Abstract
Purpose
To compare Icare ONE rebound self-tonometer (ICRBT) measurements with Goldman applanation tonometry (GAT).
Methods
A trained examiner instructed each of 60 normal subjects on use of the ICRBT. Each subject then took two measurements of his/her own pressure using the ICRBT. Finally, a different examiner, who was masked to the earlier readings, measured IOP by GAT. Bland–Altman limits of agreement (LOA), intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs), Kappa values, and paired t-test were used to assess the agreement between the two methods. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was used for correlation analysis.
Results
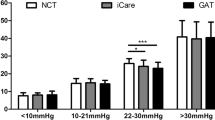
All of the subjects were able to obtain correct measurements with ICRBT after three attempts. The mean intraocular pressure with ICRBT and GAT measurements were 16.0 ± 3.3 mmHg and 13.7 ± 2.5 mmHg respectively. The mean difference between patient’s ICRBT and technician’s GAT measurements was 2.3 mmHg (p < 0.001). In 63 % (38/60) of the cases the IOP difference (ICRBT − GAT) was within ± 3 mmHg. The weighted Kappa for the IOP measurements of the two methods was 0.49 (95% CI: 0.30–0.68, p < 0.001), indicating acceptable agreement. A significantly positive correlation was found between ICRBT IOP measurements and central corneal thickness (CCT) (r = 0.48, p < 0.001). In addition, the difference in IOP measurements (ICRBT − GAT) between the two methods was positively correlated with CCT (r = 0.31, p = 0.015), indicating that greater thickness is associated with greater differences between the two methods.
Conclusion
The ICRBT was reliable in the hands of normal subjects, and may be used for self-monitoring of IOP. ICRBT measurements generally overestimated GAT measurements.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitacre MM, Stein R (1993) Sources of error with use of Goldmann type tonometers. Surv Ophthalmol 38:1–30
Whitacre MM, Stein RA, Hassanein K (1993) The effect of corneal thickness on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol 115:592–596
ElMallah MK, Asrani SG (2008) New ways to measure intraocular pressure. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 19:122–126
Kontiola AI (2000) A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 78:142–145
Danias J, Kontiola AI, Filippopoulos T, Mittag T (2003) Method for the noninvasive measurement of intraocular pressure in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:1138–1141
Cervino A (2006) Rebound tonometry: new opportunities and limitations of non-invasive determination of intraocular pressure. Br J Ophthalmol 90:1444–1446
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Castillo A, Garcia Sanchez J (2005) Reproducibility and clinical evaluation of rebound tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:4578–4580
Davies LN, Bartlett H, Mallen EA, Wolffsohn JS (2006) Clinical evaluation of rebound tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 84:206–209
Nakamura M, Darhad U, Tatsumi Y, Fujioka M, Kusuhara A, Maeda H, Negi A (2006) Agreement of rebound tonometer in measuring intraocular pressure with three types of applanation tonometers. Am J Ophthalmol 142:332–334
Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, Tosoni C, Parisi L (2006) Comparison of ICare tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma 15:213–217
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Vico E, Fernandez-Vidal A, Benitez del Castillo JM, Wasfi M, Garcia-Sanchez J (2006) Effect of corneal thickness on dynamic contour, rebound, and Goldmann tonometry. Ophthalmology 113:2156–2162
Sahin A, Niyaz L, Yildirim N (2007) Comparison of the rebound tonometer with the Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 35:335–339
Ruokonen PC, Schwenteck T, Draeger J (2007) Evaluation of the impedance tonometer TGDc-01 and iCare according to the international ocular tonometer standards ISO 8612. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245:1259–1265
Munkwitz S, Elkarmouty A, Hoffmann EM, Pfeiffer N, Thieme H (2008) Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer over a wide IOP range. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246:875–879
Chui WS, Lam A, Chen D, Chiu R (2008) The influence of corneal properties on rebound tonometry. Ophthalmology 115:80–84
Jóhannesson G, Hallberg P, Eklund A, Lindén C (2008) Pascal, ICare and Goldmann applanation tonometry–a comparative study. Acta Ophthalmol 86:614–621
Abraham LM, Epasinghe NC, Selva D, Casson R (2008) Comparison of the ICare reboundtonometer with the Goldmann applanation tonometer by experienced and inexperienced tonometrists. Eye 22:503–506
Poostchi A, Mitchell R, Nicholas S, Purdie G, Wells A (2009) The iCare rebound tonometer: comparisons with Goldmann tonometry, and influence of central corneal thickness. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 37:687–691
Vandewalle E, Vandenbroeck S, Stalmans I, Zeyen T (2009) Comparison of ICare, dynamic contour tonometer, and ocular response analyzer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in patients with glaucoma. Eur J Ophthalmol 19:783–789
Scuderi GL, Cascone NC, Regine F, Perdicchi A, Cerulli A, Recupero SM (2010) Validity and limits of the rebound tonometer (ICare®): clinical study. Eur J Ophthalmol 21:251–257
Asrani S, Chatterjee A, Wallace DK, Santiago-Turla C, Stinnett S (2011) Evaluation of the ICare rebound tonometer as a home intraocular pressure monitoring device. J Glaucoma 20:74–79
McGraw K, Wong S (1996) Forming Inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychological Methods 1:30–46
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Altman DG, Bland JM (1983) Measurement in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician 32:307–317
Bagga H, Liu JH, Weinreb RN (2009) Intraocular pressure measurements throughout the 24 h. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 20:79–83
Konstas AG, Topouzis F, Leliopoulou O, Pappas T, Georgiadis N, Jenkins JN, Stewart WC (2006) 24-hour intraocular pressure control with maximum medical therapy compared with surgery in patients with advanced open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology 113:761–765
Liang SY, Lee GA, Shields D (2009) Self-tonometry in glaucoma management—past, present and future. Surv Ophthalmol 54:450–462
Hughes E, Spry P, Diamond J (2003) 24-hour monitoring of intraocular pressure in glaucoma management: a retrospective review. J Glaucoma 12:232–236
Tarkkanen A, Ulfves K, Ulfves T (2010) Self-tonometry in glaucoma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248:1679–1681
Vasanthan Muttuvelu VD, Baggesen K, Ehlers N (2010) Precision and accuracy of the ICare tonometer - Peripheral and central IOP measurements by rebound tonometry. Acta Ophthalmol Sep 15 [Epub ahead of print]
Balkrishnan R, Bond JB, Byerly WG, Camacho FT, Anderson RT (2003) Medication-related predictors of health-related quality of life in glaucoma patients enrolled in amedicare health maintenance organization. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 1:75–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors have no proprietary interest in any aspect of this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halkiadakis, I., Stratos, A., Stergiopoulos, G. et al. Evaluation of the Icare-ONE rebound tonometer as a self-measuring intraocular pressure device in normal subjects. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250, 1207–1211 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1875-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1875-6