Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the inter- and intra-observer agreement of measurement of the iris–trabecular contact (ITC) index, a measure of the degree of angle closure, using swept source optical coherence tomography (SSOCT, CASIA SS-1000, Tomey Corporation, Nagoya, Japan).
Methods
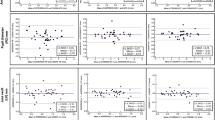
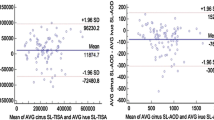
One randomly selected eye of 60 subjects was imaged under dark room conditions. The SSOCT 3-dimensional angle scan simultaneously obtains 128 radial scans of the anterior chamber for the entire circumference of the angle. Post-imaging analysis estimated the ITC index using in-built software. For intra-observer agreement for image grading, one examiner performed the grading twice in a masked fashion and random order after a 1-week interval. A second examiner graded images to assess inter-observer agreement for image grading. For intra-observer agreement for image acquisition, a single operator imaged patients twice. For inter-observer agreement for image acquisition, a single observer graded two sets of images acquired by two different operators on the same patient. Bland–Altman plots and 95 % limits of agreement (LOA) were reported.
Results
Study subjects were predominantly Chinese (54/60, 90 %) and female (42/60, 70 %), with a mean age of 65.5 years. The median ITC index for eyes with open angles (31/60) and closed angles was 20 % (95 % confidence interval [CI] — 13.6, 27.8) and 49 % (95%CI — 35.5, 69.2) respectively. The mean difference (95 % LOA) for intra-observer agreement for image grading and image acquisition were −0.8 % (−8.2, 6.5) and 0.6 % (−10.9, 9.7); corresponding inter- observer agreement were 0.1 % (−10, 10.1) and −0.3 % (−11.1, 10.5) respectively.
Conclusions
The inter- and intra-observer agreement of the ITC index, as a measure of extent of angle closure using SSOCT, was good.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leung CK, Yung WH, Yiu CK, Lam SW, Leung DY, Tse RK, Tham CC, Chan WM, Lam DS (2006) Novel approach for anterior chamber angle analysis: anterior chamber angle detection with edge measurement and identification algorithm (ACADEMIA). Arch Ophthalmol 124:1395–1401
Foster PJ, Johnson GJ (2001) Glaucoma in China: how big is the problem? Br J Ophthalmol 85:1277–1282
Wu RY, Nongpiur ME, He MG, Sakata LM, Friedman DS, Chan YH, Lavanya R, Wong TY, Aung T (2011) Association of narrow angles with anterior chamber area and volume measured with anterior-segment optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol 129:569–574
Congdon N, Wang F, Tielsch JM (1992) Issues in the epidemiology and population based screening of primary angle-closure glaucoma. SurvOphthalmol 36:411–423
Yi JH, Hong S, Seong GJ, Kang SY, Ma KT, Kim CY (2008) Anterior chamber measurements by pentacam and AS-OCT in eyes with normal open angles. Korean J Ophthalmol 22:242–245
Narayanaswamy A, Sakata LM, He MG, Friedman DS, Chan YH, Lavanya R, Baskaran M, Foster PJ, Aung T (2010) Diagnostic performance of anterior chamber angle measurements for detecting eyes with narrow angles: an anterior segment OCT study. Arch Ophthalmol 128:1321–1327
Wong HT, Lim MC, Sakata LM, Aung HT, Amerasinghe N, Friedman DS, Aung T (2009) High-definition optical coherence tomography imaging of the iridocorneal angle of the eye. Arch Ophthalmol 127:256–260
Wylegała E, Teper S, Nowinska AK, Milka M, Dobrowolski D (2009) Anterior segment imaging: Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography versus time-domain optical coherence tomography. J Cataract Refract Surg 35:1410–1414
Sasidharan R (2008) South East Asia Glaucoma Interest Group. Appendix 6A. Gonioscopy. Asia Pacific glaucoma guidelines. Scientific Communications International, HongKong
Liu S, Yu M, Ye C, Lam DS, Leung CK (2011) Anterior chamber angle imaging with swept-source optical coherence tomography: an investigation on variability of angle measurement. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:8598–8603
Rabsilber TM, Khoramnia R, Auffarth GU (2006) Anterior chamber measurements using Pentacam rotating Scheimpflug camera. J Cataract Refract Surg 32:456–459
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors have any financial/conflicting interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Financial Support
The study was supported by a Translational Clinical Research Program grant, Biomedical Research Council (BMRC), Singapore
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, SW., Baskaran, M., Zheng, C. et al. Swept source optical coherence tomography measurement of the iris–trabecular contact (ITC) index: a new parameter for angle closure. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251, 1205–1211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-012-2158-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-012-2158-6