Ophthalmol 94(1):e26–e34. https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.12829
Inazaki H, Kobayashi S, Anzai Y, Satoh H, Sato S, Inoue M, Yamane S, Kadonosono K (2017) One-year efficacy of adjunctive use of Ripasudil, a rho-kinase inhibitor, in patients with glaucoma inadequately controlled with maximum medical therapy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-017-3727-5
Nussenblatt RB, Palestine AG, Chan CC (1985) Cyclosporine therapy for uveitis: long-term followup. J Ocul Pharmacol 1(4):369–382
Jabs DA, Nussenblatt RB, Rosenbaum JT, Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature Working G (2005) Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data. Results of the First International Workshop. Am J Ophthalmol 140(3):509–516
Markomichelakis NN, Kostakou A, Halkiadakis I, Chalkidou S, Papakonstantinou D, Georgopoulos G (2009) Efficacy and safety of latanoprost in eyes with uveitic glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 247(6):775–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-009-1036-3
Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T, Kawahara T, Morishita T, Tamakawa H, Yamagami K, Inui J, Maekawa M, Narumiya S (1997) Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature 389(6654):990–994. https://doi.org/10.1038/40187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board (Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Subjects’ informed consent was not required since this was a retrospective review.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusuhara, S., Katsuyama, A., Matsumiya, W. et al. Efficacy and safety of ripasudil, a Rho-associated kinase inhibitor, in eyes with uveitic glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 256, 809–814 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-3933-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-3933-9