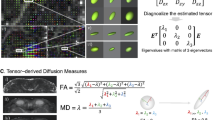
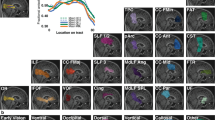
Abstract
Background
In glaucoma, damage of retinal ganglion cells may continue to the linked optic radiations. This study investigates the correlation of glaucoma severity indicators with parameters of axonal and myelin integrity of the optic radiations.
Methods
In this observational case–control study, 13 patients with normal-tension glaucoma, 13 patients with primary open-angle glaucoma, and seven control subjects (mean age, 57.6 ± 12.5 years) were randomly selected for diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the optic radiations. The results of the frequency doubling test (FDT) and the HRT-based linear discriminant functions of Burk (BLDF) and Mikelberg (MLDF) were correlated with the mean of the fractional anisotropy (FA), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), and radial diffusivity (RD) of the optic radiations. Multiple correlation analysis, corrected for age, stage of cerebral microangiopathy, diagnosis group, and gender was conducted at increasing thresholds of linear anisotropy (CL) to reduce mismeasurements because of complex fiber situations.
Results
The best correlations were found for BLDF with FA at CL threshold 0.3 (0.594, p = 0.001), with ADC at CL 0.4 (−0.511, p = 0.005), and with RD at CL 0.4 (−0.585, p = 0.001). MLDF correlated with FA at CL 0.4 (0.393, p = 0.035). The FDT score correlated with FA at CL 0 (−0.491, p = 0.007) and with RD at CL 0 (−0.375, p = 0.045).
Conclusions
In glaucoma, DTI-derived parameters of the axonal integrity (FA, ADC) and demyelination (RD) of the optic radiation are linked to HRT-based indices of glaucoma severity and to impairment of the spatial-temporal contrast sensitivity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yücel YH, Zhang Q, Weinreb RN, Kaufman PL, Gupta N (2003) Effects of retinal ganglion cell loss on mango-, parvo-, koniocellular pathways in the lateral geniculate nucleus and visual cortex in glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res 22:465–481
Weber AJ, Chen H, Hubbard WC, Kaufman PL (2000) Experimental glaucoma and cell size, density, and number in the primate lateral geniculate nucleus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:1370–1379
Gupta N, Ang LC, Noël de Tilly L, Bidaisee L, Yücel YH (2006) Human glaucoma and neural degeneration in intracranial optic nerve, lateral geniculate nucleus, and visual cortex. Br J Ophthalmol 90:674–678
van Swieten JC, van den Hout JH, van Ketel BA, Hijdra A, Wokke JH, van Gijn J (1991) Periventricular lesions in the white matter on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly: a morphometric correlation with arteriolosclerosis and dilated perivascular spaces. Brain 114:761–774
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Offenbacher H, Schmidt R, Kleinert G, Payer F, Radner H, Lechner H (1993) Pathologic correlates of incidental MRI white matter signal hyperintensities. Neurology 43:1683–1689
Wong TY, Klein R, Sharrett AR, Couper DJ, Klein BE, Liao DP, Hubbard LD, Mosley TH, Investigators ARIC (2002) Atheroslerosis Risk in Communities Study. Cerebral white matter lesions, retinopathy, and incident clinical stroke. JAMA 288:67–74
Harris A, Sergott RC, Spaeth GL, Katz JL, Shoemaker JA, Martin BJ (1994) Color Doppler analysis of ocular vessel blood velocity in normal-tension glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 118:642–649
Schmidt R, Scheltens P, Erkinjuntti T, Pantoni L, Markus HS, Wallin A, Barkhof F, Fazekas F (2004) White matter lesion progression: a surrogate endpoint for trials in cerebral small-vessel disease. Neurology 63:139–144
van Swieten JC, Geyskes GG, Derix MM, Peeck BM, Ramos LM, van Latum JC, van Gijn J (1991) Hypertension in the elderly is associated with white matter lesions and cognitive decline. Ann Neurol 30:825–830
Liao D, Cooper L, Cai J, Toole J, Bryan N, Burke G, Shahar E, Nieto J, Mosley T, Heiss G (1997) The prevalence and severity of white matter lesions, their relationship with age, ethnicity, gender, and cardiovascular disease risk factors: the ARIC Study. Neuroepidemiology 16:149–162
Breteler MM, van Swieten JC, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Claus JJ, van den Hout JH, van Harskamp F, Tanghe HL, de Jong PT, van Gijn J, Hofman A (1994) Cerebral white matter lesions, vascular risk factors, and cognitive function in a population-based study: The Rotterdam Study. Neurology 44:1246–1252
Wen W, Sachdev PS (2004) Extent and distribution of white matter hyperintensities in stroke patients: the Sydney Stroke Study. Stroke 35:2813–2819
Wong TY, Klein R, Klein BEK, Tielsch JM, Hubbard LD, Nieto FJ (2001) Retinal microvascular abnormalities and their relations with hypertension, cardiovascular diseases and mortality. Surv Ophthalmol 46:59–80
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, DiChiro G (1996) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Sotak CH (2002) The role of diffusion tensor imaging in the evaluation of ischemic brain injury – a review. NMR Biomed 15(7–8):561–569
Xu J, Sun SW, Naismith RT, Snyder AZ, Cross AH, Song SK (2008) Assessing optic nerve pathology with diffusion MRI: from mouse to human. NMR Biomed 21(9):928–940
Dong Q, Welsh RC, Chenevert TL, Carlos RC, Maly-Sundgren P, Gomez-Hassan DM, Mukherji SK (2004) Clinical applications of diffusion tensor imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 19(1):6–18
Song SK, Sun SW, Ju WK, Lin SJ, Cross AH, Neufeld AH (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. NeuroImage 20:1714–1722
Song SK, Sun SW, Ramsbottom MJ, Chang C, Russell J, Cross AH (2002) Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial but unchanged axial diffusion of water. NeuroImage 17:1429–1436
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161(2):401–407
Burk RO, Noack H, Rohrschneider K, Volcker HE (1999) Prediction of glaucomatous visual field defects by reference plane independent three-dimensional optic nerve head parameters. In: Wall M, Wild JM (eds) Perimetry Update 1998/1999: Proceedings of the XIIIth International Perimetric Society Meeting, Gardone Riviera (BS), Italy, September 6–9, 1998, Kugler, The Hague, pp 463–474
Mikelberg FS, Parfitt CM, Swindale NV, Graham SL, Drance SM, Gosine R (1995) Ability of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph to detect early glaucomatous visual field loss. J Glaucoma 4(4):242–247
Patel SC, Friedman DS, Varadkar P, Robin AL (2000) Algorithm for interpreting the results of frequency doubling perimetry. Am J Ophthalmol 129(3):323–327
El-Rafei A, Engelhorn T, Wärntges S, Dörfler A, Hornegger J, Michelson G (2011) A framework for voxel-based morphometric analysis of the optic radiation using diffusion tensor imaging in glaucoma. Magn Reson Imaging 29(8):1076–1087
Wakana S, Jiang H, Nagae-Poetscher LM, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2004) Fiber tract-based atlas of human white matter anatomy. Radiology 230(1):77–87
Castedo J, Duque A, Roa E, Rodrigo P (2006) Atlas of white matter anatomy with fiber tractography by diffusion tensor MRI. 18th Annual Meeting of the Swiss Society of Neuroradiology SGNR/SSNR, Geneva Switzerland. http://www.neurorgs.com/inv/Publi/Pdf/Poster%20Castedo.pdf. Accessed 27 August 2009
UAMS (1997) The Anatomy Project. Nashville, TN: Parthenon Publishing Group, 1997. http://anatomy.uams.edu/AnatomyHTML/atlas_html/eye_38.html. Accessed 10 September 2009
Peled S, Gudbjartsson H, Westin CF, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging shows orientation and asymmetry of white matter fiber tracts. Brain Res 780(1):27–33
Kertesz A, Black SE, Tokar G, Benke T, Carr T, Nicholson L (1988) Periventricular and subcortical hyperintensities on magnetic resonance imaging. ‘Rims, caps, and unidentified bright objects’. Arch Neurol 45(4):404–408
Garaci FG, Bolacchi F, Cerulli A, Melis M, Spanò A, Cedrone C, Floris R, Simonetti G, Nucci C (2009) Optic nerve and optic radiation neurodegeneration in patients with glaucoma: in vivo analysis with 3-T diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 252(2):496–501
Hodapp E, Parrish RK, Anderson DR (1993) Clinical decisions in glaucoma. Mosby, St. Louis, MO
Vickers JC, Schumer RA, Podos SM, Wang RF, Riederer BM, Morrison JH (1995) Differential vulnerability of neurochemically identified subpopulations of retinal neurons in a monkey model of glaucoma. Brain Res 680(1–2):23–35
Maddess T, Henry GH (1992) Performance of nonlinear visual units in ocular hypertension and glaucoma. Clin Vision Sci 7(5):371–383
White AJ, Sun H, Swanson WH, Lee BB (2002) An examination of physiological mechanisms underlying the frequency-doubling illusion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43(11):3590–3599
Yücel YH, Zhang Q, Gupta N, Kaufman PL, Weinreb RN (2000) Loss of neurons in magnocellular and parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus in glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 118:378–384
Fechtner RD, Weinreb RN (1994) Mechanisms of optic nerve damage in primary open angle glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol 39:23–42
Burk RO, Vihanninjoki K, Bartke T, Tuulonen A, Airaksinen PJ, Völcker HE, König JM (2000) Development of the standard reference plane for the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 238(5):375–384
Sun SW, Liang HF, Le TQ, Armstrong RC, Cross AH, Song SK (2006) Differential sensitivity of in vivo and ex vivo diffusion tensor imaging to evolving optic nerve injury in mice with retinal ischemia. NeuroImage 32(3):1195–1204
Sun S-W, Liang H-F, Cross AH, Song S-K (2008) Evolving Wallerian degeneration after transient retinal ischemia in mice characterized by diffusion tensor imaging. NeuroImage 40(1):1–10
Barrick TR, Charlton RA, Clark CA, Markus HS (2010) White matter structural decline in normal ageing; a prospective longitudinal study using tract based spatial statistics. Neuroimage 51(2):565–577
Hirsch JG, Bock M, Essig M, Schad LR (1999) Comparison of diffusion anisotropy measurements in combination with the FLAIR technique. Magn Reson Imaging 17:705–716
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111(3):209–219
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Bonn, Germany (excellence cluster Medical Valley EMN, Grant MVEMN-A-02), and the Johannes und Frieda Marohn-Stiftung at the University of Erlangen, Germany.
The funding organizations had no role in the design or conduct of this research, in the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data, or in preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript. .
None of the authors has any financial/ conflicting interests to disclose. The authors had full control of all primary data and agree to allow Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology to review their data if requested.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
G. Michelson and T. Engelhorn contributed equally to this work and thus share first authorship.
Parts of the study have been presented at the ARVO Annual Meeting 2010.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michelson, G., Engelhorn, T., Wärntges, S. et al. DTI parameters of axonal integrity and demyelination of the optic radiation correlate with glaucoma indices. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 251, 243–253 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1887-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1887-2