Abstract
Background
To compare the effect on corneal sensitivity between femtosecond laser-assisted laser in situ keratomileusis (FS-LASIK) and femtosecond lenticule extraction (ReLEx flex) or FS-LASIK and small-incision lenticule extraction (ReLEx smile) surgery.
Methods
Twenty-seven subjects (54 eyes) underwent FS-LASIK, 22 subjects (40 eyes) underwent ReLEx flex, and 32 subjects (61 eyes) underwent ReLEx smile surgery. Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometry (Luneau Ophthalmologie Chartres, Cedex, France) was used to evaluate corneal sensitivity preoperatively as well as at 1 week and 1 and 3 months after surgery.
Results
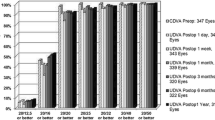
At 1 week, central, superior, nasal, and temporal corneal sensitivity in the ReLEx flex group was significantly higher than in the FS-LASIK group (P = 0.007, 0.004, 0.020, 0.004 respectively) and in the central and inferior areas at 3 months (P = 0.002, 0.009 respectively). A higher corneal sensitivity after ReLEx smile surgery was observed in every quadrant at 1 week and 1 and 3 months compared with FS-LASIK surgery (P < 0.01). Furthermore, in the ReLEx smile group, there were no statistical differences in the superior and temporal quadrants at 1 month postoperatively compared with preoperatively (5.19 ± 0.61 cm, P = 0.198 and 5.64 ± 0.48 cm, P = 0.330 respectively) and no significant differences in any quadrant at 3 months.
Conclusions
Postoperative corneal sensitivity was not remarkably changed after ReLEx smile surgery compared with FS-LASIK. This might be because ReLEx is a flapless procedure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salomão MQ, Wilson SE (2010) Femtosecond laser in laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg 36:1024–1032
Muñoz G, Albarrán-Diego C, Ferrer-Blasco T, García-Lázaro S, Cerviño-Expósito A (2010) Long-term comparison of corneal aberration changes after laser in situ keratomileusis: mechanical microkeratome versus femtosecond laser flap creation. J Cataract Refract Surg 36:1934–1944
Talamo JH, Meltzer J, Gardner J (2006) Reproducibility of flap thickness with IntraLaser FS and Moria LSK-1 and M2 microkeratomes. J Refract Surg 22:556–561
Kim JY, Kim MJ, Kim T-I, Choi HJ, Pak JH, Tchah H (2006) A femtosecond laser creates a stronger flap than a mechanical microkeratome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:599–604
Kullman G, Pineda R 2nd (2010) Alternative applications of the femtosecond laser in ophthalmology. Semin Ophthalmol 25:256–264
Blum M, Kunert K, Schröder M, Sekundo W (2010) Femtosecond lenticule extraction for the correction of myopia: preliminary 6-month results. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248:1019–1027
Shah R, Shah S, Sengupta S (2011) Results of small incision lenticule extraction: All-in-one femtosecond laser refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 37:127–137
Mian SI, Li AY, Dutta S, Musch DC, Shtein RM (2009) Dry eyes and corneal sensitivity after laser in situ keratomileusis with femtosecond laser flap creation. Effect of hinge position, hinge angle, and flap thickness. J Cataract Refract Surg 35:2092–2098
Barequet IS, Hirsh A, Levinger S (2008) Effect of thin femtosecond LASIK flaps on corneal sensitivity and tear function. J Refract Surg 24:897–902
Vroman DT, Sandoval HP, Fernández de Castro LE, Kasper TJ, Holzer MP, Solomon KD (2005) Effect of hinge location on corneal sensation and dry eye after laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg 31:1881–1887
Calvillo MP, McLaren JW, Hodge DO, Bourne WM (2004) Corneal reinnervation after LASIK: prospective 3-year longitudinal study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:3991–3996
Nassaralla BA, McLeod SD, Nassaralla JJ Jr (2003) Effect of myopic LASIK on human corneal sensitivity. Ophthalmology 110:497–502
Donnenfeld ED, Ehrenhaus M, Solomon R, Mazurek J, Rozell JC, Perry HD (2004) Effect of hinge width on corneal sensitivity and dry eye after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg 30:790–797
Kumano Y, Matsui H, Zushi I, Mawatari A, Matsui T, Nishida T, Miyazaki M (2003) Recovery of corneal sensitivity after myopic correction by laser in situ keratomileusis with a nasal or superior hinge. J Cataract Refract Surg 29:757–761
Toda I, Asano-Kato N, Komai-Hori Y, Tsubota K (2001) Dry eye after laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol 132:1–7
Battat L, Macri A, Dursun D, Pflugfelder SC (2001) Effects of laser in situ keratomileusis on tear production, clearance, and the ocular surface. Ophthalmology 108:1230–1235
Stachs O, Zhivov A, Kraak R, Hovakimyan M, Wree A, Guthoff R (2010) Structural–functional correlations of corneal innervation after LASIK and penetrating keratoplasty. J Refract Surg 26:159–167
Sekundo W (2008) Komplikationen der laserrefraktiven Hornhautchirurgie. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkol 225:R73–R82
Potgieter FJ, Roberts C, Cox IG, Mahmoud AM, Herderick EE, Roetz M, Steenkamp W (2005) Prediction of flap response. J Cataract Refract Surg 31:106–114
Sekundo W, Kunert KS, Blum M (2011) Small incision corneal refractive surgery using the small incision lenticule extraction (ReLEx smile) procedure for the correction of myopia and myopic astigmatism: results of a 6 month prospective study. Br J Ophthalmol 95:335–339
Lim T, Yang S, Kim M, Tchah H (2006) Comparison of the IntraLase femtosecond laser and mechanical microkeratome for laser in situ keratomileusis. Am J Ophthalmol 141:833–839
Vesaluoma MH, Petroll WM, Pérez-Santonja JJ, Valle TU, Alió JL, Tervo TM (2000) Laser in situ keratomileusis flap margin: wound healing and complications imaged by in vivo confocal microscopy. Am J Ophthalmol 130:564–573
Betney S, Morgan PB, Doyle SJ, Efron N (1997) Corneal temperature changes during photorefractive keratectomy. Cornea 16:158–161
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the technical support of Tianjin Eye Hospital & Eye Institute, Tianjin Key Lab of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, and the financial support from the National Natural and Science Program Grant.
Conflicts of interest and source of funding
Neither author has a financial nor proprietary interest in any material or method mentioned. This work has received a National Natural and Science Program Grant (No. 81170873).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Clinical trials registration number: ChiCTR-ONRC-12002082
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, S., Wang, Y. Comparison of corneal sensitivity between FS-LASIK and femtosecond lenticule extraction (ReLEx flex) or small-incision lenticule extraction (ReLEx smile) for myopic eyes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251, 1645–1654 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2272-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2272-0