Abstract
Background
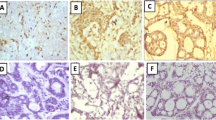
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) function in the remodelling of the extracellular matrix in morphogenesis, angiogenesis, tissue repair, and tumor invasion. Elevated levels of distinct MMPs in tumor tissue are related to worse prognosis. However, no overall consistent pattern of expression in human cancer has been identified. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the expression of MMP-1, -9, -13 and TIMP-1 in tumor epithelial cells and surrounding connective tissue in primary basal cell carcinomas (BCC) of the eyelid, and to assess their role as prognostic markers for tumor recurrence.
Methods
Surgical specimens of 49 histologically proven primary BBCs of the eyelid of different histological subtypes were included. Immunohistological studies were performed using antibodies against MMP-1, MMP-9, MMP-13 and TIMP-1, and staining intensity was analyzed semi-quantitatively.
Results
MMP-1, -9, -13, and TIMP-1 were expressed at various intensities in epithelial tumor cells and surrounding stromal cells including fibroblasts, inflammatory cells, and vascular endothelial cells in all tumor subtypes. Staining was especially prominent at the invading edge of the BCC. A statistically significant correlation was seen between increased TIMP-1 expression in tumor and/or stromal cells with the presence of MMP-13 (p = 0.007 and p < 0.0001 respectively). Moreover, TIMP-1 expression in tumor and/or stroma was significantly associated with relapse (p = 0.012 and p = 0.042 respectively).
Conclusion
MMP-9, MMP-13 and TIMP-1 expression may serve as a prognostic marker for early tumor invasiveness. Moreover, up-regulation of TIMP-1 in tumor and/or surrounding stromal cells may indicate an increased risk for BCC recurrence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farhi D, Dupin N, Palangie A, Carlotti A, Avril MF (2007) Incomplete excision of basal cell carcinoma: rate and associated factors among 362 consecutive cases. Dermatol Surg 33:1207–1214
Nagore E, Grau C, Molinero J, Fortea JM (2003) Positive margins in basal cell carcinoma: relationship to clinical features and recurrence risk. A retrospective study of 248 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 17:167–170
Sexton M, Jones DB, Maloney ME (1990) Histologic pattern analysis of basal cell carcinoma. Study of a series of 1039 consecutive neoplasms. J Am Acad Dermatol 23:1118–1126
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Werb Z (1997) ECM and cell surface proteolysis: regulating cellular ecology. Cell 91:439–442
Nelson AR, Fingleton B, Rothenberg ML, Matrisian LM (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases: biologic activity and clinical implications. J Clin Oncol 18:1135–1149
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Yu AE (2001) Proteases in invasion: matrix metalloproteinases. Semin Cancer Biol 11:143–152
Basset P, Bellocq JP, Wolf C, Stoll I, Hutin P, Limacher JM, Podhajcer OL, Chenard MP, Rio MC, Chambon P (1990) A novel metalloproteinase gene specifically expressed in stromal cells of breast carcinomas. Nature 348:699–704
Nabeshima K, Lane WS, Biswas C (1991) Partial sequencing and characterization of the tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor. Arch Biochem Biophys 285:90–96
Brennan M, Bhatti H, Nerusu KC, Bhagavathula N, Kang S, Fisher GJ, Varani J, Voorhees JJ (2003) Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is the major collagenolytic enzyme responsible for collagen damage in UV-irradiated human skin. Photochem Photobiol 78:43–48
Culhaci N, Metin K, Copcu E, Dikicioglu E (2004) Elevated expression of MMP-13 and TIMP-1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas may reflect increased tumor invasiveness. BMC Cancer 4:42
Dumas V, Kanitakis J, Charvat S, Euvrard S, Faure M, Claudy A (1999) Expression of basement membrane antigens and matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinomas. Anticancer Res 19:2929–2938
Johansson N, Airola K, Grenman R, Kariniemi AL, Saarialho-Kere U, Kahari VM (1997) Expression of collagenase-3 (matrix metalloproteinase-13) in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Am J Pathol 151:499–508
Kobayashi T, Onoda N, Takagi T, Hori H, Hattori S, Nagai Y, Tajima S, Nishikawa T (1996) Immunolocalizations of human gelatinase (type IV collagenase, MMP-9) and TIMP (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases) in normal epidermis and some epidermal tumors. Arch Dermatol Res 288:239–244
Monhian N, Jewett BS, Baker SR, Varani J (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase expression in normal skin associated with basal cell carcinoma and in distal skin from the same patients. Arch Facial Plast Surg 7:238–243
Yucel T, Mutnal A, Fay K, Fligiel SE, Wang T, Johnson T, Baker SR, Varani J (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase expression in basal cell carcinoma: relationship between enzyme profile and collagen fragmentation pattern. Exp Mol Pathol 79:151–160
Hattori Y, Nerusu KC, Bhagavathula N, Brennan M, Hattori N, Murphy HS, Su LD, Wang TS, Johnson TM, Varani J (2003) Vascular expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (collagenase-3) in basal cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol 74:230–237
Telfer NR, Colver GB, Morton CA (2008) Guidelines for the management of basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol 159:35–48
Moon SE, Dame MK, Remick DR, Elder JT, Varani J (2001) Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) during epidermal invasion of the stroma in human skin organ culture: keratinocyte stimulation of fibroblast MMP-1 production. Br J Cancer 85:1600–1605
Hiraoka N, Allen E, Apel IJ, Gyetko MR, Weiss SJ (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases regulate neovascularization by acting as pericellular fibrinolysins. Cell 95:365–377
Stetler-Stevenson WG (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis: a moving target for therapeutic intervention. J Clin Invest 103:1237–1241
Taraboletti G, Sonzogni L, Vergani V, Hosseini G, Ceruti R, Ghilardi C, Bastone A, Toschi E, Borsotti P, Scanziani E, Giavazzi R, Pepper MS, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Bani MR (2000) Posttranscriptional stimulation of endothelial cell matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 1 by endothelioma cells. Exp Cell Res 258:384–394
Bertaux B, Hornebeck W, Eisen AZ, Dubertret L (1991) Growth stimulation of human keratinocytes by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. J Invest Dermatol 97:679–685
Kleiner DE Jr, Stetler-Stevenson WG (1993) Structural biochemistry and activation of matrix metalloproteases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:891–897
Mauch C, Krieg T, Bauer EA (1994) Role of the extracellular matrix in the degradation of connective tissue. Arch Dermatol Res 287:107–114
Griffiths RW, Suvarna SK, Stone J (2005) Do basal cell carcinomas recur after complete conventional surgical excision? Br J Plast Surg 58:795–805
Silverman MK, Kopf AW, Bart RS, Grin CM, Levenstein MS (1992) Recurrence rates of treated basal cell carcinomas. Part 3: Surgical excision. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 18:471–476
Walker P, Hill D (2006) Surgical treatment of basal cell carcinomas using standard postoperative histological assessment. Australas J Dermatol 47:1–12
Auw-Haedrich C, Frick S, Boehringer D, Mittelviefhaus H (2009) Histologic safety margin in basal cell carcinoma of the eyelid: correlation with recurrence rate. Ophthalmology 116:802–806
Swetter SM, Boldrick JC, Pierre P, Wong P, Egbert BM (2003) Effects of biopsy-induced wound healing on residual basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas: rate of tumor regression in excisional specimens. J Cutan Pathol 30:139–146
Fernandes JD, de Lorenzo Messina MC, de Almeida Pimentel ER, Castro LG (2008) Presence of residual basal cell carcinoma in re-excised specimens is more probable when deep and lateral margins were positive. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 22:704–706
Deng JS, Falo LD Jr, Kim B, Abell E (1998) Cytotoxic T cells in basal cell carcinomas of skin. Am J Dermatopathol 20:143–146
Macpherson N, Lamrock E, Watt G (2010) Effect of inflammation on positive margins of basal cell carcinomas. Australas J Dermatol 51:95–98
Paavilainen V, Aaltonen M, Tuominen J, Saari KM (2007) Histological characteristics of basal cell carcinoma of the eyelid. Ophthalmic Res 39:45–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zlatarova, Z.I., Softova, E.B., Dokova, K.G. et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1, -9, -13, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in basal cell carcinomas of the eyelid. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250, 425–431 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1810-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1810-x