Abstract
Purpose
To report a novel spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) finding in children affected by tilted disc syndrome (TDS), and to correlate it with early visual field defects.
Methods
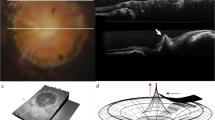
Patients between 5 and 17 years old with TDS were enrolled in this study. The diagnosis of TDS was made by stereoscopic fundus photography, when the upper edge of the optic disc protruded anteriorly relative to its lower edge. All eyes were examined with 12 radial SD-OCT B-scans of 12 mm centered on the optic disc; the fundus area encompassing the optic nerve was additionally scanned using several vertical and horizontal scans.. C-scan SD-OCT were acquired using the Macular Cube 512 x128 to create the en face image. Standard automated perimetry 24–2 tests were performed on all patients.
Results
Thirty-eight eyes of 20 pediatric patients with TDS syndrome were enrolled during this 24-months clinical trial. Their mean age was 10.9 ± 2.7 years (range 7–15 years), 12 (60%) were male and eight (40%) were female. The OCT images of the optic discs showed a protrusion of the upper edge of Bruch’s membrane and choroid at the nasal edge of the optic disc in 39.5% of the eyes. The retinal nerve fiber tissue appeared to be herniated into this protrusion and bent superiorly in 15 eyes. This severe bending corresponded to early visual field anomalies that were not reduced by corrective lenses in 46.7% of the eyes.
Conclusion
Visual field defects that do not improve by increased myopic correction in TDS may be due to the severe bending of the retinal nerve fiber tissue, which would impair axonal flow.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shinohara K, Moriyama M, Shimada N, Nagaoka N, Ishibashi T, Tokoro T, Ohno-Matsui K (2013) Analyses of shape of eyes and structure of optic nerves in eyes with tilted disc syndrome by swept-source optical coherence tomography and three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Eye (Lond) 27(11):1233–1241
Maruko I, Iida T, Sugano Y, Oyamada H, Sekiryu T (2011) Morphologic choroidal and scleral changes at the macula in tilted disc syndrome with staphyloma using optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(12):8763–8768
Dehghani C, Nowroozzadeh MH, Shankar S, Razeghinejad MR (2010) Ocular refractive and biometric characteristics in patients with tilted disc syndrome. Optometry 81(12):688–694
Furuta M, Iida T, Maruko I, Kishi S, Sekiryu T (2013) Submacular choroidal neovascularization at the margin of staphyloma in tilted disk syndrome. Retina 33(1):71–76
Donati MC, Miele A, Abbruzzese G, Giuntoli M, Giansanti F, Menchini U (2013) Treatment of macular serous neuroretinal detachment in tilted disk syndrome: report of 3 cases. Eur J Ophthalmol 23(2):267–270
Ohno-Matsui K, Shimada N, Nagaoka N, Tokoro T, Mochizuki M (2011) Choroidal folds radiating from the edge of an inferior staphyloma in an eye with tilted disc syndrome. Jpn J Ophthalmol 55(2):171–173
Milani P, Pece A, Pierro L, Seidenari P, Radice P, Scialdone A (2010) Bevacizumab for macular serous neuroretinal detachment in tilted disk syndrome. J Ophthalmol 2010:970580
Alkabes M, Pichi F, Nucci P, Massaro D, Dutra Medeiros M, Corcostegui B, Mateo C (2014) Anatomical and visual outcomes in high myopic macular hole (HM-MH) without retinal detachment: a review. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 252(2):191–199
Giuffre G (1986) The spectrum of visual field defects in tilted disc syndrome. Neuro-Ophthalmology 6:239–246
Young SE, Walsh FB, Knox DL (1976) Tilted disc syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 82:16–23
Apple DJ, Rabb MF, Walsh PM (1982) Congenital anomalies of the optic disc. Surv Ophthalmol 27:3–41
Brito PN, Vieira MP, Falcão MS, Faria OS, Falcão-Reis F (2013) Optical coherence tomography study of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer and choroidal thickness in eyes with tilted optic disc. J Glaucoma. PMID: 23429636 [Epub ahead of print]
Lee SY, Kim TW, Hwang JM, Park KH, Kim DM, Kim SH (2012) Peripapillary retinal nerve fibre thickness profile with optical coherence tomography in congenital tilted disc syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol 90(5):e412–e413
Balducci N, Morara M, Veronese C, Torrazza C, Pichi F, Ciardella AP (2014) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness modification after internal limiting membrane peeling. Retina 34(4):655–663
Hwang YH, Yoo C, Kim YY (2012) Characteristics of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in eyes with myopic optic disc tilt and rotation. J Glaucoma 21(6):394–400
Chung JK, Yoo YC (2011) Correct calculation circle location of optical coherence tomography in measuring retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in eyes with myopic tilted discs. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(11):7894–7900
Hwang YH, Yoo C, Kim YY (2012) Myopic optic disc tilt and the characteristics of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma 21(4):260–265
Cohen SY, Dubois L, Nghiem-Buffet S, Fajnkuchen F, Delahaye-Mazza C, Quentel G, Gaudric A, Tadayoni R (2013) Spectral domain optical coherence tomography analysis of macular changes in tilted disk syndrome. Retina 33(7):1338–1345
Lempert P, Porter L (1998) Dysversion of the optic disc and axial length measurements in a presumed amblyopic population. J AAPOS 2(4):207–213
Park KA, Park SE, Oh SY (2013) Long-term changes in refractive error in children with myopic tilted optic disc compared to children without tilted optic disc. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54(13):7865–7870
Samarawickrama C, Mitchell P, Tong L, Gazzard G, Lim L, Wong TY, Saw SM (2011) Myopia-related optic disc and retinal changes in adolescent children from Singapore. Ophthalmology 118(10):2050–2057
Altman B (1983) Drugs in pediatric ophthalmology. In: Harley RD (ed) Pediatric ophthalmology, 2nd Edition. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Wright KW (2012) Pediatric examination. In: Wright KW, Strube YJ (Eds) Pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus. Oxford University Press, New York
Kim TW, Kim M, Weinreb RN, Woo SJ, Park KH, Hwang JM (2012) Optic disc change with incipient myopia of childhood. Ophthalmology 119(1):21–26, e1-3
Pichi F, Lembo A, Morara M, Veronese C, Alkabes M, Nucci P, Ciardella AP (2014). Early and late inner retinal changes after inner limiting membrane peeling. Int Ophthalmol 34(2):437–446
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pichi, F., Romano, S., Villani, E. et al. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography findings in pediatric tilted disc syndrome. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 252, 1661–1667 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2701-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-014-2701-8