Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this descriptive study was to evaluate the clinical response to rituximab (RTX) in patients with scleritis due to granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), in patients who had proved refractory to treatment with systemic glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive agents.
Methods
Retrospective analysis of interventional case series. Single referral center study. Eight patients (12 affected eyes) due to scleritis secondary to GPA, refractory to conventional treatment were included to receive RTX as therapy for remission induction. RTX was administered as a 1-g infusion every 2 weeks, for a total of 2 g. Patient follow-up included clinical evaluation (systemic and ophthalmologic), B-cell subset (CD19, CD20, CD22) counts, proteinase-3 anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (PR-3 ANCA), and Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score for Wegener's granulomatosis (BVAS-WG). Outcomes were response to treatment and achievement of remission, as well as number of ocular relapses.
Results
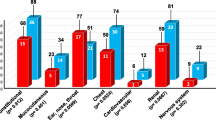
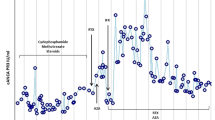
The main indication for treatment was refractory necrotising anterior scleritis. Four weeks after completion of treatment with RTX, all patients showed clear clinical improvement, with no further progression. In all patients, an absolute depletion of B cells was confirmed in the first 6 weeks after treatment. Seven patients (87.5 %) achieved remission of inflammatory activity in 7 months or less. However, three patients experienced ocular relapse, which comprised reactivation of the anterior scleritis, uveitis, and posterior scleritis, and two patients required a second dose of RTX, with immediate improvement.
Conclusions
RTX is useful in the treatment of refractory necrotising scleritis in patients with GPA. Of note, in those who relapse after remission, RTX can be successfully used for retreatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watkins AS, Kempen JH, Choi D, Liesegang TL, Pujari SS, Newcomb C et al (2009) Ocular disease in patients with ANCA-positive vasculitis. J Ocul Biol Dis Infor 3:12–19
Flores-Suárez LF, Villa AR (2007) Spectrum of Wegener granulomatosis in a Mexican population. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1107:400–409
Specks U, Fervenza FC, McDonald TJ, Hogan MC (2001) Response of Wegener’s granulomatosis to anti-CD20 chimeric monoclonal antibody therapy. Arthritis Rheum 44:2836–2840
Jones RB, Tervaert JW, Hauser T et al (2010) Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med 363:211–220
Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, Bloch DA et al (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum 33:1101–1107
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K et al (1994) Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum 37:187–192
Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J et al (2004) Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 350:2572–2581
Hellmich B, Flossmann O, Gross WL et al (2007) EULAR recommendations for conducting clinical studies and/or clinical trials in systemic vasculitis: focus on anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:605–617
Aries PM, Hellmich B, Voswinkel J et al (2006) Lack of efficacy of rituximab in Wegener's granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis 65:853–858
Aries PM, Hellmich B, Reinhold-Keller E, Gross WL (2004) High-dose intravenous azathioprine pulse treatment in refractory Wegener's granulomatosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:1307–1308
Taylor SR, Salama AD, Joshi L, Pusey CD, Lightman SL (2009) Rituximab is effective in the treatment of refractory ophthalmic Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum 60:1540–1547
Joshi L, Lightman SL, Salama AD, Shirodkar AL, Pusey CD, Taylor SR (2011) Rituximab in refractory ophthalmic Wegener's granulomatosis: PR3 titers may predict relapse, but repeat treatment can be effective. Ophthalmology 118:2498–2503
Joshi L, Tanna A, McAdoo SP et al (2015) Long-term Outcomes of Rituximab Therapy in Ocular Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Impact on Localized and Nonlocalized Disease. Ophthalmology 122:1262–1268
Jones RB, Ferraro AJ, Chaudhry AN, Brogan P, Salama AD, Smith KG (2009) A multicenter survey of rituximab therapy for refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 60:2156–2168
Keogh KA, Wylam ME, Stone JH, Specks U (2005) Induction of remission by B lymphocyte depletion in eleven patients with refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 52:262–268
Cartin-Ceba R, Golbin JM, Keogh KA et al (2012) Rituximab for remission induction and maintenance in refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's): ten-year experience at a single center. Arthritis Rheum 64:3770–3778
Miloslavsky EM, Specks U, Merkel PA et al (2013) Clinical outcomes of remission induction therapy for severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 65:2441–2449
Besada E, Koldingsnes W, Nossent JC (2014) Serum immunoglobulin levels and risk factors for hypogammaglobulinaemia during long-term maintenance therapy with rituximab in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:1818–1824
Huerva V, Sanchez MC, Traveset A, Jurjo C, Ruiz A (2010) Rituximab for peripheral ulcerative keratitis with wegener granulomatosis. Cornea 29:708–710
Suhler EB, Lim LL, Beardsley RM et al (2014) Rituximab therapy for refractory scleritis: results of a phase I/II dose ranging, randomized, clinical trial. Ophthalmology 121:1885–1891
Zaja F, Vianelli N, Volpetti S et al (2010) Low-dose rituximab in adult patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Eur J Haematol 85:329–334
Gómez-Almaguer D, Tarín-Arzaga L, Moreno-Jaime B, Jaime-Pérez JC, Ceballos-López AA, Ruiz-Argüelles GJ et al (2013) High response rate to low-dose rituximab plus high-dose dexamethasone as frontline therapy in adult patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Eur J Haematol 90:494–500
Acknowledgments
Roche Mexico provided rituximab as compassionate treatment for seven of the eight patients.
This work was presented in part at the 2013 annual meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the local ethics committee. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for RTX administration. All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Author contributions
Design of the study: CRG and LFFS. Conduct of the study CRG and LFFS. Collection, management, and analysis of the data: JCSO, LFFS. Interpretation of the data: CRG, JCSO and LFFS. Preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript: JCSO, CRG and LFFS.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Recillas-Gispert and Serna-Ojeda certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Dr. Flores-Suárez served as consultant for Roche Mexico and discloses having received honoraria (less than 1000 USD) and having provided expert opinion and participation in national licensing approval of the drug of study for its indication in the treatment for remission induction of ANCA-associated vasculitis at the Comisión Federal para la Protección contra Riesgos Sanitarios (COFEPRIS), Mexico.
Financial disclosures
Claudia Recillas-Gispert: no commercial relationship. Juan Carlos Serna-Ojeda: no commercial relationship. Luis Felipe Flores-Suárez: Roche Mexico: Code C (consultant).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Recillas-Gispert, C., Serna-Ojeda, J.C. & Flores-Suárez, L.F. Rituximab in the treatment of refractory scleritis in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s). Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 253, 2279–2284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-015-3198-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-015-3198-5